Question: Consider the following functions: void check_answer (vector &foo, unsigned i) { if (i = foo.size()) return; if (foo[i]=42) else cout < < Life, the
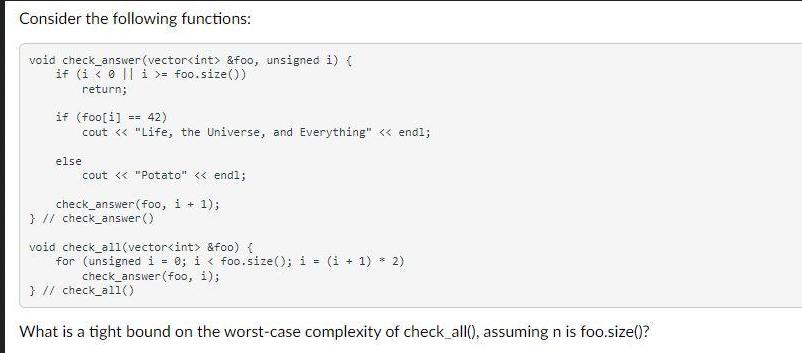
Consider the following functions: void check_answer (vector &foo, unsigned i) { if (i = foo.size()) return; if (foo[i]=42) else cout < < "Life, the Universe, and Everything" < < endl; cout < < "Potato" < < endl; check_answer (foo, i + 1); } // check_answer() void check_all(vector &foo) { for (unsigned i = 0; i < foo.size(); i = (i + 1) * 2) check_answer (foo, i); } // check_all() What is a tight bound on the worst-case complexity of check_all(), assuming n is foo.size()?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


