Question: Consider the following linear programming problem for questions 12-17 (15 points each) A company produces Lounge Chairs and Small Sofas. It uses Two Labor Types
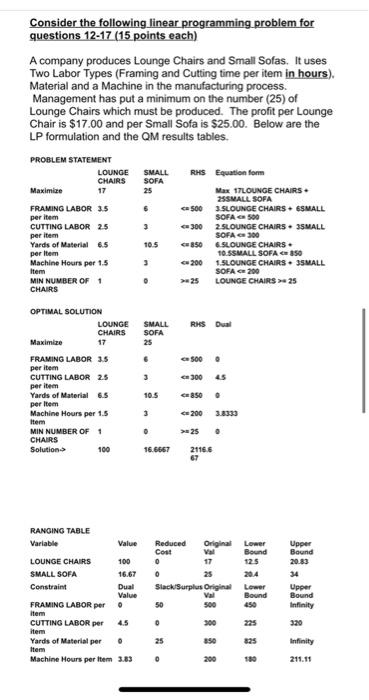

Consider the following linear programming problem for questions 12-17 (15 points each) A company produces Lounge Chairs and Small Sofas. It uses Two Labor Types (Framing and Cutting time per item in hours). Material and a Machine in the manufacturing process. Management has put a minimum on the number (25) of Lounge Chairs which must be produced. The profit per Lounge Chair is $17.00 and per Small Sofa is $25.00. Below are the LP formulation and the QM results tables PROBLEM STATEMENT LOUNGE SMALL RHS Equation form CHAIRS SOFA Maximize 25 Max 17LOUNGE CHAIRS 29SMALL SOFA FRAMING LABOR 3.5 6 3.SLOUNGE CHAIRS SMALL per item SOFA 500 CUTTING LABOR 25 300 2. SLOUNGE CHAIRS. SMALL SOFA 300 Yards of Material 6.5 10.5 6-SLOUNGE CHAIRS per Item 10.SSMALL SOFA 350 Machine Hours per 1.5 3 200 1.SLOUNGE CHAIRS. 3SMALL Item SOFA G 200 MIN NUMBER OF 1 . 25 LOUNGE CHAIRS > 25 CHAIRS 500 3 per item RHS Dual SMALL SOFA 25 6 OPTIMAL SOLUTION LOUNGE CHAIRS Maximize 17 FRAMING LABOR 35 per item CUTTING LABOR 25 per item Yards of Material 6.5 per Item Machine Hours per 1.5 Item MIN NUMBER OF 1 CHAIRS Solution 100 2 500 3005 3 105 8500 3 ce 200 3.8333 . > 25 . 16.6667 2116.6 RANGING TABLE Variable Value Reduced Original Lower Upper Cost Bound Bound LOUNGE CHAIRS 1000 17 12.5 20.83 SMALL SOFA 16.67 0 20.4 34 Constraint Dual Slack/Surplus Original Lower Upper Value Val Bound Bound FRAMING LABOR per . 50 500 Infinity Item CUTTING LABOR per 4.5 0 320 item Yards of Material per . 850 825 Infinity Item Machine Hours per Item 3.83 0 200 189 211.11 Reduced Original Lower Cost Val Bound 0 17 12.5 0 25 Slack/Surplus Original Lower Val Bound 50 500 450 **** Upper Bound 20.83 34 Upper Bound Variable Value LOUNGE CHAIRS 100 SMALL SOFA 16.67 Constraint Dual Value FRAMING LABOR per o item CUTTING LABOR per 45 item Yards of Material per . Item Machine Hours per Item 3.03 MIN NUMBER OF 0 CHAIRS 0 300 225 320 25 850 825 Infinity . 75 200 211.11 180 o 100 12. What are the optimal number of Lounge Chairs and Small Sofas to produce and what is the total profit? 13. Which constraints are active, meaning that all of the resource is used in the optimal solution? 14. For the Cutting Labor per item constraint, how much additional profit can be made by adding 10 hours of Cutting Labor per item resource available? 15. What is the amount of increase in profit for each Machine Hour added and what is the maximum number of yards that can be added for this amount of profit increase? 16. How much profit is added if you are given an additional 50 Yards of Material? 17. By how much can I increase the profit per Small Sofa before the solution shifts to another comer point? Consider the following linear programming problem for questions 12-17 (15 points each) A company produces Lounge Chairs and Small Sofas. It uses Two Labor Types (Framing and Cutting time per item in hours). Material and a Machine in the manufacturing process. Management has put a minimum on the number (25) of Lounge Chairs which must be produced. The profit per Lounge Chair is $17.00 and per Small Sofa is $25.00. Below are the LP formulation and the QM results tables PROBLEM STATEMENT LOUNGE SMALL RHS Equation form CHAIRS SOFA Maximize 25 Max 17LOUNGE CHAIRS 29SMALL SOFA FRAMING LABOR 3.5 6 3.SLOUNGE CHAIRS SMALL per item SOFA 500 CUTTING LABOR 25 300 2. SLOUNGE CHAIRS. SMALL SOFA 300 Yards of Material 6.5 10.5 6-SLOUNGE CHAIRS per Item 10.SSMALL SOFA 350 Machine Hours per 1.5 3 200 1.SLOUNGE CHAIRS. 3SMALL Item SOFA G 200 MIN NUMBER OF 1 . 25 LOUNGE CHAIRS > 25 CHAIRS 500 3 per item RHS Dual SMALL SOFA 25 6 OPTIMAL SOLUTION LOUNGE CHAIRS Maximize 17 FRAMING LABOR 35 per item CUTTING LABOR 25 per item Yards of Material 6.5 per Item Machine Hours per 1.5 Item MIN NUMBER OF 1 CHAIRS Solution 100 2 500 3005 3 105 8500 3 ce 200 3.8333 . > 25 . 16.6667 2116.6 RANGING TABLE Variable Value Reduced Original Lower Upper Cost Bound Bound LOUNGE CHAIRS 1000 17 12.5 20.83 SMALL SOFA 16.67 0 20.4 34 Constraint Dual Slack/Surplus Original Lower Upper Value Val Bound Bound FRAMING LABOR per . 50 500 Infinity Item CUTTING LABOR per 4.5 0 320 item Yards of Material per . 850 825 Infinity Item Machine Hours per Item 3.83 0 200 189 211.11 Reduced Original Lower Cost Val Bound 0 17 12.5 0 25 Slack/Surplus Original Lower Val Bound 50 500 450 **** Upper Bound 20.83 34 Upper Bound Variable Value LOUNGE CHAIRS 100 SMALL SOFA 16.67 Constraint Dual Value FRAMING LABOR per o item CUTTING LABOR per 45 item Yards of Material per . Item Machine Hours per Item 3.03 MIN NUMBER OF 0 CHAIRS 0 300 225 320 25 850 825 Infinity . 75 200 211.11 180 o 100 12. What are the optimal number of Lounge Chairs and Small Sofas to produce and what is the total profit? 13. Which constraints are active, meaning that all of the resource is used in the optimal solution? 14. For the Cutting Labor per item constraint, how much additional profit can be made by adding 10 hours of Cutting Labor per item resource available? 15. What is the amount of increase in profit for each Machine Hour added and what is the maximum number of yards that can be added for this amount of profit increase? 16. How much profit is added if you are given an additional 50 Yards of Material? 17. By how much can I increase the profit per Small Sofa before the solution shifts to another comer point
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


