Question: Consider the following tree-structured CSP that encodes a coloring problem in which neighboring nodes cannot have the same color. The domains of each node are
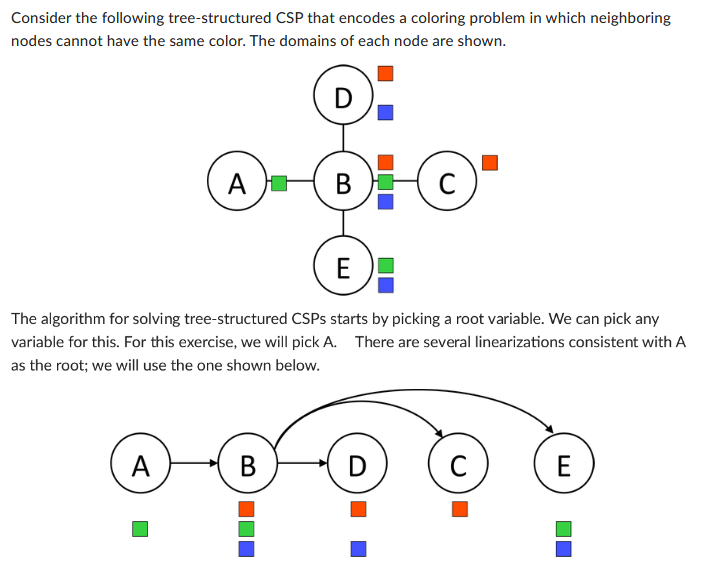
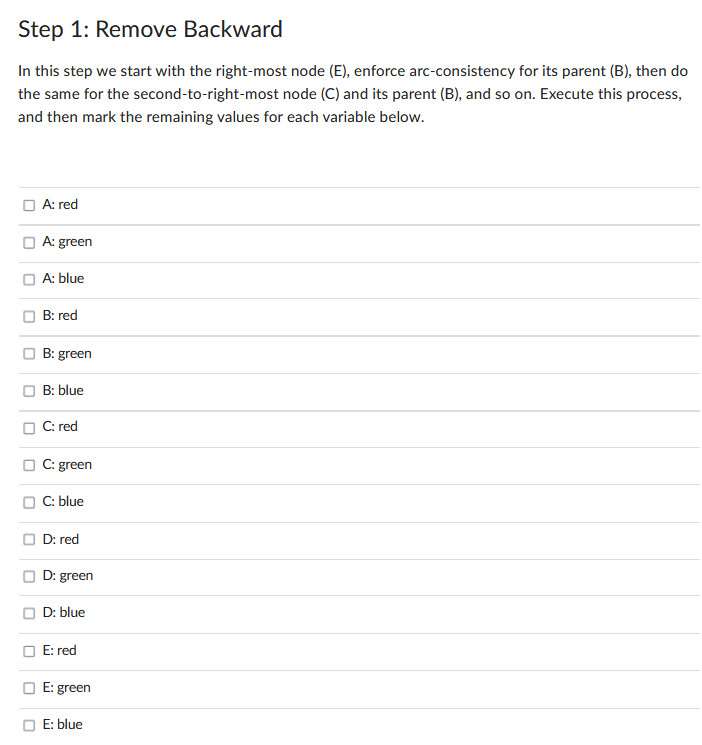
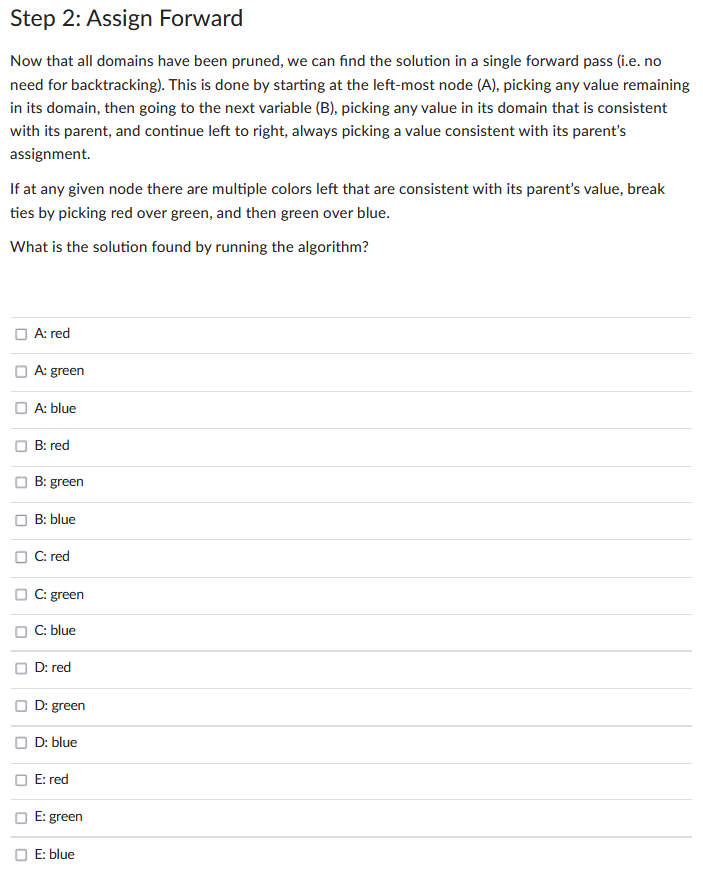
Consider the following tree-structured CSP that encodes a coloring problem in which neighboring nodes cannot have the same color. The domains of each node are shown. The algorithm for solving tree-structured CSPs starts by picking a root variable. We can pick any variable for this. For this exercise, we will pick A. There are several linearizations consistent with A as the root; we will use the one shown below. Step 1: Remove Backward In this step we start with the right-most node (E), enforce arc-consistency for its parent (B), then do the same for the second-to-right-most node (C) and its parent (B), and so on. Execute this process, and then mark the remaining values for each variable below. A: red A: green A: blue B: red B: green B: blue C: red C: green C: blue D: red D: green D: blue E: red E: green E: blue Step 2: Assign Forward Now that all domains have been pruned, we can find the solution in a single forward pass (i.e. no need for backtracking). This is done by starting at the left-most node (A), picking any value remaining in its domain, then going to the next variable (B), picking any value in its domain that is consistent with its parent, and continue left to right, always picking a value consistent with its parent's assignment. If at any given node there are multiple colors left that are consistent with its parent's value, break ties by picking red over green, and then green over blue. What is the solution found by running the algorithm? A: red A: green A: blue B: red B: green B: blue C: red C: green C: blue D: red D: green D: blue E: red E: green E: blue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


