Question: Consider the initial value problem, $$ (-1 x+4 y) y^{prime}=(x-8) sqrt{3}{y-8), yleft(x_{0} ight)=y_{0} $$ If $x_{0}=6$, then for what value of $y_{0}$ is a solution
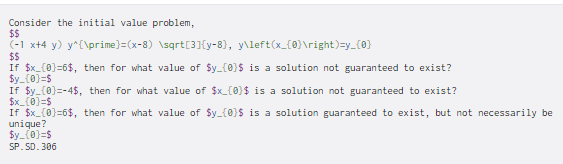
Consider the initial value problem, $$ (-1 x+4 y) y^{\prime}=(x-8) \sqrt{3}{y-8), y\left(x_{0} ight)=y_{0} $$ If $x_{0}=6$, then for what value of $y_{0}$ is a solution not guaranteed to exist? $y_{0}=$ If $y[0]=-4$, then for what value of $x_{0}$ is a solution not guaranteed to exist? $x_{0}=$ If $x_{0}=6$, then for what value of $y_{0}$ is a solution guaranteed to exist, but not necessarily be unique? $y_{0}=$ SP.SD. 306
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


