Question: Consider the network shown below with each link labeled by its bandwidth. Suppose width of a path is defined as the bandwidth of the bottleneck
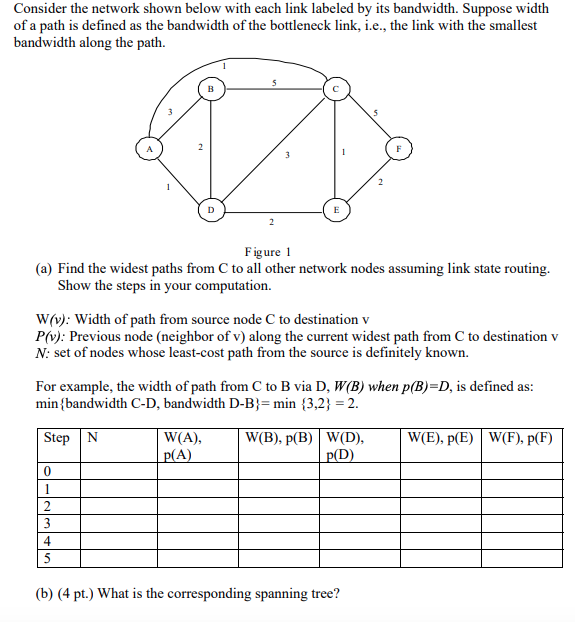
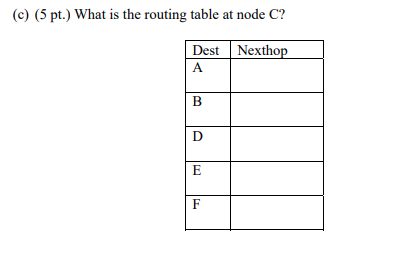
Consider the network shown below with each link labeled by its bandwidth. Suppose width of a path is defined as the bandwidth of the bottleneck link, i.e., the link with the smallest bandwidth along the path. Figure 1 (a) Find the widest paths from C to all other network nodes assuming link state routing. Show the steps in your computation. W(v): Width of path from source node C to destination v P(v): Previous node (neighbor of v) along the current widest path from C to destination v N: set of nodes whose least-cost path from the source is definitely known. For example, the width of path from C to B via D. W(B) when p(B)-D, is defined as: min {bandwidth C-D, bandwidth D-B}=min (3,2} = 2. Step W (A), p(A) W(B), p(B) W(D) P(D) W(E), P(E) W(F), p(F) (b) (4 pt.) What is the corresponding spanning tree? (c) (5 pt.) What is the routing table at node C? Dest Nexthop Consider the network shown below with each link labeled by its bandwidth. Suppose width of a path is defined as the bandwidth of the bottleneck link, i.e., the link with the smallest bandwidth along the path. Figure 1 (a) Find the widest paths from C to all other network nodes assuming link state routing. Show the steps in your computation. W(v): Width of path from source node C to destination v P(v): Previous node (neighbor of v) along the current widest path from C to destination v N: set of nodes whose least-cost path from the source is definitely known. For example, the width of path from C to B via D. W(B) when p(B)-D, is defined as: min {bandwidth C-D, bandwidth D-B}=min (3,2} = 2. Step W (A), p(A) W(B), p(B) W(D) P(D) W(E), P(E) W(F), p(F) (b) (4 pt.) What is the corresponding spanning tree? (c) (5 pt.) What is the routing table at node C? Dest Nexthop
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


