Question: Consider the one-dimensional data set shown in Table 4.12. (a) Classify the data point x = 5.0 according to its 1-, 3-, 5-, and 9-nearest
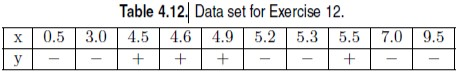
Consider the one-dimensional data set shown in Table 4.12. (a) Classify the data point x = 5.0 according to its 1-, 3-, 5-, and 9-nearest neighbors (using majority vote). (b) Repeat the previous analysis using the distance-weighted voting approach described in Section 4.3.1.

Table 4.12 Data set for Exercise 12. x0.53.0 4.5 4.6 4.95.25.3 5.5 7.0 9.5 4.3.1 Algorithm A high-level summary of the nearest neighbor classification method is given in Algorithm 4.2. The algorithm computes the distance (or similarity) between each test instance z - (x.y') and all the training examples (x,y) E D to determine its nearest neighbor list, D.. Such computation can be costly if the number of training examples is large. However, efficient indexing techniques 210 Chapter 4 Classification: Alternative Techniques Algorithm 4.2 The k-nearest neighbor classifier 1: Let k be the number of nearest neighbors and D be the set of training examples. 2: for each test instance z (x',y) do 3: Compute d(x', x). the distance between z and every example, (x, y) E D 4: Select D. D, the set of k closest training examples to z 6: end for are available to reduce the computation needed to find the nearest neighbors of a test instance. Once the nearest neighbor list is obtained, the test instance is classified based on the majority class of its nearest neighbors: Majority Voting: y - argmax I(yi)4.5) (xi)ED where u is a class label, yi s the class label for one of the nearest neighbors. and I(-) is an indicator function that returns the value 1 if its argument is true and 0 otherwise. In the majority voting approach, every neighbor has the same impact on the classification. This makes the algorithm sensitive to the choice of k, as shown in Figure 4.6. One way to reduce the impact of k is to weight the influence of each nearest neighbor x according to its distance: w- 1/d(x', xi)2. As a result, training examples that are located far away from z have a weaker impact on the classification compared to those that are located close to z. Using the distance-weighted voting scheme, the class label can be determined as follows t, x I(u (xiJiED. Distance-Weighted Voting: y'-argmax s). (4.6) Table 4.12 Data set for Exercise 12. x0.53.0 4.5 4.6 4.95.25.3 5.5 7.0 9.5 4.3.1 Algorithm A high-level summary of the nearest neighbor classification method is given in Algorithm 4.2. The algorithm computes the distance (or similarity) between each test instance z - (x.y') and all the training examples (x,y) E D to determine its nearest neighbor list, D.. Such computation can be costly if the number of training examples is large. However, efficient indexing techniques 210 Chapter 4 Classification: Alternative Techniques Algorithm 4.2 The k-nearest neighbor classifier 1: Let k be the number of nearest neighbors and D be the set of training examples. 2: for each test instance z (x',y) do 3: Compute d(x', x). the distance between z and every example, (x, y) E D 4: Select D. D, the set of k closest training examples to z 6: end for are available to reduce the computation needed to find the nearest neighbors of a test instance. Once the nearest neighbor list is obtained, the test instance is classified based on the majority class of its nearest neighbors: Majority Voting: y - argmax I(yi)4.5) (xi)ED where u is a class label, yi s the class label for one of the nearest neighbors. and I(-) is an indicator function that returns the value 1 if its argument is true and 0 otherwise. In the majority voting approach, every neighbor has the same impact on the classification. This makes the algorithm sensitive to the choice of k, as shown in Figure 4.6. One way to reduce the impact of k is to weight the influence of each nearest neighbor x according to its distance: w- 1/d(x', xi)2. As a result, training examples that are located far away from z have a weaker impact on the classification compared to those that are located close to z. Using the distance-weighted voting scheme, the class label can be determined as follows t, x I(u (xiJiED. Distance-Weighted Voting: y'-argmax s). (4.6)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


