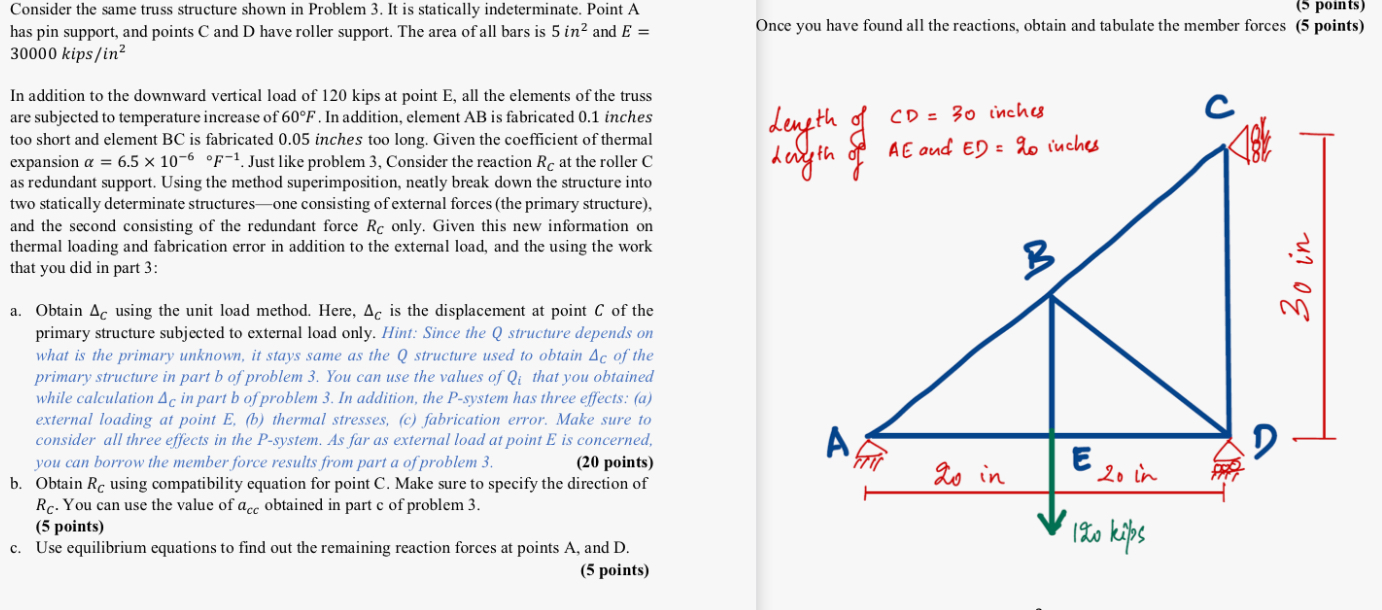
Question: Consider the same truss structure shown in Problem 3 . It is statically indeterminate. Point A has pin support, and points C and D have
Consider the same truss structure shown in Problem It is statically indeterminate. Point A has pin support, and points C and D have roller support. The area of all bars is mathrmin and E kipsin
In addition to the downward vertical load of kips at point E all the elements of the truss are subjected to temperature increase of circ F In addition, element A B is fabricated inches too short and element BC is fabricated inches too long. Given the coefficient of thermal expansion alphatimes quadcirc F Just like problem Consider the reaction RC at the roller C as redundant support. Using the method superimposition, neatly break down the structure into two statically determinate structuresone consisting of external forces the primary structure and the second consisting of the redundant force RC only. Given this new information on thermal loading and fabrication error in addition to the external load, and the using the work that you did in part :
a Obtain DeltaC using the unit load method. Here, DeltaC is the displacement at point C of the primary structure subjected to external load only. Hint: Since the Q structure depends on what is the primary unknown, it stays same as the Q structure used to obtain DeltaC of the primary structure in part b of problem You can use the values of Qi that you obtained while calculation DeltaC in part b of problem In addition, the P system has three effects: a external loading at point Eb thermal stresses, c fabrication error. Make sure to consider all three effects in the Psystem. As far as external load at point E is concerned, you can borrow the member force results from part a of problem
points
b Obtain RC using compatibility equation for point C Make sure to specify the direction of RC You can use the value of ac c obtained in part c of problem
points
c Use equilibrium equations to find out the remaining reaction forces at points A and D
Once you have found all the reactions, obtain and tabulate the member forces points
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


