Question: . Consider the steady - state diffusion of a protein across a tissue that consists of two phases ( a cellular phase and an acellular
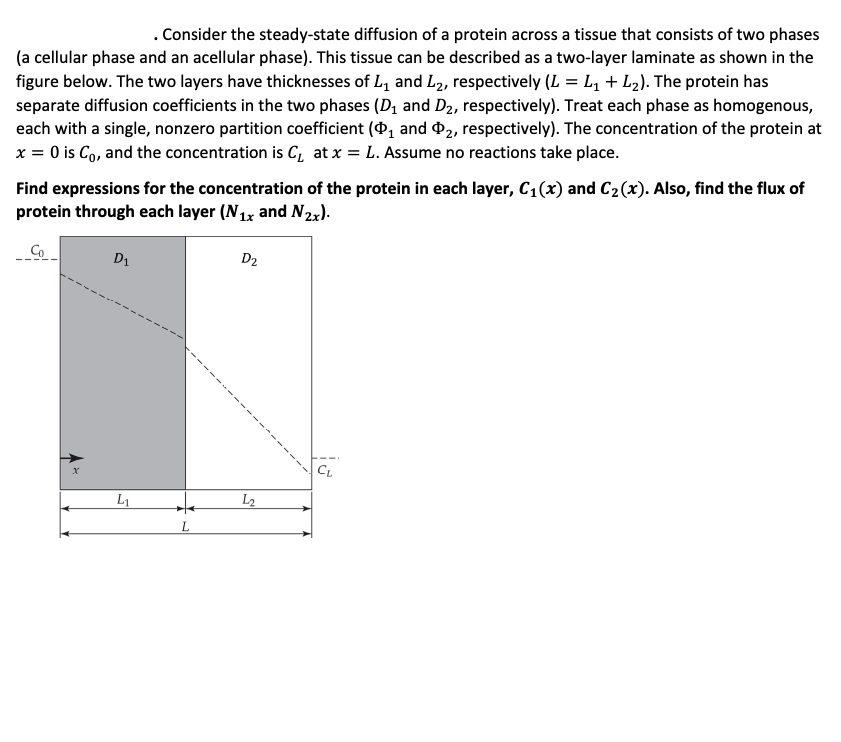
Consider the steadystate diffusion of a protein across a tissue that consists of two phases
a cellular phase and an acellular phase This tissue can be described as a twolayer laminate as shown in the
figure below. The two layers have thicknesses of and respectively The protein has
separate diffusion coefficients in the two phases and respectively Treat each phase as homogenous,
each with a single, nonzero partition coefficient and respectively The concentration of the protein at
is and the concentration is at Assume no reactions take place.
Find expressions for the concentration of the protein in each layer, and Also, find the flux of
protein through each layer and :
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


