Question: Consider the valuation methods we discussed in this class. the case does not provide information for you to conduct a valuation, but you may have

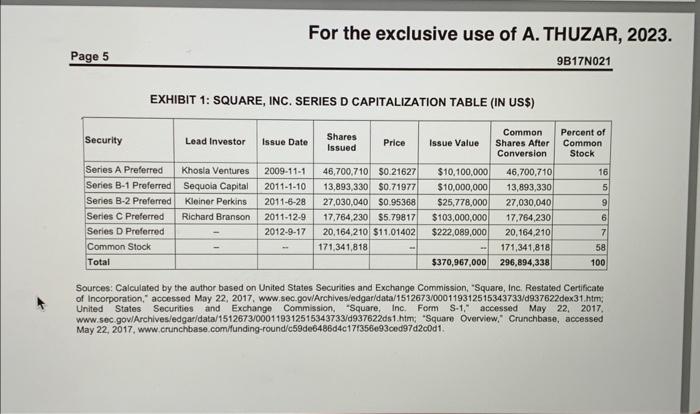
SERIES E Square ultimately decided to address its need for capital by seeking $150 million in new financing from the venture capital market. 38 It offered investors the following terms: 9,700,289 shares of Series E preferred stock at a price of $15.46345 - a 40 per cent increase over the $11.01402 price of the preferred D Series issued in 2012 and a 7,050 per cent increase over the $0.21627 price in the 2009 A Series offering (see Exhibit 5). While many of the terms were similar to those offered in its previous rounds, there were some differences. Like those in the previous A, B-1, B-2, C, and D rounds, the Series E shares were convertible into common stock at the option of the holder on a one-for-one basis, and they had a " 1 liquidation preference," such that investors could receive their initial investment before any payment was made to common stockholders in the event of any "liquidation or winding up" "t9 of the company, if the investors chose not to convert their shares into common stock. 40 All of the classes were non-participating, so they could choose to receive their liquidation preference or convert their shares into equity, but they could not do both. 41 While the Series E shareholders would be entitled to a number of votes equal to the number of shares of common stock into which the preferred stock was convertible on general voting issues, the shareholders would not be able to elect an exclusive member of the board of directors - something the Series B and C shareholders were able to do. 42 The most striking terms related to anti-dilution provisions commonly referred to as ratchets. Two types of ratchets were included. One, known as a weighted-average ratchet, was common; a survey in the first quarter of 2014 by venture capital law firm Fenwick and West LLP found that 95 per cent of all offerings had similar provisions. 4 This provision stipulated that if the company issued shares in a non-public offering at a price lower than $15.46345, the conversion price would be lowered to the ratio of the total value of issue proceeds measured prior to this offering divided by the total number of shares outstanding measured after this offering. The other ratchet was an IPO ratchet, which specified that in the event of a public offering for less than $18.55614, the conversion price would be adjusted such that the Series E preferred shares were convertible into "(A) the number of shares of common stock issuable on conversion of such share of Series E preferred stock; and (B) an additional number of shares of common stock equal to (x) the difference between $18.55614 and the public offering price (y) divided by the public offering share price," Goldman Sachs and Sapphire Ventures, as well as any other investors offered these terms, had only a limited amount of time to consider the terms. 4 The offer price of $15.46345 was apparently designed to reach a $6 amount of the company wasn't able to exit at this value? What if the firm ended up For the exclusive use of A. THUZAR, 2023. Page 5 9B17N021 EXHIBIT 1: SQUARE, INC. SERIES D CAPITALIZATION TABLE (IN US\$) Sources: Calculated by the author based on United States Securities and Exchange Commission, "Square, Inc. Restated Certificate of Incorporation," accessed May 22, 2017, www sec-gov/Archives/edgar/data/1512673/000119312515343733/d937622dex31.him, United States Securitios and Exchango Commission, "Square, Inc. Form S-1," accessed May 22, 2017. Www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1512673/000119312515343733/d937622ds1.him; "Square Overviow," Crunchbase, accessed May 22, 2017, www crunchbase.comilunding-round/c59de6486d4c17/356093ced97d2cod1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


