Question: Consider the vector field, u = (3xz, 2xy, -yz). Write the expressions for determining V u based on the 2nd-order central difference approximation of
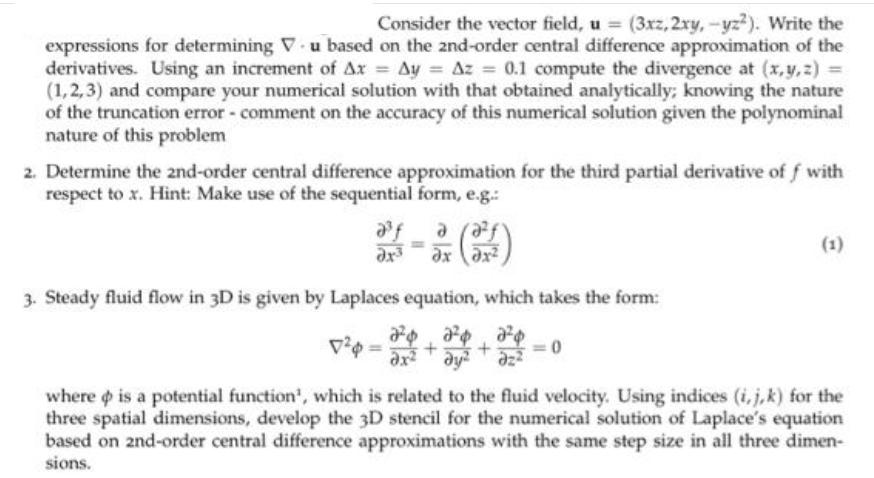


Consider the vector field, u = (3xz, 2xy, -yz). Write the expressions for determining V u based on the 2nd-order central difference approximation of the derivatives. Using an increment of Ax Ay Az = 0.1 compute the divergence at (x,y,z) = (1,2,3) and compare your numerical solution with that obtained analytically; knowing the nature of the truncation error - comment on the accuracy of this numerical solution given the polynominal nature of this problem 2. Determine the 2nd-order central difference approximation for the third partial derivative off with respect to x. Hint: Make use of the sequential form, e.g.: a a 3. Steady fluid flow in 3D is given by Laplaces equation, which takes the form: (1) + where is a potential function', which is related to the fluid velocity. Using indices (i,j,k) for the three spatial dimensions, develop the 3D stencil for the numerical solution of Laplace's equation based on 2nd-order central difference approximations with the same step size in all three dimen- sions. 4. A square floor plate of length L in both directions is subject to machine vibration loading in which the vibration force density (i.e. force per unit floor area) is given by the expression: w=100 sin (2) sin (2) cos(t) where x and y are spatial dimensions (unit m, and I is time-w is in units of kN/m. Consider L=10 m, use numerical integration to determine the the total force on the plate as a function of time (use a reasonable discretization step size). 5. Numerical gradient: A vibrating rod can be idealized as a 1D problem (rod along the x-direction), and satisfies the 1D wave equation. (2) where u is the rod displacement, x is the position along the rod (x=0-L for a rod of length L), t is time, and c is the wave speed (related to the stiffness of the rod, c=E/p). In the second-half of this course, you will learn how to solve such equations - for now we will focus on how we can use the obtained numerical solution, u(x,t), to determine derived quantities. (a) Determining strain: At t = 1.0s, the displacements at x = [0.3,0.4,0.5] are computed as u(x,t= 1.0) [0.809, 0.951, 1.000]. Use forward, backward and central differences to estimate the shear strain in the rod, du/ax. (b) Determine velocity: At the location x = 0.3 the rod displacement was u(x = 0.3, t = 1.0) = 0.809, at two other times in addition (t = [0.9,1.0, 1.1]) it was obtained as: u(x = 0.3,t) = (0.655,0.809,0.655]. Use forward, backward, and central differences to estimate the velocity, du/t.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The images youve uploaded contain several numerical problems related to vector fields fluid dynamics and wave equations among others Below is a breakdown of the questions and the necessary steps to so... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


