Question: Consider two fluids placed between two parallel flat plates of infinite length and width. The flow is steady, incompressible, parallel, and laminar. The upper plate
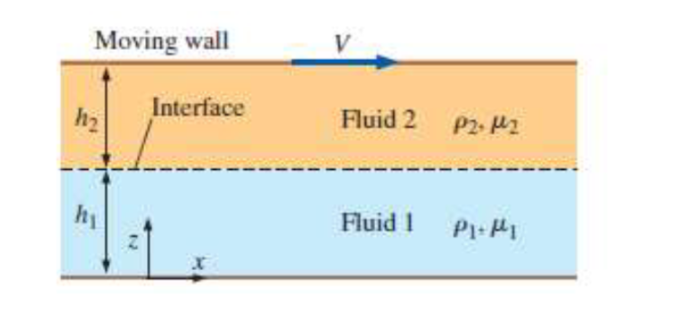
Consider two fluids placed between two parallel flat plates of infinite length and width. The flow is steady, incompressible, parallel, and laminar. The upper plate moves with velocity V to the right, and the lower plate is at rest. Gravity acts in the z direction down in the figure There is no forcing pressure gradient pushing the fluid through the channel: the flow is established solely by the viscous effects created by the moving upper plate. You can ignore surface tension effects and assume the interface is horizontal. The pressure at the bottom of the flow z is equal to PtableMoving wall,VhInterface,Fluid rho mu hFluid rho mu
a List all the appropriate boundary conditions for both velocity and pressure
Solve for the velocity field hint: split the solution into two portions, one for each
fluid. Generate expressions for U as a function of z and U as a function of z
b Let fluid and fluid be unused motor oil, both at deg C Also let h mm h mm and V ms Comment on the results.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


