Question: Considering that child processes keep executing even after their parent(s) have terminated, what is the output of the following C program? #include #include #include int
Considering that child processes keep executing even after their parent(s) have terminated, what is the output of the following C program?
#include#include #include int value = 10; int main() { pid_t pid1, pid2; printf("value1 = %d ", value); pid1 = fork(); printf("value2 = %d ", value); pid2 = fork(); printf("value3 = %d ", value); if (pid1 > 0 && pid2 > 0) //&& is the AND operator printf("value4 = %d ", value); exit(0); }
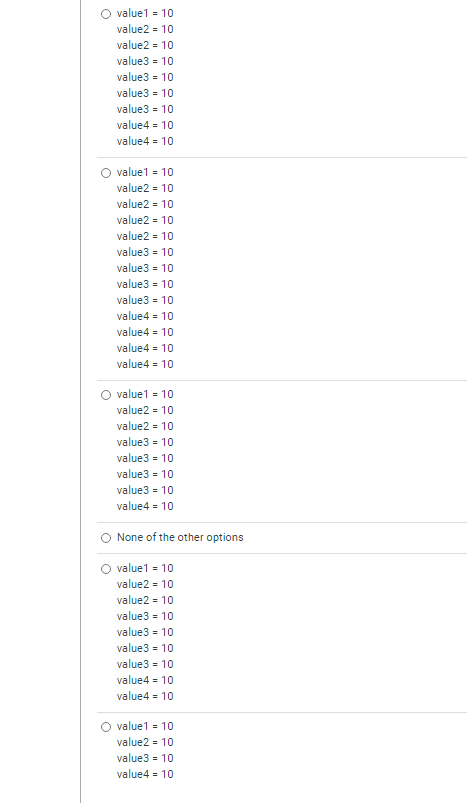
O value 1 = 10 value2 = 10 value2 = 10 value 3 = 10 value3 = 10 value3 = 10 value3 = 10 value4 = 10 value4 = 10 value 1 = 10 value2 = 10 value2 = 10 value2 = 10 value2 = 10 value3 = 10 value3 = 10 value3 = 10 value 3 = 10 value4 = 10 value4 = 10 value4 = 10 value4 = 10 O value 1 = 10 value2 = 10 value2 = 10 value 3 = 10 value 3 = 10 value3 = 10 value3 - 10 value4 = 10 O None of the other options value1 - 10 value2 = 10 value2 = 10 value 3 = 10 value3 = 10 value 3 = 10 value 3 = 10 value4 = 10 value4 = 10 O value 1 = 10 value2 - 10 value3= 10 value4 = 10
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


