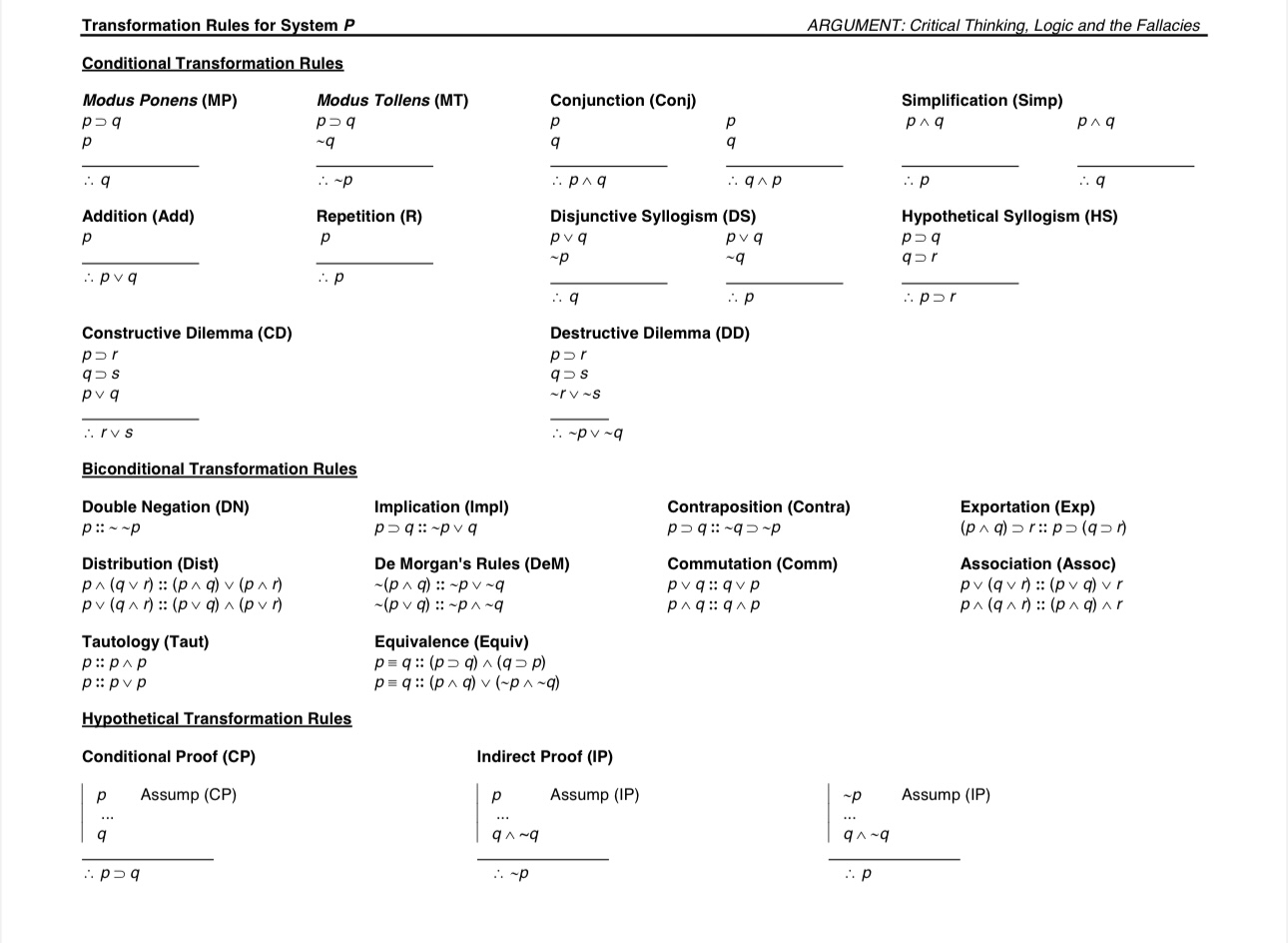
Question: Construct a proof for the following argument using the transformation rules of system P of propositional logic. 1.X?(Q??(P?Y)) Premise 2.~X?(Z?P) Premise 3.Y?~(Q?P) Premise /:.Z?~Y Transformation
Construct a proof for the following argument using the transformation rules of system P of propositional logic.
1.X?(Q??(P?Y)) Premise
2.~X?(Z?P) Premise
3.Y?~(Q?P) Premise /:.Z?~Y
Transformation Rules for System P ARGUMENT: Critical Thinking, Logic and the Fallacies Conditional Transformation Rules Modus Ponens (MP) Modus Tollens (MT) Conjunction (Conj) Simplification (Simp) P PAq PAq p .. 9 .. ~p .. PAq .. qAp . P .. q Addition (Add) Repetition (R) Disjunctive Syllogism (DS) Hypothetical Syllogism (HS) p pv q pv q paq -p qar :. pvq :. P .. q : per Constructive Dilemma (CD) Destructive Dilemma (DD) per pv q irvs : ~pv-q Biconditional Transformation Rules Double Negation (DN) Implication (Impl) Contraposition (Contra) Exportation (Exp) p::~ ~p p=q:: ~pvq paq::~q>~p (p A q) > r :: p= (q>n) Distribution (Dist) De Morgan's Rules (DeM) Commutation (Comm) Association (Assoc) pA (q vr) :: ( p A q ) v ( par) (PA q ) :-pv-q pv q :: qvp pv (q vn) :: (pvq) vr pv ( q An) :: ( p v q ) ( p vr) (p v q) ::-pa-q PAq:: qAp PA (qAn) :: ( PA q )Ar Tautology (Taut) Equivalence (Equiv) p :: PAP D = q:: (p= q) ~ (q = p) p :: pvp p= q:: (p q) v(-pa-q) Hypothetical Transformation Rules Conditional Proof (CP) Indirect Proof (IP) p Assump (CP) p Assump (IP) -P Assump (IP) .. ... ... Q :. P>q :. ~p .. p
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


