Question: Construct an argument that helps you arrive at an answer to the question provided below by picking from the list of reasoning elements available in
Construct an argument that helps you arrive at an answer to the question provided below by picking from the list of reasoning elements available in the "Items" column. Click and drag to place the elements, in order, in the "Reasoning Space" box. Connecting words to clarify your argument are also available.
While all of the reasoning elements that are necessary to correctly answer this question are present, you may wish to add something that is not represented. In this case, use a blank tile to create a custom element that you can insert into your argument. Please note that every reasoning element provided contains a true statement (i.e. there is no complete reasoning element in the "Items" column which gives incorrect information).
Question: The following is the overall reaction for a multi-step process:
2 N2O5 (g) --> 4 NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
If the variation in N2O5 concentration over time for the overall reaction is shown below, what is the rate law for the reaction? 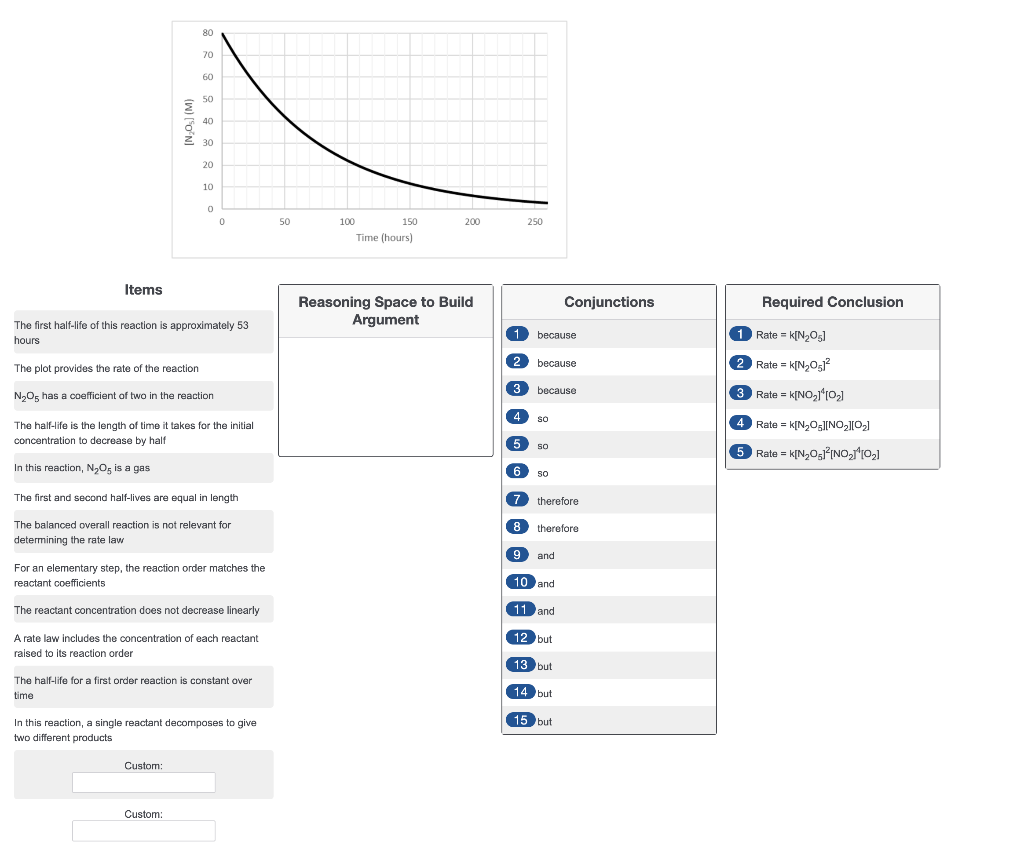
80 70 60 50 (w) (ON 40 Z 30 20 10 0 0 50 200 250 100 150 Time (hours) Items Conjunctions Required Conclusion Reasoning Space to Build Argument The first half-life of this reaction is approximately 53 hours 1 because 1 Rate = k[N205] The plot provides the rate of the reaction 2 Rate = k[N20512 2 because 3 because N2O5 has a coefficient of two in the reaction Rate = k[NO_110,1 SO 4 Rate = k[N OINO2102] The half-life is the length of time it takes for the initial concentration to decrease by half 5 SO 5 Rate = k[N2012/NO, 1102] In this reaction, N, O, is a gas 6 so The first and second half-lives are equal in length 7 therefore The balanced overall reaction is not relevant for determining the rate law 8 therefore 9 and For an elementary step, the reaction order matches the reactant coefficients 10 and The reactant concentration does not decrease linearly 11 and 12 but A rate law includes the concentration of each reactant raised to its reaction order 13 but The half-life for a first order reaction is constant over time 14 but 15 but In this reaction, a single reactant decomposes to give two different products Custom: Custom
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


