Question: . Convert this Bayesian network into an equivalent Markov network. Con- vert the resulting Markov network into an equivalent Bayesian network. Let H be evidence
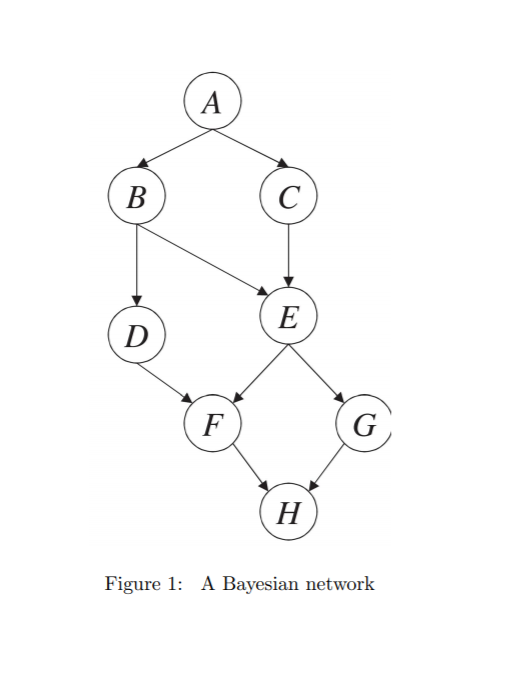
. Convert this Bayesian network into an equivalent Markov network. Con- vert the resulting Markov network into an equivalent Bayesian network. Let H be evidence variables. Trace the operations of Bucket elimination for computing Pr(H = h) along the order (A, E, B, C, D, F, G). Is the ordering (A, E, B, C, D, F, G) optimal? What is the treewidth of this network (assume that H is an evidence variable and so the resulting network does not contain H? Construct a tree decomposition for this network (again assume that H is an evidence variable). Show how the junction tree propagation algorithm will operate on this tree decomposition. Show the expression for each message. Figure 1: A Bayesian network . Convert this Bayesian network into an equivalent Markov network. Con- vert the resulting Markov network into an equivalent Bayesian network. Let H be evidence variables. Trace the operations of Bucket elimination for computing Pr(H = h) along the order (A, E, B, C, D, F, G). Is the ordering (A, E, B, C, D, F, G) optimal? What is the treewidth of this network (assume that H is an evidence variable and so the resulting network does not contain H? Construct a tree decomposition for this network (again assume that H is an evidence variable). Show how the junction tree propagation algorithm will operate on this tree decomposition. Show the expression for each message. Figure 1: A Bayesian network
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


