Question: = coordinates, as shown. Two immiscible fluids flow in the x direction driven by a pressure gradient. The fluids are located between fixed parallel plates
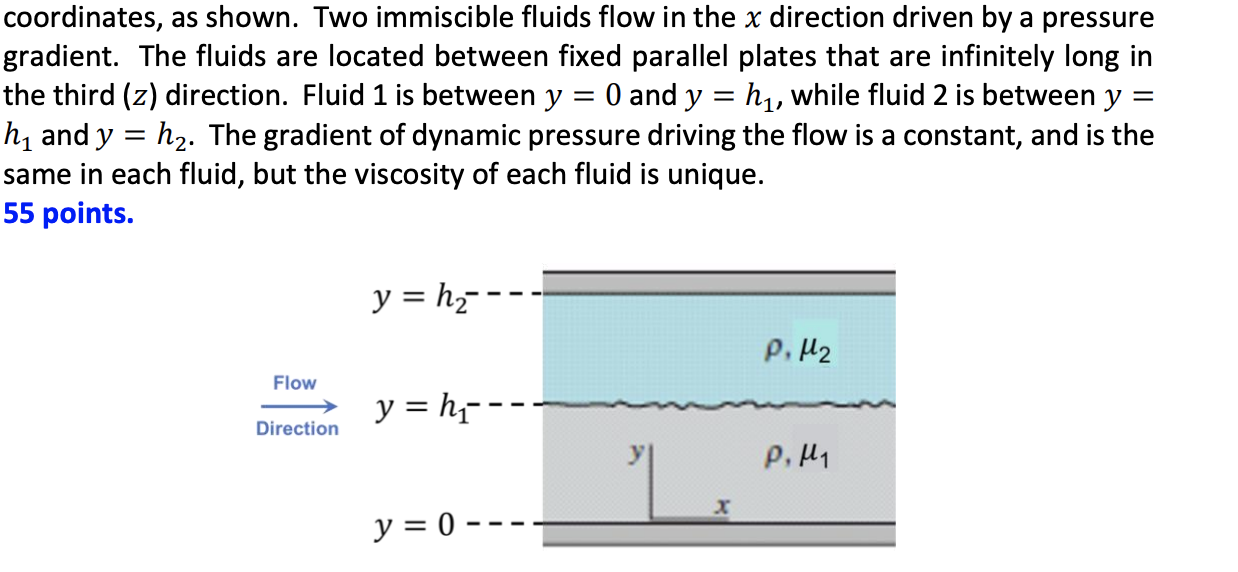
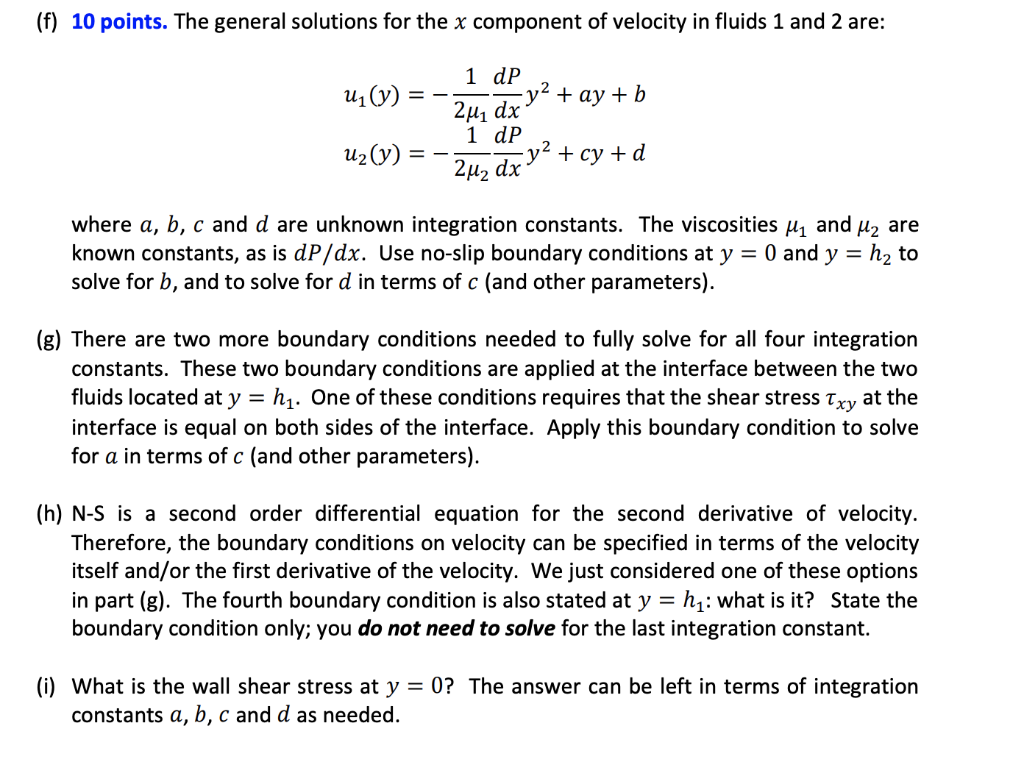
= coordinates, as shown. Two immiscible fluids flow in the x direction driven by a pressure gradient. The fluids are located between fixed parallel plates that are infinitely long in the third (z) direction. Fluid 1 is between y : 0 and y = hq, while fluid 2 is between y hy and y = h2. The gradient of dynamic pressure driving the flow is a constant, and is the same in each fluid, but the viscosity of each fluid is unique. 55 points. y = hz- P. 42 Flow y = h --- Direction P.M1 x y = 0 - (f) 10 points. The general solutions for the x component of velocity in fluids 1 and 2 are: uz(y) = 1 dp -y2 + ay + b 2u, dx 1 dp 2M2 dx y' + cy + d uz(y) where a, b, c and d are unknown integration constants. The viscosities Hi and M2 are known constants, as is dP/dx. Use no-slip boundary conditions at y = 0 and y = h2 to solve for b, and to solve for d in terms of c (and other parameters). (g) There are two more boundary conditions needed to fully solve for all four integration constants. These two boundary conditions are applied at the interface between the two fluids located at y = h . One of these conditions requires that the shear stress Txy at the interface is equal on both sides of the interface. Apply this boundary condition to solve for a in terms of c (and other parameters). (h) N-S is a second order differential equation for the second derivative of velocity. Therefore, the boundary conditions on velocity can be specified in terms of the velocity itself and/or the first derivative of the velocity. We just considered one of these options in part (g). The fourth boundary condition is also stated at y = h : what is it? State the boundary condition only; you do not need to solve for the last integration constant. (i) What is the wall shear stress at y = 0? The answer can be left in terms of integration constants a, b, c and d as needed
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


