Question: Correlation ariate Normal Distribution: Correlation Correlation of Bivariate Normal Random Variables If X and Y have a bivariate normal distribution with joint probability density function
Correlation


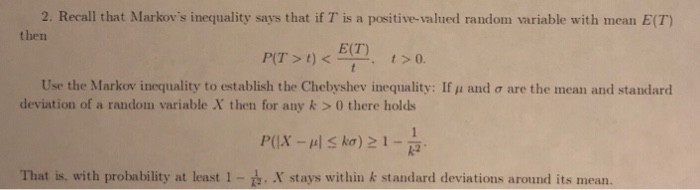

ariate Normal Distribution: Correlation Correlation of Bivariate Normal Random Variables If X and Y have a bivariate normal distribution with joint probability density function fxr(x, y, Gx, Gy, Hx, Hy, P), the correlation between X and Y is p. (5.23) For Bivariate Normal Random Variables Zero Correlation Implies Independence If X and Y have a bivariate normal distribution with p = 0, then X and Y are independent. (5.24). RightTriangle changes state In setBase or setHeight public void setBase [int newBase) { this base - newBase; setHypotenuse ( ) ; setChanged ( ) ; notifyObservers () ; public void setHeight [int newHeight) this . height - newHeight; getHypotenuse () ; setChanged ( ) ; notifyObservers () ;2. Recall that Markov's inequality says that if T' is a positive-valued random variable with mean E(T) then E(T) P(T > 1 ) 0 there holds P(1X - #| Ska) 21 - 1 That is. with probability at least 1 - 2. X stays within & standard deviations around its mean.SECTION 5.2. The Weak Law of Large Numbers Problem 4. In order to estimate f, the true fraction of smokers in a large population. Alvin selects n people at random. His estimator Mn is obtained by dividing Sn, the number of smokers in his sample, by n, i.e., Mn = Sn. Alvin chooses the sample size n to be the smallest possible number for which the Chebyshev inequality yields a guarantee that P(IMn - 1 Z E) 56, where e and o are some prespecified tolerances. Determine how the value of n recom- mended by the Chebyshev inequality changes in the following cases. (a) The value of e is reduced to half its original value. (b) The probability o is reduced to half its original value
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


