Question: Correlation vs causationhttps://youtu.be/8B271L3NtAw Correlation: A statistical measure of the strength of the relationship between the relative association of two variables (symbol ) Causation: Indicates a
Correlation vs causationhttps://youtu.be/8B271L3NtAw
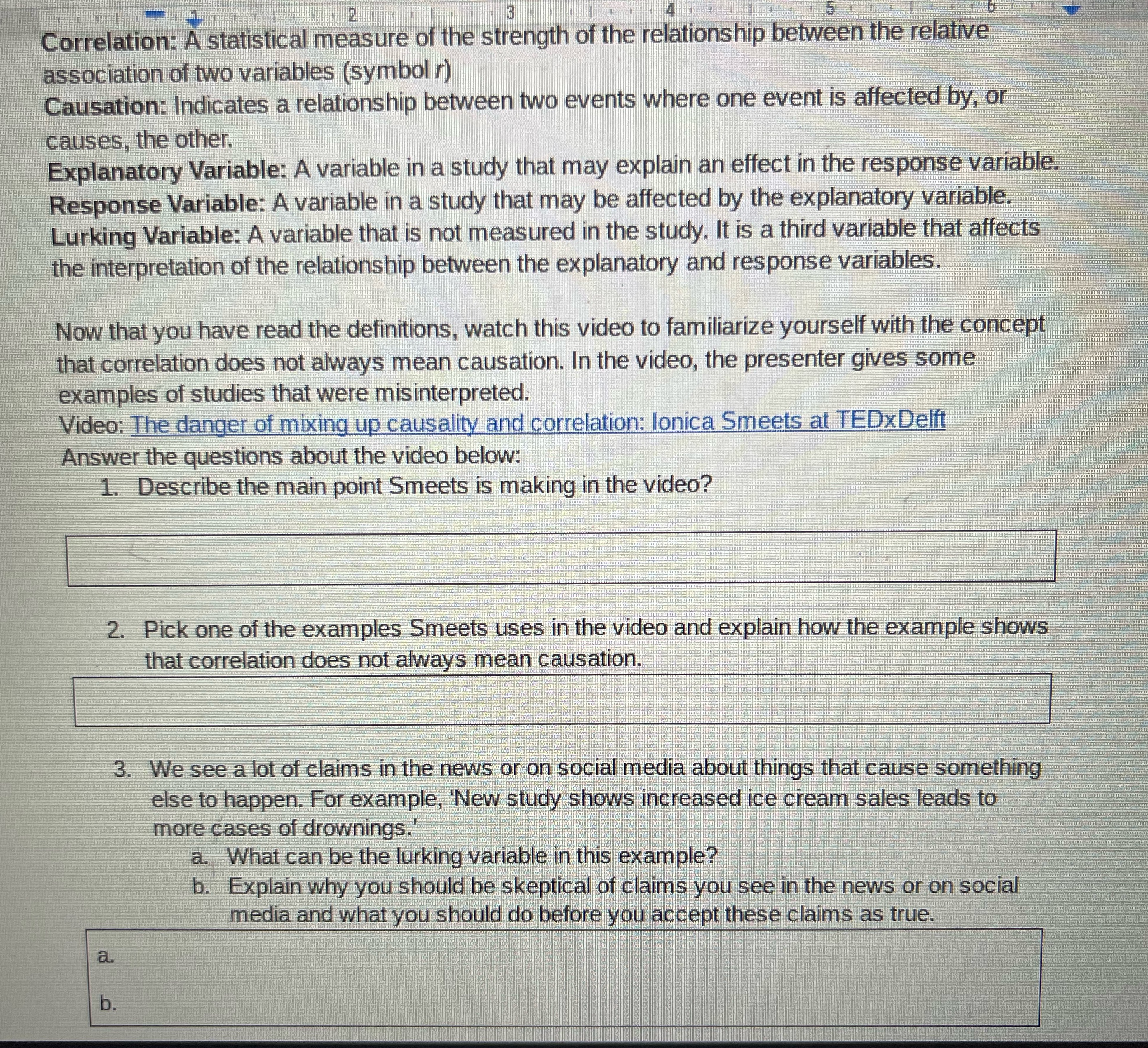
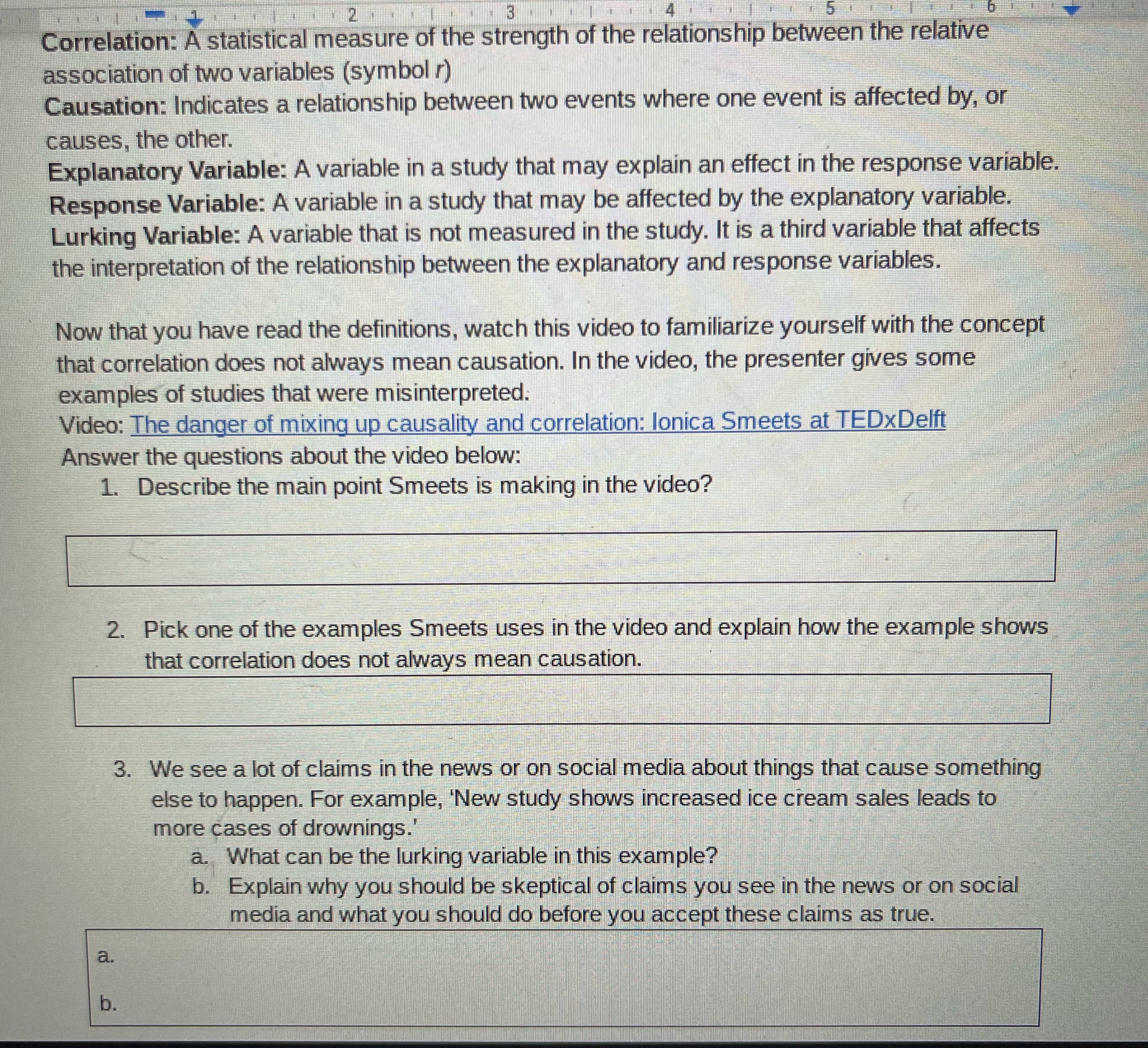
Correlation: A statistical measure of the strength of the relationship between the relative association of two variables (symbol ) Causation: Indicates a relationship between two events where one event is affected by, or causes, the other. Explanatory Variable: A variable in a study that may explain an effect in the response variable. Response Variable: A variable in a study that may be affected by the explanatory variable. Lurking Variable: A variable that is not measured in the study. It is a third variable that affects the interpretation of the relationship between the explanatory and response variables. Now that you have read the definitions, watch this video to familiarize yourself with the concept that correlation does not always mean causation. In the video, the presenter gives some examples of studies that were misinterpreted. Video: The danger of mixing up causality and correlation: lonica Smeets at TEDxDelft Answer the questions about the video below: 1. Describe the main point Smeets is making in the video? 2. Pick one of the examples Smeets uses in the video and explain how the example shows that correlation does not always mean causation. 3. We see a lot of claims in the news or on social media about things that cause something else to happen. For example, 'New study shows increased ice cream sales leads to more cases of drownings. a. What can be the lurking variable in this example? b. Explain why you should be skeptical of claims you see in the news or on social media and what you should do before you accept these claims as true. a. D
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


