Question: Could you explain more clearly on Steps 4-6 in step 2(question b)? I haven't learnt how to calculate the expected number of customers who leave

 Could you explain more clearly on Steps 4-6 in step 2(question b)? I haven't learnt how to calculate the expected number of customers who leave the system. I only learnt the formula in Little's law(i.e. I_q = T_q; I_serv = T_serv; I_sys=T_sys). Could you use that in the explanation?
Could you explain more clearly on Steps 4-6 in step 2(question b)? I haven't learnt how to calculate the expected number of customers who leave the system. I only learnt the formula in Little's law(i.e. I_q = T_q; I_serv = T_serv; I_sys=T_sys). Could you use that in the explanation?
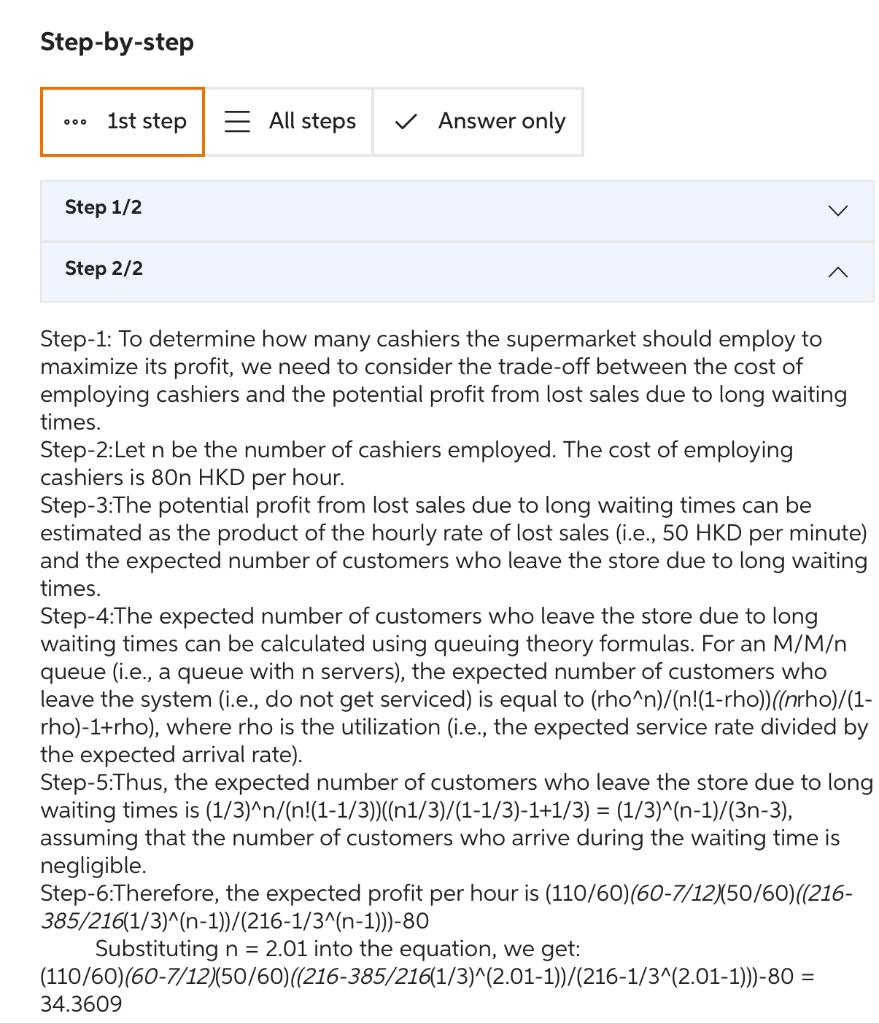
Question 4 Multi-Server Queue A supermarket manager is trying to decide how many cashers to employ for the peak time. The service times for check outs are exponentially distributed with a mean service time of 3 minutes. Customer arrivals to cashiers follow a Poisson arrival process with an average 110 customers per hour. a. What is the minimum number of cashers that would be needed to have the utilization less than one? b. If the waiting time is too long, customers might leave the store or even do not enter the store. It is estimated that for every minute of waiting time, the supermarket loses a potential profit of 50HKD every hour from lost sales. The hourly wage for a casher is 80HKD/ hour. How many cashers should the supermarket employ to maximize its profit? (Keep four decimal places.) Please answer the question (b) step by step and include the clear explanation. Step-by-step Step 1/2 Step 2/2 Step-1: To determine how many cashiers the supermarket should employ to maximize its profit, we need to consider the trade-off between the cost of employing cashiers and the potential profit from lost sales due to long waiting times. Step-2:Let n be the number of cashiers employed. The cost of employing cashiers is 80nHKD per hour. Step-3:The potential profit from lost sales due to long waiting times can be estimated as the product of the hourly rate of lost sales (i.e., 50 HKD per minute) and the expected number of customers who leave the store due to long waiting times. Step-4:The expected number of customers who leave the store due to long waiting times can be calculated using queuing theory formulas. For an M/M queue (i.e., a queue with n servers), the expected number of customers who leave the system (i.e., do not get serviced) is equal to (rn)/(n!(1rho))(( nrho) /(1 rho)-1+rho), where rho is the utilization (i.e., the expected service rate divided by the expected arrival rate). Step-5:Thus, the expected number of customers who leave the store due to long waiting times is (1/3)n/(n!(11/3))((n1/3)/(11/3)1+1/3)=(1/3)(n1)/(3n3), assuming that the number of customers who arrive during the waiting time is negligible. Step-6:Therefore, the expected profit per hour is (110/60)(607/12)(50/60)((216 385/216(1/3)(n1))/(2161/3(n1)))80 Substituting n=2.01 into the equation, we get: (110/60)(607/12)(50/60)((216385/216(1/3)(2.011))/(2161/3(2.011)))80= 34.3609
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


