Question: Could you explain step to step how you got the answer for 1,2,3 v2.cengagenow.com B C Home CengageNOWv2 | Online teaching and learning resource from
Could you explain step to step how you got the answer for 1,2,3
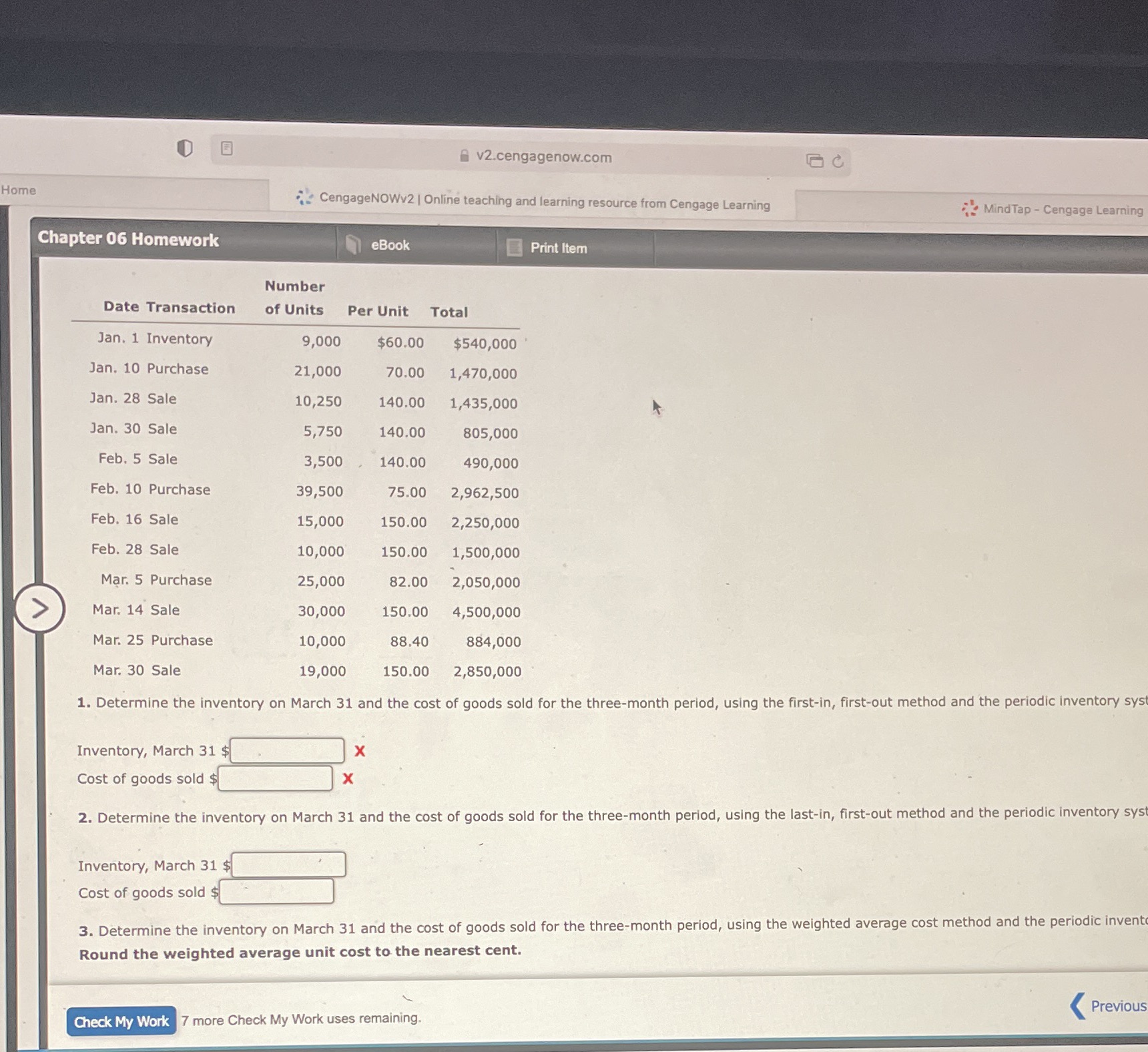
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


