Question: Create a decision tree and fully analyze it to determine the optimal decision to make at every decision node. What is the expected value (benefit
Create a decision tree and fully analyze it to determine the optimal decision to make at every decision node. What is the expected value (benefit score) of this situation?
***PLEASE SHOW STEPS***
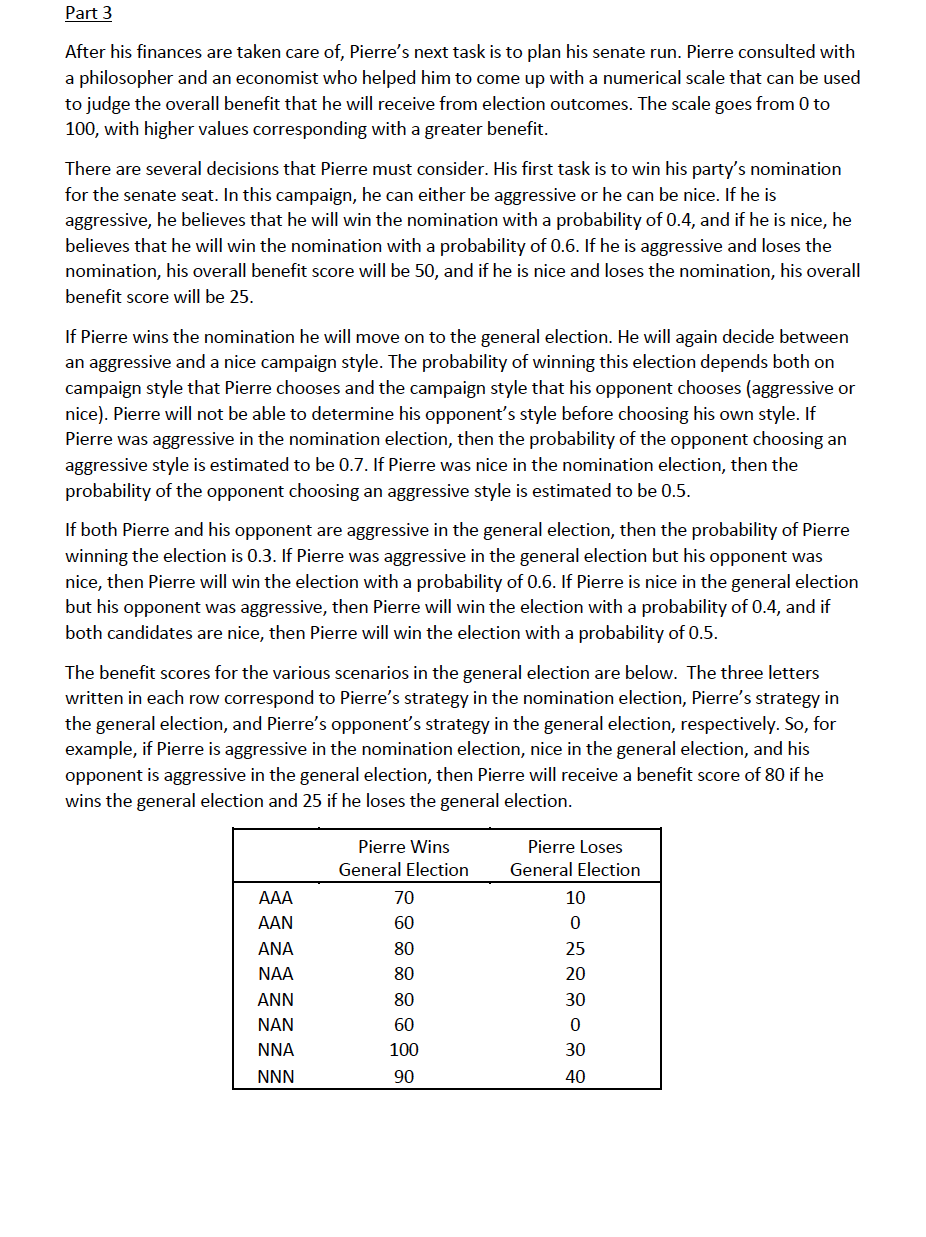
Part 3 After his finances are taken care of, Pierre's next task is to plan his senate run. Pierre consulted with a philosopher and an economist who helped him to come up with a numerical scale that can be used to judge the overall benefit that he will receive from election outcomes. The scale goes from 0 to 100, with higher values corresponding with a greater benefit. There are several decisions that Pierre must consider. His first task is to win his party's nomination for the senate seat. In this campaign, he can either be aggressive or he can be nice. If he is aggressive, he believes that he will win the nomination with a probability of 0.4, and if he is nice, he believes that he will win the nomination with a probability of 0.6. If he is aggressive and loses the nomination, his overall benefit score will be 50, and if he is nice and loses the nomination, his overall benefit score will be 25. If Pierre wins the nomination he will move on to the general election. He will again decide between an aggressive and a nice campaign style. The probability of winning this election depends both on campaign style that Pierre chooses and the campaign style that his opponent chooses (aggressive or nice). Pierre will not be able to determine his opponent's style before choosing his own style. If Pierre was aggressive in the nomination election, then the probability of the opponent choosing an aggressive style is estimated to be 0.7. If Pierre was nice in the nomination election, then the probability of the opponent choosing an aggressive style is estimated to be 0.5. If both Pierre and his opponent are aggressive in the general election, then the probability of Pierre winning the election is 0.3. If Pierre was aggressive in the general election but his opponent was nice, then Pierre will win the election with a probability of 0.6. If Pierre is nice in the general election but his opponent was aggressive, then Pierre will win the election with a probability of 0.4, and if both candidates are nice, then Pierre will win the election with a probability of 0.5. The benefit scores for the various scenarios in the general election are below. The three letters written in each row correspond to Pierre's strategy in the nomination election, Pierre's strategy in the general election, and Pierre's opponent's strategy in the general election, respectively. So, for example, if Pierre is aggressive in the nomination election, nice in the general election, and his opponent is aggressive in the general election, then Pierre will receive a benefit score of 80 if he wins the general election and 25 if he loses the general election. Pierre Wins General Election 70 Pierre Loses General Election 10 60 0 80 80 25 20 AAA AAN ANA NAA ANN NAN NNA NNN 80 60 100 30 0 30 90 40Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


