Question: Create a program domain.cpp that uses three classes point.h, shape.h and domain.h and compiles with the provided main program checkpack.cpp. The provided files should not
Create a program domain.cpp that uses three classes point.h, shape.h and domain.h and compiles with the provided main program checkpack.cpp. The provided files should not be modified.
The Domain class defines the rectangular region of fixed size (600x500) in which the shapes are packed.
void addShape(const Shape* p) is a function used to add a Shape pointer to the vector of Shape pointers s.
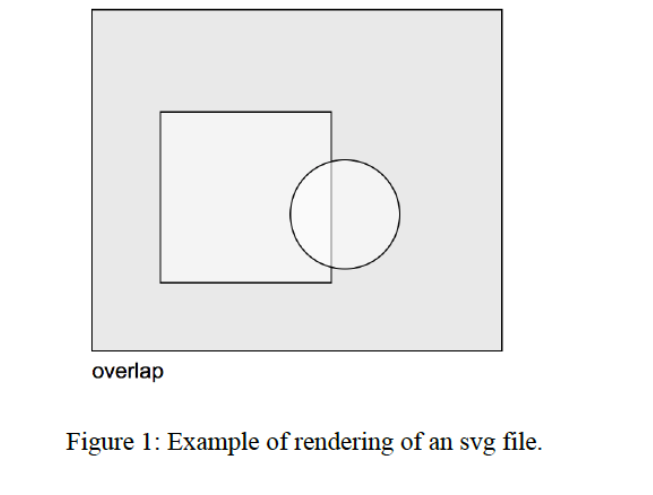
void draw(void) is a function that generates the entire svg output. It first checks whether all shapes fit into the Domain (hint: this can be done by defining a Rectangle object representing the domain and using the Shapes fits_in functions). It checks whether there are overlaps between shapes (using the Shapes overlaps functions). On the basis of these tests, it determines the diagnostic message (ok, overlap or does not fit). It then prints the svg header, the svg representations of all shapes (using the Shapes draw() functions), the diagnostic message, and the svg trailer on standard output. See the example test output svg files for details about the svg output format and the contents of the svg header and trailer.
//
// Point.h
//
#ifndef POINT_H
#define POINT_H
#include
class Point
{
public:
Point(void) : x(0), y(0) {}
Point(int xin, int yin) : x(xin), y(yin) {}
int norm2(void) const { return x*x + y*y; }
Point operator+(const Point& rhs) const;
Point operator-(const Point& rhs) const;
int x, y;
};
std::ostream& operator
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Point& p);
#endif
//
// Shape.h
//
#ifndef SHAPE_H
#define SHAPE_H
#include "Point.h"
#include
class Circle;
class Rectangle;
class Shape
{
public:
virtual ~Shape(void) {}
virtual bool overlaps(const Shape& s) const = 0;
virtual bool overlaps(const Circle& r) const = 0;
virtual bool overlaps(const Rectangle& r) const = 0;
virtual bool fits_in(const Rectangle& r) const = 0;
virtual void draw(void) const = 0;
};
class Rectangle : public Shape
{
public:
Rectangle(void): position(Point(0,0)), width(0), height(0) {}
Rectangle(Point p, int w, int h) :
position(p), width(w), height(h) {}
virtual ~Rectangle(void);
virtual bool overlaps(const Shape& r) const;
virtual bool overlaps(const Circle& r) const;
virtual bool overlaps(const Rectangle& r) const;
virtual bool fits_in(const Rectangle& r) const;
virtual void draw(void) const;
const Point position; // position of the lower left corner
const int width, height;
};
class Circle : public Shape
{
public:
Circle(void): center(Point(0,0)), radius(0) {}
Circle(Point c, int r) : center(c),radius(r) {}
virtual ~Circle(void);
virtual bool overlaps(const Shape& s) const;
virtual bool overlaps(const Circle& r) const;
virtual bool overlaps(const Rectangle& r) const;
virtual bool fits_in(const Rectangle& r) const;
virtual void draw(void) const;
Point center;
int radius;
};
#endif
//
// Domain.h
//
#include "Shape.h"
#include
#include
class Domain
{
public:
Domain(void);
~Domain(void);
void addShape(const Shape* p);
void draw(void);
private:
int sizex, sizey;
std::vector
};
//
// checkpack.cpp
//
#include "Domain.h"
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Domain d;
char type;
int x,y,w,h,r;
cin >> type;
while (cin)
{
if ( type == 'C' )
{
cin >> x >> y >> r;
Shape* p = new Circle(Point(x,y),r);
d.addShape(p);
}
else if ( type == 'R' )
{
cin >> x >> y >> w >> h;
Shape* p = new Rectangle(Point(x,y),w,h);
d.addShape(p);
}
cin >> type;
}
d.draw();
}
overlap Figure 1: Example of rendering of an svg file. overlap Figure 1: Example of rendering of an svg file
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


