Question: Create a sparse matrix vector with a linked list then creat a sparese matrix using linked list. I have done problem 1 and tested it
Create a sparse matrix vector with a linked list then creat a sparese matrix using linked list.
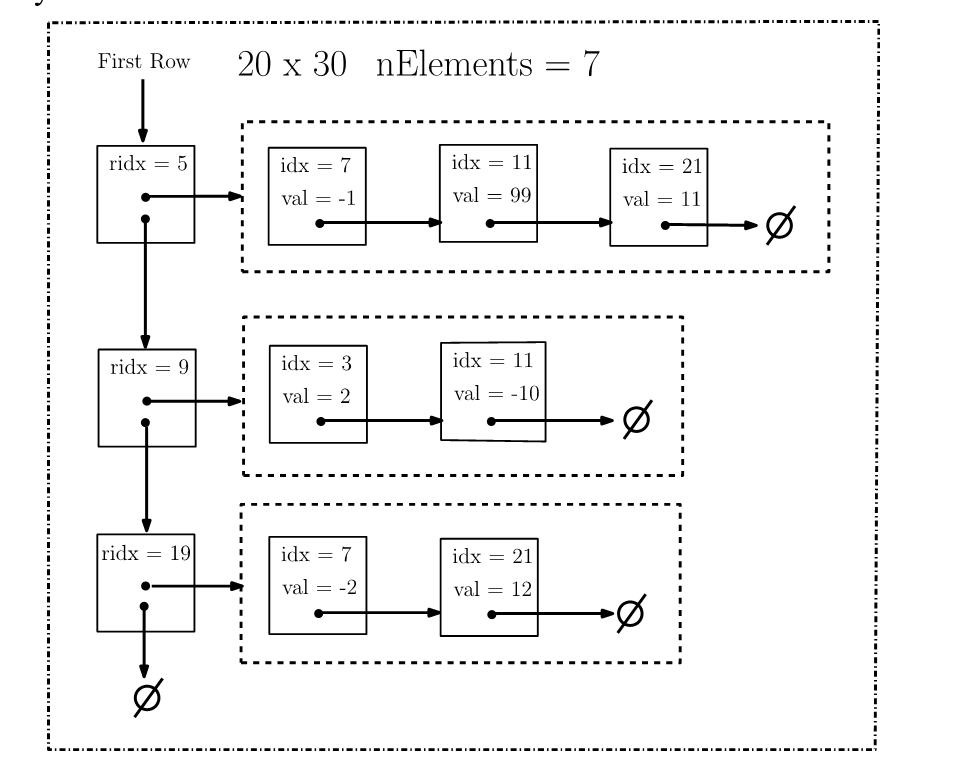
I have done problem 1 and tested it , which is to create LLsparseVector class, now I'm stuck on problem 2. I have started it but not sure if im on the right track at all. My exact problem is, I'm not sure how to: "RowHead nodes correspond to nonzero rows. Each rowhead node stores a LLSparseVec, storing a nonzero row. It also has a pointer to the next rowhead". I undertand the logic why we would want to use for each row a LLSparseVec, but how can a row head node store a LLSparseVec? For example giving this input in a text file (that woudl be with out doing any operations yet, but that's okay I havent gotten that far yet). Also the arrayMain class is just an example given please disregard it as it is not part of the project. Thank you in advance
MATRIX 10 20 SET 0 11 1 SET 0 8 1 SET 8 2 1 CLEAR 0 8 CLEAR 2 8 SET 8 11 1 END
my output would be :
FINAL_MATRIX NROWS 10 NCOLS 20 NELEMS 3 NUM_ROWS 2 ROW 0 RIDX 0 CIDX 11 VAL 1 ROW 8 RIDX 8 CIDX 2 VAL 1 RIDX 8 CIDX 11 VAL 1 END
This are the exact instructions:
Problem 1: Sparse Vector Using Linked List (5 pts)
Implement the linked list sparse vector class (LLSparseVec.java) so that LLMainClass can be executed.
Nodes in the linked list are nonzero elements of the vector, sorted according to their indices. The length of a vector is specified at construction.
When an element is set to zero, the corresponding node should be removed!
Implement the constructor, accessor methods, getElement, setElement, clearElement, getAllIndices, getAllValues. In otherwords, when LLMainClass is called using VEC argument and with a single input file, the program should be able to run correctly and give the same output as ArrayMainClass.
Implement both the addition, subtraction and multiplication methods in LLSparseVec. The method subtraction(otherV) means the current vector minus otherV.
The algorithm has to be O(m), in which m is the maximum number of nonzero elements in a vector (length of the list). To achieve this, you cannot simply use get and set in Problem 1. Only algorithms with O(m) complexity will get credits. The smart-merge method in HW1 is a good place to start. But note the difference here.
All operations return a new sparse vector object, storing the result.
If the two vectors length do not match, return a null object.
When LLMainClass is called using VEC argument and with multiple input files, the program should be able to run correctly and give the same output as ArrayMainClass.
Examples:
Problem 2: Sparse Matrix Using Linked List (5 pts)
Implement the linked list sparse matrix class (LLSparseMat.java) so that LLMainClass can be executed with MAT argument.
RowHead nodes correspond to nonzero rows. Each rowhead node stores a LLSparseVec, storing a nonzero row. It also has a pointer to the next rowhead.
When a row becomes empty (no nonzero elements), the rowhead should be removed.
Implement the constructor, accessor methods:
getElement, setElement, clearElement, numElements (returns number of non-zero elements).
getRowIndices returns an array of indices of rows with nonzero elements.
getOneRowColIndices returns an array of nonzero column indices of the row. Use LLSparseVec.getAllIndices().
getOneRowValues returns an array of nonzero values. Use LLSparseVec.getAllValues().
NOTE that these methods should all be linear to the number of nonzero rows or nonzero elements.
Sanity check: when LLMainClass is called using MAT argument and with a single input file, the program should be able to run correctly and give the same output as ArrayMainClass.
Problem 3: Sparse Matrix Operation Linked List (5 points)
Implement the addition, subtraction and multiplication methods in LLSparseM.
The algorithm has to be O(m), in which m is the maximum number of nonzero elements in a matrix. To achieve this, you cannot simply use get and set in Problem 3. Only algorithms with O(m) complexity will get credits.
All operations return a new sparse matrix object, storing the result. The method subtraction(otherM) means the current vector minus otherM.
If the two matrices dimensions (nrows, ncols) do not match, return a null object.
When LLMainClass is called using MAT argument and with multiple input files, the program should be able to run correctly and give the same output as ArrayMainClass.
public interface SparseVec {
// problem 1
int getLength(); //return the length of the vector
int numElements(); //return total number of nonzero elements in the vector
int getElement(int idx); //return the element at a given idx
void clearElement(int idx); //set the element at idx to zero
void setElement(int idx, int val); //set the element at idx to val
// get all nonzero indices
int[] getAllIndices();
// get all nonzero values
int[] getAllValues();
SparseVec addition(SparseVec otherV); // this vector + otherV
// return a new vector storing the result
SparseVec subtraction(SparseVec otherV); // this vector - otherV
// return a new vector storing the result
SparseVec multiplication(SparseVec otherV); // this matrix .* otherV
// return a new vector storing the result
}
public interface SparseM {
// problem 2
int nrows(); //return number of rows
int ncols(); //return number of columns
int numElements(); //return total number of nonzero elements in the matrix
int getElement(int ridx, int cidx); //return the element at a given entry (ridx, cidx),
void clearElement(int ridx, int cidx); //set the element at (ridx,cidx) to zero
void setElement(int ridx, int cidx, int val); //set the element at (ridx,cidx) to val
// get indices of non-empty rows, sorted
int[] getRowIndices();
// get indices of non-empty cols, sorted
int[] getOneRowColIndices(int ridx);
// get values of a given row
int[] getOneRowValues(int ridx);
// methods for problem 3
SparseM addition(SparseM otherM); // this matrix + otherM
// return a new matrix storing the result
SparseM subtraction(SparseM otherM); // this matrix - otherM
// return a new matrix storing the result
SparseM multiplication(SparseM otherM); // this matrix .* with otherM
// return a new matrix storing the result
}
/*------ This Node class is to be used in a doubly linked list ---*/
public class Node
{
private int data;
private int index;
private int ridx;
private Node prev; // reference to the previous node in the list
private Node next; // reference to the succeeding node in the list
// Default constructor
public Node() {};
// Constructor that sets up a prev and a next.
public Node(int idx,int d, Node p, Node n)
{
index = idx;
data = d;
prev = p;
next = n;
}
// Constructor that holds row index and links to a previous and next row index
public Node(int ridx, Node prevRidx, Node nextRidx)
{
this.ridx = ridx;
prev = prevRidx;
next = nextRidx;
}
public int getData() { return data; }
public int getIndex() { return index; }
public int getRidx() { return ridx; }
public Node getPrev() { return prev; }
public Node getNext() { return next; }
public void setData(int d) { data = d; }
public void setPrev(Node p) { prev = p; }
public void setNext(Node n) { next = n; }
}// ---------------- End Node class ----------
public class LLSparseVec implements SparseVec
{
private int len; // length of LLVector
private int nElements = 0; // number of nonzero elements, set to zero;
private Node header = null; // header sentinel, dummy node
private Node trailer = null; // trailer sentinel, dummy node
// Constructor
public LLSparseVec(int len)
{
if( len
this.len = len;
//Create the Vector
header = new Node(); // creating header
trailer = new Node(); // creating trailer
header.setNext(trailer); // header is followed by trailer
trailer.setPrev(header); // trailer is preceded by header
}
// check if the given index is out of bounds
private boolean outOfBounds(int idx)
{
return((idx = len));
}
@Override
public int getLength() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return len;
}
@Override
public int numElements() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return nElements;
}
@Override
public int getElement(int idx) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// If index is out of bounds or list empty exit
if(outOfBounds(idx))
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Node temp = header.getNext();
while(temp != trailer)
{
if(idx == temp.getIndex())
return temp.getData();
// If index is
if(idx
break;
temp = temp.getNext();
}
return 0;
}
@Override
public void clearElement(int idx) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(outOfBounds(idx)) // If index out of bounds exit
return;
Node temp = header.getNext();
Node predecessor;
Node sucessor;
while(temp != trailer)
{
if(idx == temp.getIndex())
{
predecessor = temp.getPrev();
sucessor = temp.getNext();
predecessor.setNext(sucessor);
sucessor.setPrev(predecessor);
nElements--;
}
// If index is
if(idx
break;
temp = temp.getNext();
}
}
@Override
public void setElement(int idx, int val) {
//System.out.println(" idx " + idx + " value " + val);
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(outOfBounds(idx))
throw new IllegalStateException("ERROR, index out of bounds.");
// If the list is empty add between header and trailer.
else if(numElements() == 0 && val != 0)
addBetween(idx, val, header, trailer);
// If val = 0 remove the index
else if(val == 0)
clearElement(idx);
// In the case that index added is smaller than the first node's index
else if ( idx
addBetween(idx, val, header, header.getNext());
// In the case the index added is greater than the last node's index
else if ( idx > trailer.getPrev().getIndex())
addBetween(idx, val, trailer.getPrev(), trailer);
else
{
Node temp = header.getNext();
while(temp != trailer)
{
if( idx == temp.getIndex() && val != temp.getData())
{
temp.setData(val);
return;
}
else if(idx == temp.getIndex() && val == temp.getData() )
return;
if( idx
{
addBetween(idx, val, temp.getPrev(), temp);
return;
}
temp = temp.getNext();
}
}
}
@Override
public int[] getAllIndices() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int[] idx = new int[nElements];
Node tempIdx = header.getNext();
for(int i = 0; tempIdx != trailer; i++)
{
idx[i] = tempIdx.getIndex();
tempIdx = tempIdx.getNext();
}
return idx;
}
@Override
public int[] getAllValues() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int[] val = new int[nElements];
Node tempVal = header.getNext();
for(int i = 0; tempVal != trailer; i++)
{
val[i] = tempVal.getData();
tempVal = tempVal.getNext();
}
return val;
}
private void addBetween(int idx, int val, Node predecessor, Node successor)
{ // create and link a new node
Node newest = new Node (idx, val, predecessor, successor);
predecessor.setNext(newest);
successor.setPrev(newest);
nElements++;
}
@Override
public SparseVec addition(SparseVec otherV) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(this.len != otherV.getLength())
return null; //exit if lengths not even.
SparseVec newVec = new LLSparseVec(len);
int temp;
for(int i = 0; i
{
temp = this.getElement(i) + otherV.getElement(i);
newVec.setElement(i, temp);
}
return newVec;
}
@Override
public SparseVec subtraction(SparseVec otherV) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(this.len != otherV.getLength())
return null; //exit if lengths not even.
SparseVec newVec = new LLSparseVec(len);
int temp;
for(int i = 0; i
{
temp = this.getElement(i) - otherV.getElement(i);
newVec.setElement(i, temp);
}
return newVec;
}
@Override
public SparseVec multiplication(SparseVec otherV) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(this.len != otherV.getLength())
return null; //exit if lengths not even.
SparseVec newVec = new LLSparseVec(len);
int temp;
for(int i = 0; i
{
temp = this.getElement(i) * otherV.getElement(i);
newVec.setElement(i, temp);
}
return newVec;
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.File;
public class LLMainClass {
public static SparseM ParseMatrix(String file_name){
Scanner sc = null;
String tmps;
SparseM M = null;
try {
sc = new Scanner(new File(file_name));
while (sc.hasNext()) {
tmps = sc.next();
if(tmps.equals("MATRIX")){
// initialize the matrix
int nr = sc.nextInt();
int nc = sc.nextInt();
M = new LLSparseM(nr,nc);
}else if(tmps.equals("END")){
// finished, return the matrix
sc.close();
return M;
}else if(tmps.equals("SET")){
// set an element
int ridx = sc.nextInt(); // row index
int cidx = sc.nextInt(); // col index
int val = sc.nextInt(); // value
M.setElement(ridx, cidx, val);
}else if(tmps.equals("CLEAR")){
// clear an element
int ridx = sc.nextInt(); // row index
int cidx = sc.nextInt(); // col index
M.clearElement(ridx, cidx);
}
}
sc.close();
return M;
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
public static SparseVec ParseVector(String file_name){
Scanner sc = null;
String tmps;
SparseVec V = null;
try {
sc = new Scanner(new File(file_name));
while (sc.hasNext()) {
tmps = sc.next();
if(tmps.equals("VECTOR")){
// initialize the matrix
int len = sc.nextInt();
V = new LLSparseVec(len);
}else if(tmps.equals("END")){
// finished, return the matrix
sc.close();
return V;
}else if(tmps.equals("SET")){
// set an element
int idx = sc.nextInt(); // index
int val = sc.nextInt(); // value
V.setElement(idx, val);
}else if(tmps.equals("CLEAR")){
// clear an element
int idx = sc.nextInt(); // index
V.clearElement(idx);
}
}
sc.close();
return V;
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
int n = args.length;
if(n
System.out.println("java LLMainClass VEC/MAT File1 A/M File2 ...");
return;
}
String fname;
String operator;
String dtype = args[0]; // matrix or vector
if(dtype.equals("VEC")){
fname = args[1];
SparseVec V = ParseVector(fname); // read V from the first file
if(V == null){
// if invalid input file, print NULL and exit
System.out.println("NULL: Illegal Input File "+fname);
return;
}
SparseVec tmpV;
for(int i = 2; i
operator = args[i];
fname = args[i+1];
tmpV = ParseVector(fname); // read tmpM from the next file
if(tmpV == null) // if the file is invalid, skip
{ System.out.println("NULL: Illegal Input File "+fname);
return;
}
if(operator.equals("A"))
V = V.addition(tmpV); // add tmpV to V
else if(operator.equals("S"))
V = V.subtraction(tmpV); // multiply tmpV to V
else if(operator.equals("M"))
V = V.multiplication(tmpV); // multiply tmpV to V
else{
System.out.println("NULL: Illegal operator: " + operator );
return;
}
if(V == null) // operation failed
{ System.out.println("NULL: Operator "+operator+" Failed, Fname "+fname);
return;
}
}
// output the final matrix
System.out.println("Final_Vector");
int[] idx = V.getAllIndices();
int[] val = V.getAllValues();
int len, ne;
len = V.getLength(); // length
ne = V.numElements(); // number of elements
System.out.println("LENGTH " + len + " NELEMS " + ne);
for(int i = 0; i
System.out.println("IDX " + idx[i] + " VAL " + val[i]);
System.out.println("END");
}else if(dtype.equals("MAT")){
fname = args[1];
SparseM M = ParseMatrix(fname); // read M from the first file
if(M == null){
// if invalid input file, print NULL and exit
System.out.println("NULL: Illegal Matrix Input, Fname " + fname);
return;
}
SparseM tmpM;
for(int i = 2; i
operator = args[i];
fname = args[i+1];
tmpM = ParseMatrix(fname); // read tmpM from the next file
if(tmpM == null) // if the file is invalid, skip
{ System.out.println("NULL: Illegal Input, Fname " + fname);
return;
}
if(operator.equals("A"))
M = M.addition(tmpM); // add tmpM to M
else if(operator.equals("S"))
M = M.subtraction(tmpM); // multiply tmpV to V
else if(operator.equals("M"))
M = M.multiplication(tmpM); // multiply tmpM to M
else{
System.out.println("NULL: Illegal operator: " + operator );
return;
}
if(M == null) // if the file is invalid, skip
{ System.out.println("NULL: Operation "+operator + " Failed, Fname "+ fname);
return;
}
}
// output the final matrix
System.out.println("FINAL_MATRIX");
int nr, nc, ne;
nr = M.nrows(); // number of rows
nc = M.ncols(); // number of columns
ne = M.numElements(); // number of elements
System.out.println("NROWS " + nr + " NCOLS " + nc + " NELEMS " + ne);
// print the matrix in rows
int[] ridx_list = M.getRowIndices();
System.out.println("NUM_ROWS "+ridx_list.length);
for(int ridx : ridx_list){
System.out.println("ROW "+ridx);
int[] one_row_cidx_list = M.getOneRowColIndices(ridx);
int[] one_row_vals_list = M.getOneRowValues(ridx);
for(int i = 0; i
System.out.println("RIDX "+ridx+" CIDX " + one_row_cidx_list[i] + " VAL " + one_row_vals_list[i]);
}
System.out.println("END");
}else{
System.out.println("The first argument has to be either VEC or MAT, meaning the data is Vector or Matrix");
return;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("NULL: Something is wrong");
return;
}
}
}
public class LLSparseM implements SparseM
{
private int nrows, ncols;
private int nElements = 0; // number of nonzero elements, initialized to be zero
private Node header;
private Node trailer;
// Constructor
public LLSparseM(int nr, int nc){
if(nr
if(nc
nrows = nr;
ncols = nc;
header = new Node(); // creating header
trailer = new Node(); // creating trailer
header.setNext(trailer); // header is followed by trailer
trailer.setPrev(header); // trailer is preceded by header
}
// check if the given (ridx, cidx) is out of bounds
private boolean outOfBounds(int ridx, int cidx){
return((ridx = nrows) || (cidx = ncols));
}
@Override
public int nrows() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public int ncols() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public int numElements() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public int getElement(int ridx, int cidx) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public void clearElement(int ridx, int cidx) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void setElement(int ridx, int cidx, int val) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(outOfBounds(ridx,cidx))
return;
else if(val == 0)
clearElement(ridx,cidx);
// In the case that there is no next row, matrix is empty
else if (header.getNext() == trailer && val != 0)
addBetweenRow(ridx, cidx, val, header, trailer);
else if( ridx
addBetweenRow(ridx, cidx, val, header, header.getNext());
// In the case that row index is greater than the last row in the list.
else if( ridx > trailer.getPrev().getRidx() )
addBetweenRow(ridx, cidx, val, trailer.getPrev(), trailer);
else
{
}
}
public void addBetweenRow(int ridx, int cidx, int val, Node prevRidx, Node nextRidx)
{
LLSparseVec newest = new LLSparseVec(ncols);
prevRidx.setNext(newest);
newest.setElement(cidx, val);
}
@Override
public int[] getRowIndices() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public int[] getOneRowColIndices(int ridx) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public int[] getOneRowValues(int ridx) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public SparseM addition(SparseM otherM) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public SparseM subtraction(SparseM otherM) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public SparseM multiplication(SparseM otherM) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
}
First Row 20 x 30 nElements-7 | idx = 7 val-1 idx 11 val 99 rids 5 idx- 21 val 11 idx = 3 val 2 idx- 11 val-10 idx - 21 val--2 val12 First Row 20 x 30 nElements-7 | idx = 7 val-1 idx 11 val 99 rids 5 idx- 21 val 11 idx = 3 val 2 idx- 11 val-10 idx - 21 val--2 val12
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


