Question: Create an HLA Assembly language program that prompts for a single integer value from the user and prints an arrow pattern like the one shown
Create an HLA Assembly language program that prompts for a single integer value from theuser and prints an arrow pattern like the one shown below. If the number is negative, don't print anything at all.
Here are some example program dialogues to guide your efforts:
Feed Me:
X
XX
XXX
XX
X
Feed Me:
Feed Me:
X
XX
XXX
XXXX
XXXXX
XXXX
XXX
XX
X
In an effort to help you focus on building an Assembly program, Id like to offer you the followingC statements matches the program specifications stated above. If you like, use them as the basis forbuilding your Assembly program.
SAMPLE C CODE:
int i j n;
printf "Feed Me:;
scanfd &n ;
the top half of the arrow...
for i ; i n; i
for j ; j i; j
printfX;
printf
;
the bottom half of the arrow...
for i n ; i ; i
for j ; j i; j
printfX;
printf
;
program progID; #include "stdlib.hhf;
static
variable declarations
begin progID;
statements
end progID;
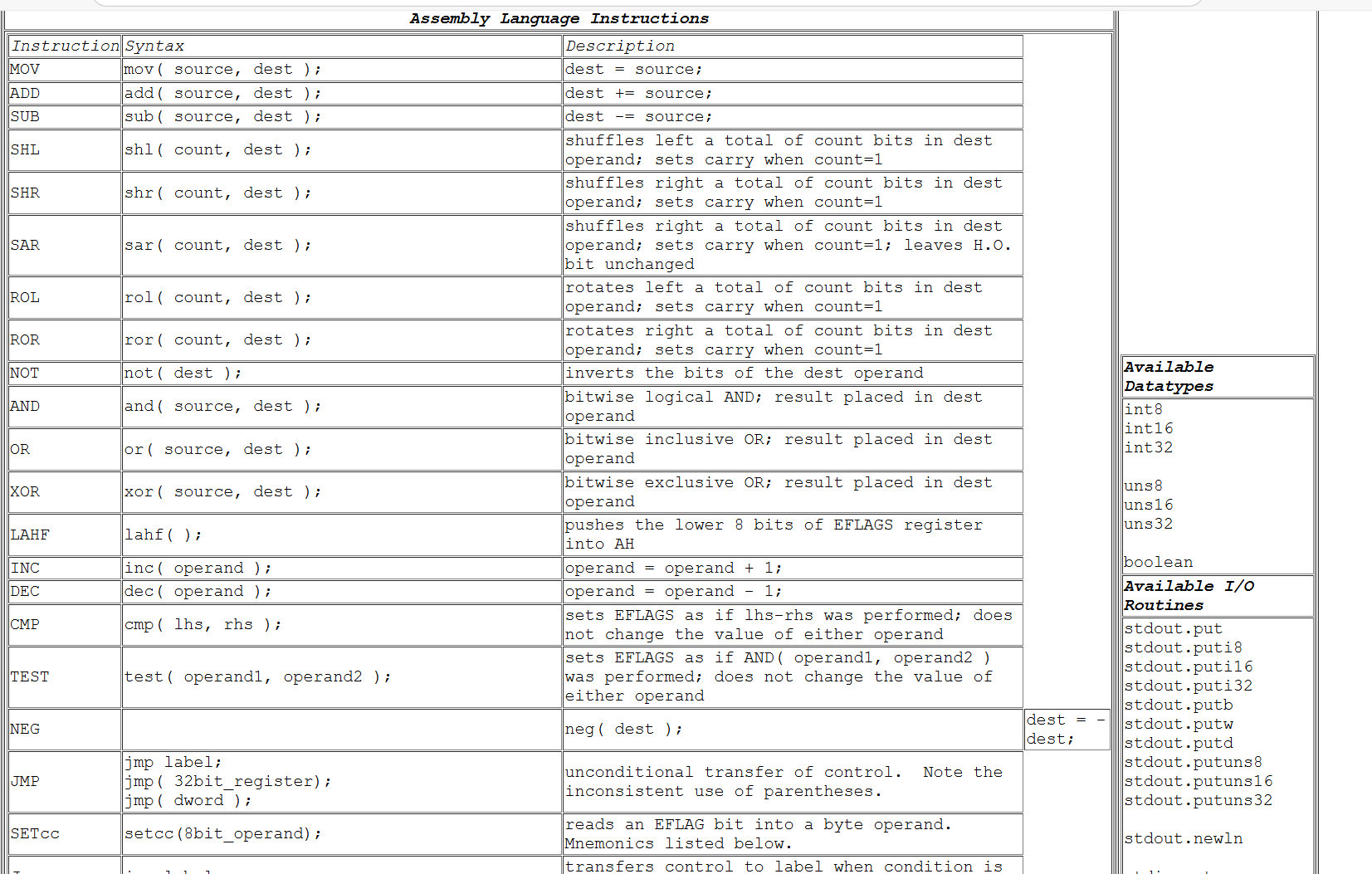
Assembly Language Instructions
begintabularccc
hline Instruction & Syntax & Description
hline MOV & mov source, dest ; & dest source;
hline ADD & add source, dest ; & dest source;
hline SUB & sub source, dest ; & dest source;
hline SHL & shl count, dest ; & shuffles left a total of count bits in dest operand; sets carry when count
hline SHR & shr count, dest ; & shuffles right a total of count bits in dest operand; sets carry when count
hline SAR & sar count, dest ; & shuffles right a total of count bits in dest operand; sets carry when count; leaves HO bit unchanged
hline ROL & rol count, dest ; & rotates left a total of count bits in dest operand; sets carry when count
hline ROR & ror count, dest ; & rotates right a total of count bits in dest operand; sets carry when count
hline NOT & not dest ; & inverts the bits of the dest operand
hline AND & and source, dest ; & bitwise logical AND; result placed in dest operand
hline OR & or source, dest ; & bitwise inclusive OR; result placed in dest operand
hline XOR & xor source, dest ; & bitwise exclusive OR; result placed in dest operand
hline LAHF & lahf; & pushes the lower bits of EFLAGS register into AH
hline INC & inc operand ; & operand operand ;
hline DEC & dec operand ; & operand operand ;
hline CMP & cmp lhs rhs ; & sets EFLAGS as if lhsrhs was performed; does not change the value of either operand
hline TEST & test operand operand; & sets EFLAGS as if AND operand operand was performed; does not change the value of either operand
hline NEG & & neg dest ;
hline JMP &
jmp label;
jmpbitregister;
jmp dword ;
& unconditional transfer of control. Note the inconsistent use of parentheses.
hline SETcc & setccbitoperand; & reads an EFLAG bit into a byte operand. Mnemonics listed below.
hline
endtabular
Available Datatypes
int
int
int
uns
uns
uns
boolean
Available IO
Routines
stdout.put
stdout.puti
stdout.puti
stdout.puti
stdout.putb
stdout.putw
stdout.putd
stdout.putuns
stdout.putuns
stdout.putuns
stdout.newln begintabularlll
hline JMP & begintabularl
jmp label;
jmp bitregister;
jmp dword;
endtabular & begintabularl
unconditional transfer of control. Note the
inconsistent use of parentheses.
endtabular
hline SETcC & setccbitoperand; & begintabularl
reads an EFLAG bit into a byte operand.
Mnemonics listed below.
endtabular
hline hline JCc & jcc label; & begintabularl
transfers control to label when condition is
met. Mnemonics listed below.
endtabular
hline hline
endtabular
begintabularccc
hline multicolumncMnemonics For SETcc and Jcc Instructions
hline Abbreviation & Meaning & Example
hline C & Set if Carry & SETC
hline NC & Set if Carry & SETNC
hline Z & Set if Zero & SETZ
hline NZ & Set if Zero & SETNZ
hline S & Set if Sign & SETS
hline NS & Set if Sign & SETNS
hline & Set if Overflow & SETO
hline NO & Set if Overflow & SETNO
hline E & Set if Equal & SETE
hline NE & Set if Not Equal & SETNE
hline NA & Set if not & SETNA
hline BE & Set if & SETBE
hline NAE & Set if not & SETNAE
hline B & Set if & SETB
hline NB & Set if not & SETNB
hline NBE & Set if not & SETNBE
hline A & Set if & SETA
hline AE & Set if & SETAE
hline G & Set if greater than & SETG
hline NLE & Set if not less than or equal & SETNLE
hline GE & Set if greater than or equal & SETGE
hline NL & Set if not less than & SETNE
hline L & Set if less than & SETL
hline NGE & Set if not greater than or equal & SETNGE
hline LE & Set if less than or equal & SETLE
hline NG & Set if not greater than & SETNG
hline
endtabular
stdout.putuns
stdout.putuns
stdout.putuns
stdout.newln
stdin.get
stdin.geti
stdin.geti
stdin.geti
stdin.getuns
stdin.getuns
stdin.getuns
stdin.getb
stdi ngetw
stdin.getd
Snipping Tool
Screenshot copied to clipboard and save
Sele
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


