Question: CST8116 Lab Exercise 04 (225) Instructions The five parts of the Software Development Process as presented by Cay Horstmann [1] will be used as
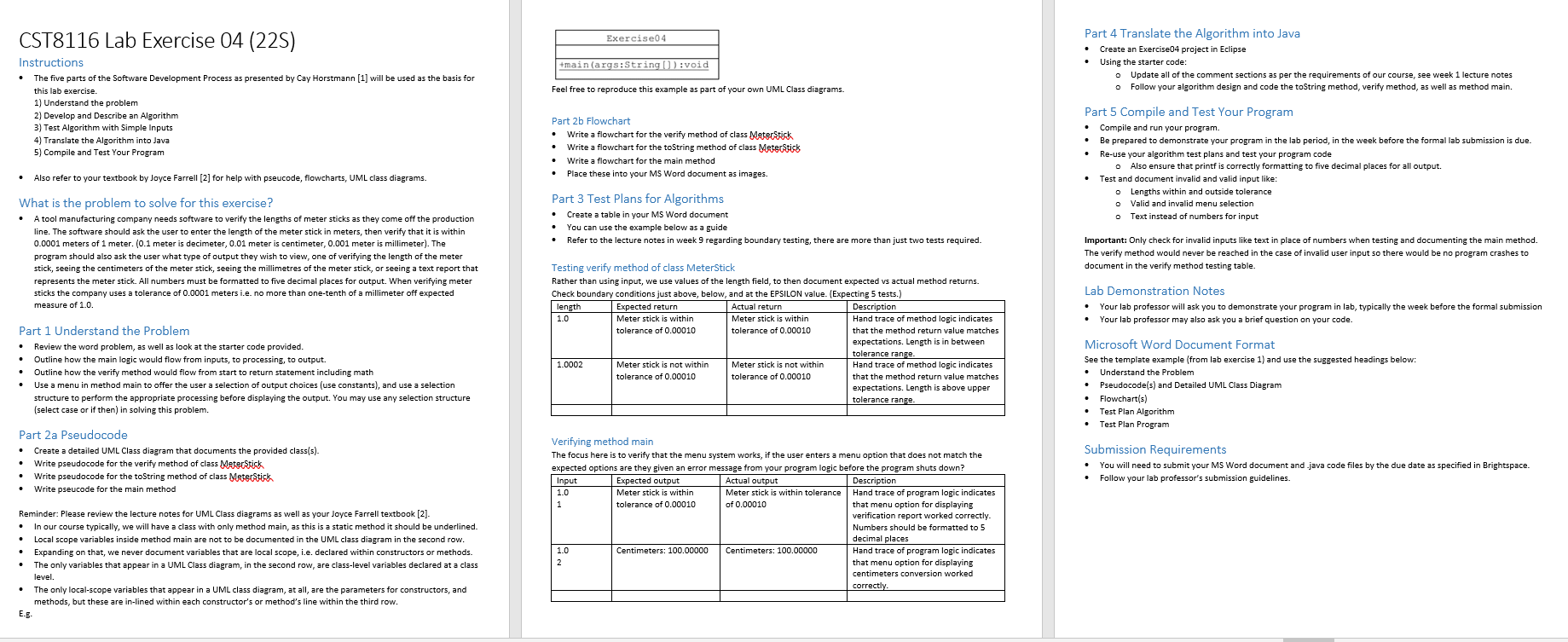
CST8116 Lab Exercise 04 (225) Instructions The five parts of the Software Development Process as presented by Cay Horstmann [1] will be used as the basis for this lab exercise. 1) Understand the problem 2) Develop and Describe an Algorithm 3) Test Algorithm with Simple Inputs 4) Translate the Algorithm into Java 5) Compile and Test Your Program Also refer to your textbook by Joyce Farrell [2] for help with pseucode, flowcharts, UML class diagrams. What is the problem to solve for this exercise? A tool manufacturing company needs software to verify the lengths of meter sticks as they come off the production line. The software should ask the user to enter the length of the meter stick in meters, then verify that it is within 0.0001 meters of 1 meter. (0.1 meter is decimeter, 0.01 meter is centimeter, 0.001 meter is millimeter). The program should also ask the user what type of output they wish to view, one of verifying the length of the meter stick, seeing the centimeters of the meter stick, seeing the millimetres of the meter stick, or seeing a text report that represents the meter stick. All numbers must be formatted to five decimal places for output. When verifying meter sticks the company uses a tolerance of 0.0001 meters i.e. no more than one-tenth of a millimeter off expected measure of 1.0. Part 1 Understand the Problem Review the word problem, as well as look at the starter code provided. Outline how the main logic would flow from inputs, to processing, to output. Outline how the verify method would flow from start to return statement including math Use a menu in method main to offer the user a selection of output choices (use constants), and use a selection structure to perform the appropriate processing before displaying the output. You may use any selection structure (select case or if then) in solving this problem. Part 2a Pseudocode Create a detailed UML Class diagram that documents the provided class(s). Write pseudocode for the verify method of class Meter Stick Write pseudocode for the toString method of class Meterstick Write pseucode for the main method Reminder: Please review the lecture notes for UML Class diagrams as well as your Joyce Farrell textbook [2]. In our course typically, we will have a class with only method main, as this is a static method it should be underlined. Local scope variables inside method main are not to be documented in the UML class diagram in the second row. Expanding on that, we never document variables that are local scope, i.e. declared within constructors or methods. The only variables that appear in a UML Class diagram, in the second row, are class-level variables declared at a class level. E.B. The only local-scope variables that appear in a UML class diagram, at all, are the parameters for constructors, and methods, but these are in-lined within each constructor's or method's line within the third row. Exercise04 +main(args:String[]):void Feel free to reproduce this example as part of your own UML Class diagrams. Part 2b Flowchart Write a flowchart for the verify method of class Meter Stick Write a flowchart for the toString method of class Meter Stick Write a flowchart for the main method Place these into your MS Word document as images. Part 3 Test Plans for Algorithms Create a table in your MS Word document You can use the example below as a guide Refer to the lecture notes in week 9 regarding boundary testing, there are more than just two tests required. Testing verify method of class MeterStick Rather than using input, we use values of the length field, to then document expected vs actual method returns. Check boundary conditions just above, below, and at the EPSILON value. (Expecting 5 tests.) length 1.0 Expected return Meter stick is within tolerance of 0.00010 1.0002 Meter stick is not within tolerance of 0.00010 Input 1.0 Actual return Meter stick is within tolerance of 0.00010 Meter stick is not within tolerance of 0.00010 Expected output Meter stick is within tolerance of 0.00010 Actual output Meter stick is within tolerance of 0.00010 Description Hand trace of method logic indicates that the method return value matches expectations. Length is in between tolerance range. Hand trace of method logic indicates that the method return value matches expectations. Length is above upper tolerance range. Part 4 Translate the Algorithm into Java Create an Exercise04 project in Eclipse Using the starter code: Update all of the comment sections as per the requirements of our course, see week 1 lecture notes Follow your algorithm design and code the toString method, verify method, as well as method main. Part 5 Compile and Test Your Program Compile and run your program. Be prepared to demonstrate your program in the lab period, in the week before the formal lab submission is due. Re-use your algorithm test plans and test your program code Also ensure that printf is correctly formatting to five decimal places for all output. Test and document invalid and valid input like: Lengths within and outside tolerance Valid and invalid menu selection o Text instead of numbers for input Important: Only check for invalid inputs like text in place of numbers when testing and documenting the main method. The verify method would never be reached in the case of invalid user input so there would be no program crashes to document in the verify method testing table. Lab Demonstration Notes Your lab professor will ask you to demonstrate your program in lab, typically the week before the formal submission Your lab professor may also ask you a brief question on your code. Microsoft Word Document Format See the template example (from lab exercise 1) and use the suggested headings below: Understand the Problem Pseudocode(s) and Detailed UML Class Diagram Flowchart(s) Test Plan Algorithm Verifying method main The focus here is to verify that the menu system works, if the user enters a menu option that does not match the expected options are they given an error message from your program logic before the program shuts down? Description Hand trace of program logic indicates that menu option for displaying verification report worked correctly. Numbers should be formatted to 5 decimal places Hand trace of program logic indicates that menu option for displaying centimeters conversion worked correctly. Test Plan Program Submission Requirements You will need to submit your MS Word document and java code files by the due date as specified in Brightspace. Follow your lab professor's submission guidelines. 1.0 Centimeters: 100.00000 Centimeters: 100.00000 2
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (145 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Problem Overview A tool manufacturing company needs software to verify the lengths of meter sticks as they come off the production line The software should ensure that the length entered by the user i... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


