Question: cu expect w USUID HOV.UUU CUI PRODUCIS I Dex on the corris Classeu pedury costs fexcluding costs of the distributed product, as follows. Account Supplies
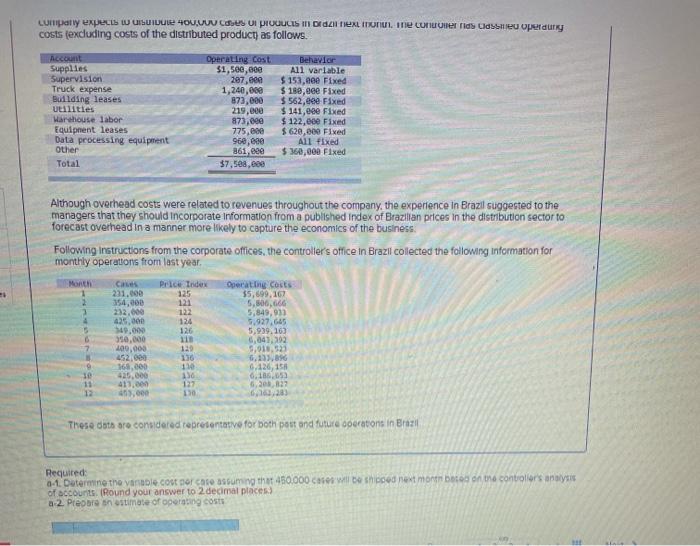
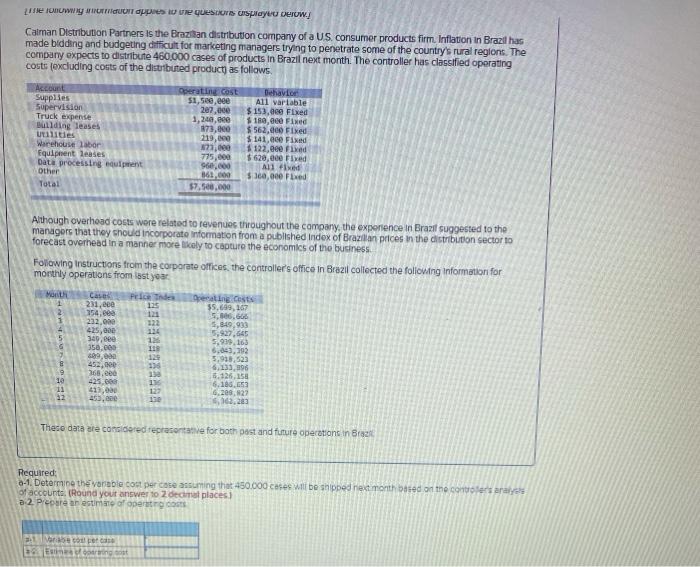
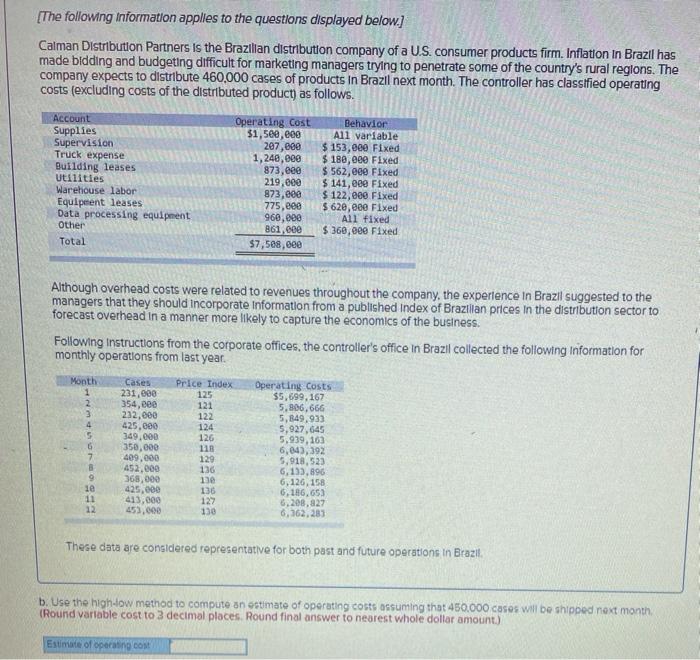
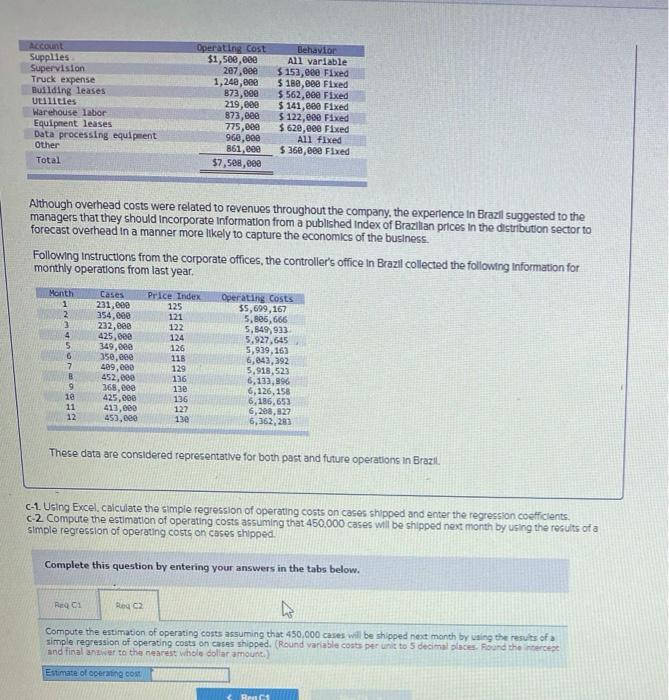
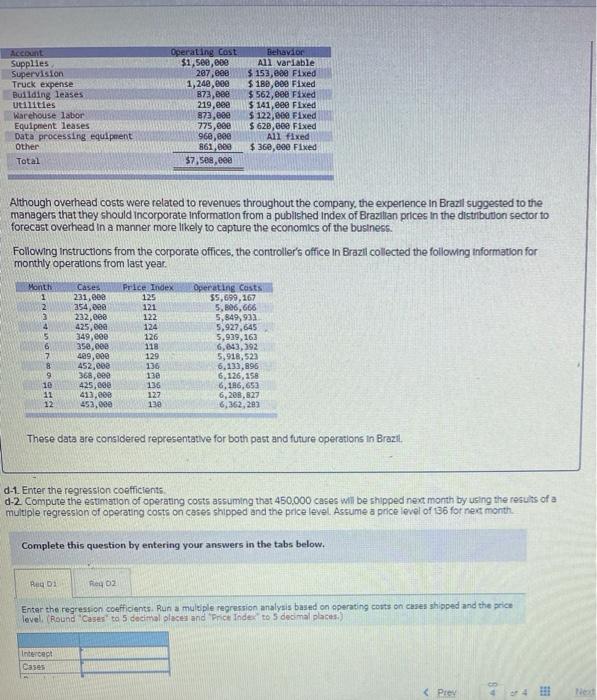
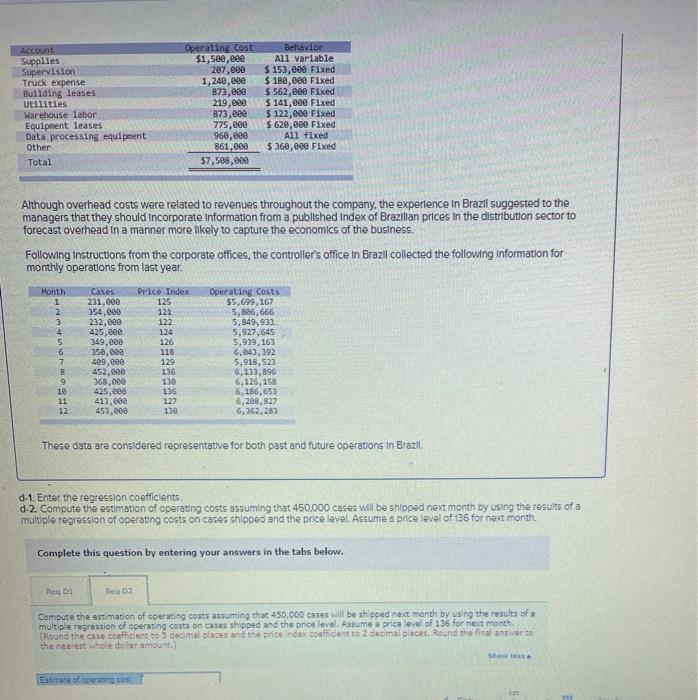
cu expect w USUID HOV.UUU CUI PRODUCIS I Dex on the corris Classeu pedury costs fexcluding costs of the distributed product, as follows. Account Supplies Supervision Truck expense Building leases utilities Warehouse labor Equipment leases Data processing equipment Other Total Operating cost $1,500,000 207.com 1,240,000 873,000 219,000 873,000 775,600 960,830 861, eee $7,588,600 Behavior All variable $ 153,eee Fixed $ 180, eee Fixed $ 562,eee Fixed $141,eee Fixed $ 122,eee Fixed $ 620,000 Fixed All Fixed $360,000 Fixed Although overhead costs were related to revenues throughout the company, the experience in Brazil suggested to the managers that they should incorporate Information from a published index of Brazilian prices in the distribution sector to forecast overhead in a manner more likely to capture the economics of the business Following Instructions from the corporate offices, the controller's office in Brazil collected the following information for monthly operations from last year, C Operating costs $5,699.10 354,000 Month 1 Price Index 271,00 4 5 6 7 232.000 435,000 149.000 550,000 400,000 452.000 168,000 425,000 413.000 0.000 122 124 126 11 120 136 11 150 127 130 5.506,666 5,849,900 9.927.645 5,939.16) 6,04),192 9,018,533 1,135, 6.120,158 6.1,65 5.202.22 6,102 30 11 12 These dots are considered representative for both post and future operations in Brazil Required 0.1. Determine the variable cost or care assuming the 450.000 es will be shipped next montes on the controller's analysis of accounts (Round your answer to 2 decimal places a 2. Preobre estimate of operating costs the onowwy IT apps Reques payu Dew/ Caiman Distribution Partners is the Brazilian distribution company of a US consumer products firm. Inflation in Brazil has made bidding and budgeting difficult for marketing managers trying to penetrate some of the country's rural regions. The company expects to distribute 460.000 cases of products in Brazil next month. The controller has classified operating couts (excluding costs of the distributed product) as follows Account Supplies Supervision Truck expense Bullding leases Utilities Warehouse labor Equipment leases Data processing equipment Other Total Operating cost $1,500,000 207.000 1,200,00 173,000 219,000 21.000 775,000 96.000 361.00 $7.500.000 Dehavior A11 variable $ 153,000 Fixed $ 180,00 Fixed $562.000 Fixed $141,000 Fixed $ 122,00 Fixed $ 620,000 Fixed Al fixed $ 160,00 Fixed Although overhead costs were related to revenues throughout the company, the experience in Brazil suggested to the managers that they should incorporate Information from a published index of Brazilian prices in the distribution sector to forecast overhead in a manner more likely to capture the economics of the business Following instructions from the corporate offices, the controller's office in Brazil collected the following information for monthly operations from last year Marit 1 1 Case 231,eee 354, eee 232.000 425,000 340.000 350.000 09.00 453,000 360.00 425.000 413,00 450.000 Price Tade 125 121 222 11 126 11 125 134 5 Operating costs 35.6, 167 5.00.66 4,849.930 5.989.163 6.643,792 5,918,523 6.133.196 5.126.158 6.186. 6.209.22 103,203 9 23 11 127 Theco data are considered representative for both past and future operation in Braz Required: 041. Determine the variable cont per core assuming that 450.000 cases will be shipped next month based on the controles analys of account. (Round your answer to decimal places) a 2 Piecare an estimate of operating Variable nost [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Calman Distribution Partners is the Brazilian distribution company of a U.S. consumer products firm. Inflation in Brazil has made bidding and budgeting difficult for marketing managers trying to penetrate some of the country's rural regions. The company expects to distribute 460,000 cases of products In Brazil next month. The controller has classified operating costs (excluding costs of the distributed product) as follows. Account Supplies Supervision Truck expense Building leases Utilities Warehouse Labor Equiperent leases Data processing equipment Other Total Operating cost Behavior $1,500,000 All variable 207,000 $ 153,000 Fixed 1,248,000 $ 180,000 Fixed 873,000 $ 562,000 Fixed 219.000 $ 141, eee Fixed 873,000 $ 122,000 Fixed 775, eee 5620, ese Fixed 960,000 All fixed 861,000 $360,000 Fixed $7,508,8ee Although overhead costs were related to revenues throughout the company, the experience in Brazil suggested to the managers that they should incorporate Information from a published index of Brazilian prices in the distribution sector to forecast overhead in a manner more likely to capture the economics of the business. Following Instructions from the corporate offices, the controller's office in Brazil collected the following information for monthly operations from last year. Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Cases 231,000 354,000 222,000 425,600 349.000 350,000 499.000 452,000 368,000 425,000 413,000 453,000 Price Index 125 121 122 124 126 118 129 136 13 136 127 130 Operating costs $5,699,167 5,806,666 5,849.933 5,927,645 5,939,163 6,643,392 5.918,523 6,133,896 6,126,158 6,186,653 6,208.827 6,362,283 le 11 12 These data are considered representative for both past and future operations in Brazil b. Use the high-low method to compute an estimate of operating costs assuming that 450.000 cases will be shipped next month. (Round variable cost to 3 decimal places. Round final answer to nearest whole dollar amount) Estimate of operating cost Account Supplies Supervision Truck expense Building leases Utilities Warehouse labor Equipment leases Data processing equipment Other Total Operating cost $1,500,000 207,eee 1,248,000 873,000 219,000 873,000 775,000 960,000 861,000 $7,500,000 Behavior All variable $ 153,000 Fixed $ 180,880 Fixed $ 562,000 Fixed $ 141,600 Fixed $ 122,000 Fixed $ 620,600 Fixed All fixed $360,088 Fixed Although overhead costs were related to revenues throughout the company, the experience in Brazil suggested to the managers that they should Incorporate Information from a published index of Brazilian prices in the distribution sector to forecast overhead in a manner more likely to capture the economics of the business. Following Instructions from the corporate offices, the controller's office in Brazil collected the following information for monthly operations from last year. Month Cases 1 231,600 2 354,000 3232,800 4 425,000 5 349,888 6 350,000 17 409,000 B 452,000 9 368,000 10 425,000 11 413,000 12 453, cee Price Index 125 121 122 124 126 115 129 Operating costs $5,699,167 5,886,666 5,849,933 5,927,645 5,939,163 6,043,392 5,918,523 5,133,896 6,126,158 6,186,650 6,208,327 6,362,283 136 130 136 122 13e These data are considered representative for both past and future operations in Brazil C-1. Using Excel. calculate the simple regression of operating costs on cases shipped and enter the regression coefficients C-2 Compute the estimation of operating costs assuming that 450,000 cases will be shipped next month by using the results of a simple regression of operating costs on cases shipped Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. RO Roq Compute the estimation of operating costs assuming that 450.000 cases will be shipped next month by using the resuts of simple regression of operating costs on cases shipped. (Round variable costs per unit to 5 decimal places. Found the recept and final antwer to the nearest whole collar amount.) Estimate of operating cost RCA Account Supplies Supervision Truck expense Building leases Utilities Warehouse labor Equipment leases Data processing equipment Other Total Operating cost $1,see,100 207,600 1,240,000 B72,000 219,000 873,000 775,000 960, eee 861,000 57. see, eee Behavior All variable $ 153,680 Fixed $ 180,000 Fixed $ 562,000 Fixed $ 141,eee Fixed $ 122,000 Fixed $ 620,000 Fixed All fixed $360,000 Fixed Although overhead costs were related to revenues throughout the company, the experience in Brazil suggested to the managers that they should incorporate Information from a published index of Brazilian prices in the distribution sector to forecast overhead in a manner more likely to capture the economics of the business. Following Instructions from the corporate offices, the controller's office in Brazil collected the following information for monthly operations from last year. Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Cases 231.000 354,000 232,000 425,000 349,00 350,000 499,000 452,000 368,eee 425.00 413.000 452.000 Price Index 125 121 122 124 126 118 129 136 130 136 127 130 Operating costs 55,699,167 5,806,666 5,849,93 5,927,645 5,939,162 6,643,392 5,918.523 6,133,896 6,126,158 6,186,653 6,208,627 6,362,203 9 10 11 12 These data are considered representative for both past and future operations in Brazil. d-1. Enter the regression coefficients d-2 Compute the estation of operating costs assuming that 450,000 cases will be shipped next month by using the results of a multiple regression of operating costs on cases shipped and the price level. Assume a price level of 136 for next month Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Re: Reg oz Enter the regression coefficients. Run a multiple regression analysis based on operating costs on cases shipped and the price level (Round "Cases" to 5 decimal places and Price Index to decimal places) Interact Cases 8
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


