Question: Customer CUS ID (PRO Order Order No. (PK) places Includes CUS Name CUS ID (FO Item Order No. (FKO Item Code (PK Item Name Quantity
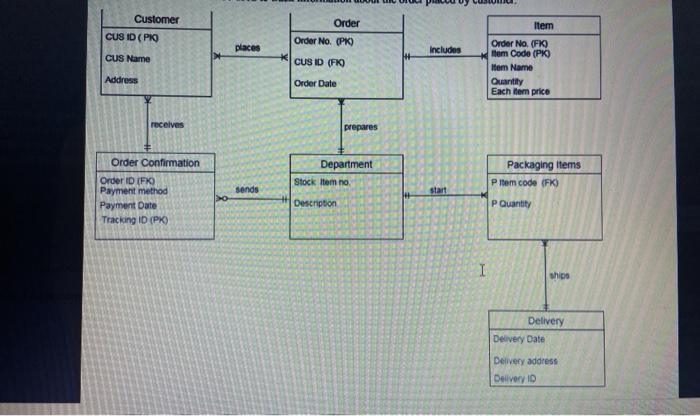





Customer CUS ID (PRO Order Order No. (PK) places Includes CUS Name CUS ID (FO Item Order No. (FKO Item Code (PK Item Name Quantity Each ter price Address Order Date receives prepares Order Confirmation Department Stock Item no Packaging items PItem code (FK) sends start Order ID FIO Payment method Payment Date Tracking ID (PK) Description P Quantity I ships Delivery Delivery Date Delivery address Delivery ID 1 Expand and enhance your database design to include Supertype and Subtype entities. You have the choice to decide if the Specialization Hierarchy is Disjoint or Overlapping and if the constraints are Partial or Complete. Make sure you apply this to no less than 2 Entities. If in above database you did not provide any entities that could be Extended then make sure you add to your Database design entities that could be categorized. 2 Improve your database design by make sure your tables are Normalized. To solve this go through the check list provided with this assignment and make sure you have done all the recommendation given to you. Note: This Check list is recommended for your use anytime you design a database 3- Create at least 1 recursive relationship. Data-Modeling Checklist Below is a check list of conditions that you need to account for when you design a database 1. Business rules Properly document and verify all business rules with the end users Ensure that all business rules are written precisely, clearly, and simply The business rules must help identify entities, attributes, relationships, and constraints Identify the source of all business rules, and ensure that each business rule is justified, dated, and signed off by an approving authority 2. Data modeling Naming conventions: all names should be limited in length (database-dependent size) 3. Entity names: should be nouns that are familiar to business and should be short and meaningful Should document abbreviations, synonyms, and aliases for each entity Should be unique within the model For composite entities, may include a combination of abbreviated names of the entities linked through the composite entity 4. Attribute names: . 4- Attribute names: . Should be unique within the entity Should use the entity abbreviation as a prefix Should be descriptive of the characteristic Should use suffixes such as _ID, _NUM, or _CODE for the PK attribute Should not be a reserved word Should not contain spaces or special characters such as @, I, or & 5- Relationship names: Should be active or passive verbs that clearly indicate the nature of the relationship 6- Entities: Each entity should represent a single subject Each entity should represent a set of distinguishable entity instances 7. Attributes: . Should be simple and single-valued (atomic data) Should document default values, constraints, synonyms, and aliases Derived attributes should be clearly identified and include source(s) Should not be redundant unless this is required for transaction accuracy, performance, or maintaining a history Nonkey attributes must be fully dependent on the PK attribute 8. Relationships: Should clearly identify relationship participants Should clearly define participation, connectivity, and document cardinality 9. ER model: Should be validated against expected processes: inserts, updates, and deletions Should evaluate where, when and how to maintain a history . Should not contain redundant relationships except as required Should minimize data redundancy to ensure single-place updates Should conform to the minimal data rule: All that is needed is there, and all that is there is needed Firstly, you have to improve the database design by following the 3 instructions given in 2nd photo and make new normalised database design. After that, see that checklist that database design must have to follow. You can take 6-7 hours for completing this. Customer CUS ID (PRO Order Order No. (PK) places Includes CUS Name CUS ID (FO Item Order No. (FKO Item Code (PK Item Name Quantity Each ter price Address Order Date receives prepares Order Confirmation Department Stock Item no Packaging items PItem code (FK) sends start Order ID FIO Payment method Payment Date Tracking ID (PK) Description P Quantity I ships Delivery Delivery Date Delivery address Delivery ID 1 Expand and enhance your database design to include Supertype and Subtype entities. You have the choice to decide if the Specialization Hierarchy is Disjoint or Overlapping and if the constraints are Partial or Complete. Make sure you apply this to no less than 2 Entities. If in above database you did not provide any entities that could be Extended then make sure you add to your Database design entities that could be categorized. 2 Improve your database design by make sure your tables are Normalized. To solve this go through the check list provided with this assignment and make sure you have done all the recommendation given to you. Note: This Check list is recommended for your use anytime you design a database 3- Create at least 1 recursive relationship. Data-Modeling Checklist Below is a check list of conditions that you need to account for when you design a database 1. Business rules Properly document and verify all business rules with the end users Ensure that all business rules are written precisely, clearly, and simply The business rules must help identify entities, attributes, relationships, and constraints Identify the source of all business rules, and ensure that each business rule is justified, dated, and signed off by an approving authority 2. Data modeling Naming conventions: all names should be limited in length (database-dependent size) 3. Entity names: should be nouns that are familiar to business and should be short and meaningful Should document abbreviations, synonyms, and aliases for each entity Should be unique within the model For composite entities, may include a combination of abbreviated names of the entities linked through the composite entity 4. Attribute names: . 4- Attribute names: . Should be unique within the entity Should use the entity abbreviation as a prefix Should be descriptive of the characteristic Should use suffixes such as _ID, _NUM, or _CODE for the PK attribute Should not be a reserved word Should not contain spaces or special characters such as @, I, or & 5- Relationship names: Should be active or passive verbs that clearly indicate the nature of the relationship 6- Entities: Each entity should represent a single subject Each entity should represent a set of distinguishable entity instances 7. Attributes: . Should be simple and single-valued (atomic data) Should document default values, constraints, synonyms, and aliases Derived attributes should be clearly identified and include source(s) Should not be redundant unless this is required for transaction accuracy, performance, or maintaining a history Nonkey attributes must be fully dependent on the PK attribute 8. Relationships: Should clearly identify relationship participants Should clearly define participation, connectivity, and document cardinality 9. ER model: Should be validated against expected processes: inserts, updates, and deletions Should evaluate where, when and how to maintain a history . Should not contain redundant relationships except as required Should minimize data redundancy to ensure single-place updates Should conform to the minimal data rule: All that is needed is there, and all that is there is needed Firstly, you have to improve the database design by following the 3 instructions given in 2nd photo and make new normalised database design. After that, see that checklist that database design must have to follow. You can take 6-7 hours for completing this
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


