Question: (CycleElements) Write a void method, cycleIntegers, that will take a built-in array of int and circularly shift the elements one element right. Example: x 3

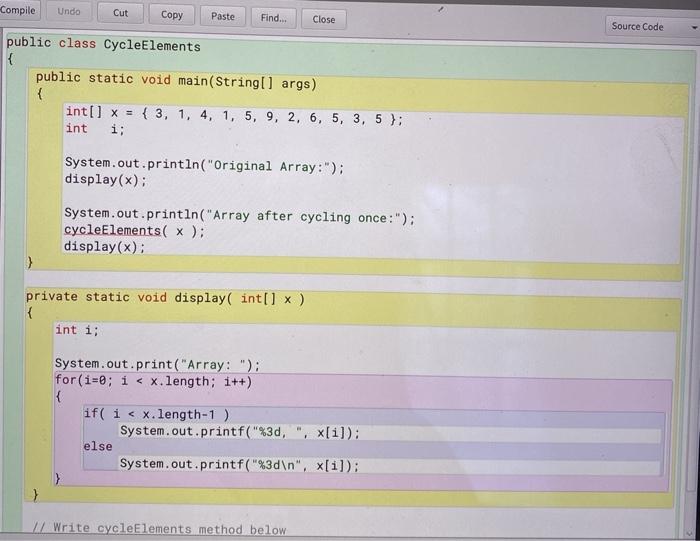
(CycleElements) Write a void method, cycleIntegers, that will take a built-in array of int and circularly shift the elements one element right. Example: x 3 14 15 2 53 9 5 cycleIntegers (x) will alter the array x as follows. X5 3 1 4 1592 6 5 3 Sample Output: 5, 9. 2, 6, 5, Original Array: Array: 3, 1, Array after cycling once: Array: 3, 1, 4, 3. 5 1, 5, 9, 2 6, 5, 3 (JoinArrays) Write a method, joinArrays, which receives two ArrayList of Integer, and concatenates them (joins them together to make one, larger array). The method will not alter the two original ArrayLists but will return a new ArrayList of Integer. Example: S 4 3 21 8 7 6 Z joinArrays (x,y) will return a new array as follows. * 5 4 3 2 1 8 76 Sample Output: Original arrays: Array: 5, 4, 3. Array: 8, 7, 6 Result of join(x,y). Array: 5, 3, 2 1 2, 1, 8, 7, 6 Compile Undo Cut Copy Paste Find... Close Source Code public class CycleElements { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] x = { 3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5 }; int i; System.out.println("Original Array:"); display(); System.out.println("Array after cycling once:"); cycleElements( x ): display(x): } private static void display( int[] x) { int i; System.out.print("Array: "); for(i=0; i // Write cycleElements method below
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


