Question: (d) (e) Critically evaluate the strict alternation algorithm with reference to the mutual exclusion problem. [6 Marks] What reasonable safeguards might be built into an
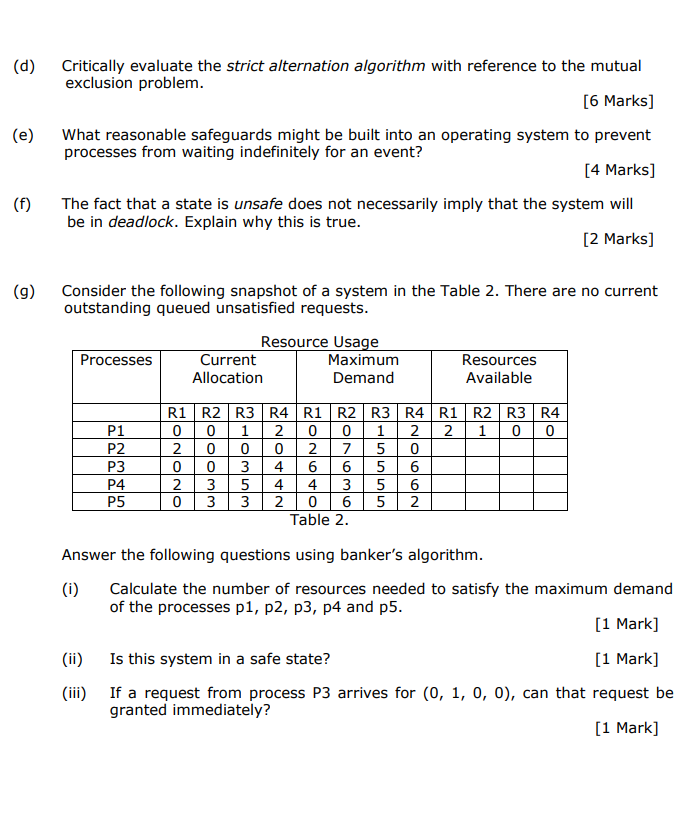
(d) (e) Critically evaluate the strict alternation algorithm with reference to the mutual exclusion problem. [6 Marks] What reasonable safeguards might be built into an operating system to prevent processes from waiting indefinitely for an event? [4 Marks] The fact that a state is unsafe does not necessarily imply that the system will be in deadlock. Explain why this is true. [2 marks] (f) (9) Consider the following snapshot of a system in the Table 2. There are no current outstanding queued unsatisfied requests. Processes Resource Usage Current Maximum Allocation Demand Resources Available R2 R3 R4 1 0 0 P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 R1 R2 R3 R4 R1 R2 R3 R4 R1 0 0 1 | 2 0 0 1 2 2 2 0 0 0 2 7 5 0 0 3 4 6 6 5 6 2 5 4 4 3 5 6 0 3 3 2 0 6 5 2 Table 2. Answer the following questions using banker's algorithm. (i) Calculate the number of resources needed to satisfy the maximum demand of the processes p1, P2, P3, P4 and p5. [1 Mark] (ii) Is this system in a safe state? [1 Mark] (iii) If a request from process P3 arrives for (0, 1, 0, 0), can that request be granted immediately? [1 Mark]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


