Question: D E F G 1 . B C 1 Chapter 6: Applying Excel 2 3 Data 4 Selling price per unit $50 5 Manufacturing costs:
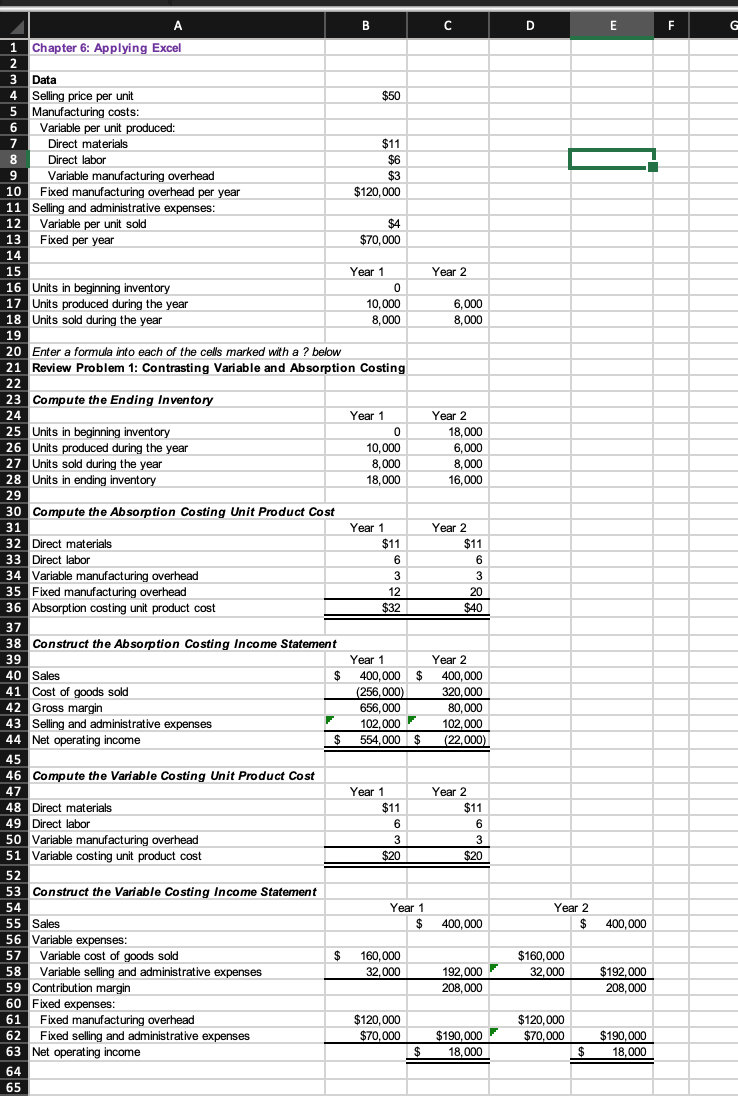
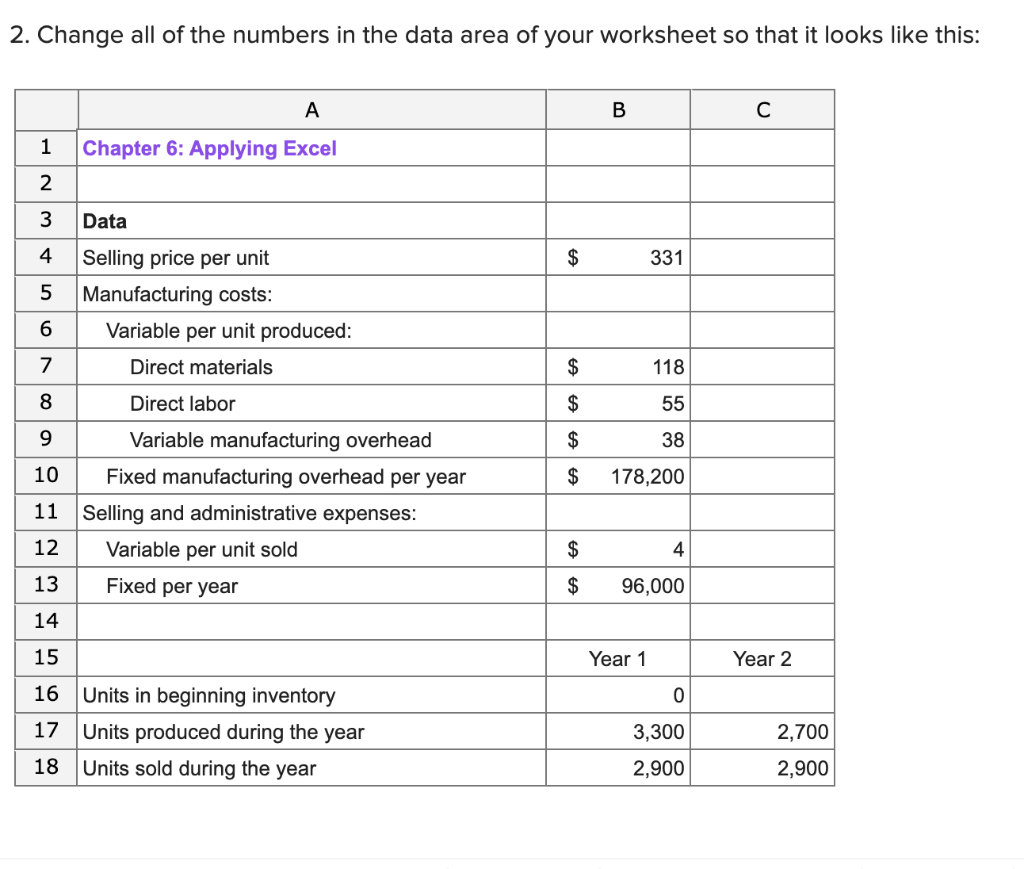
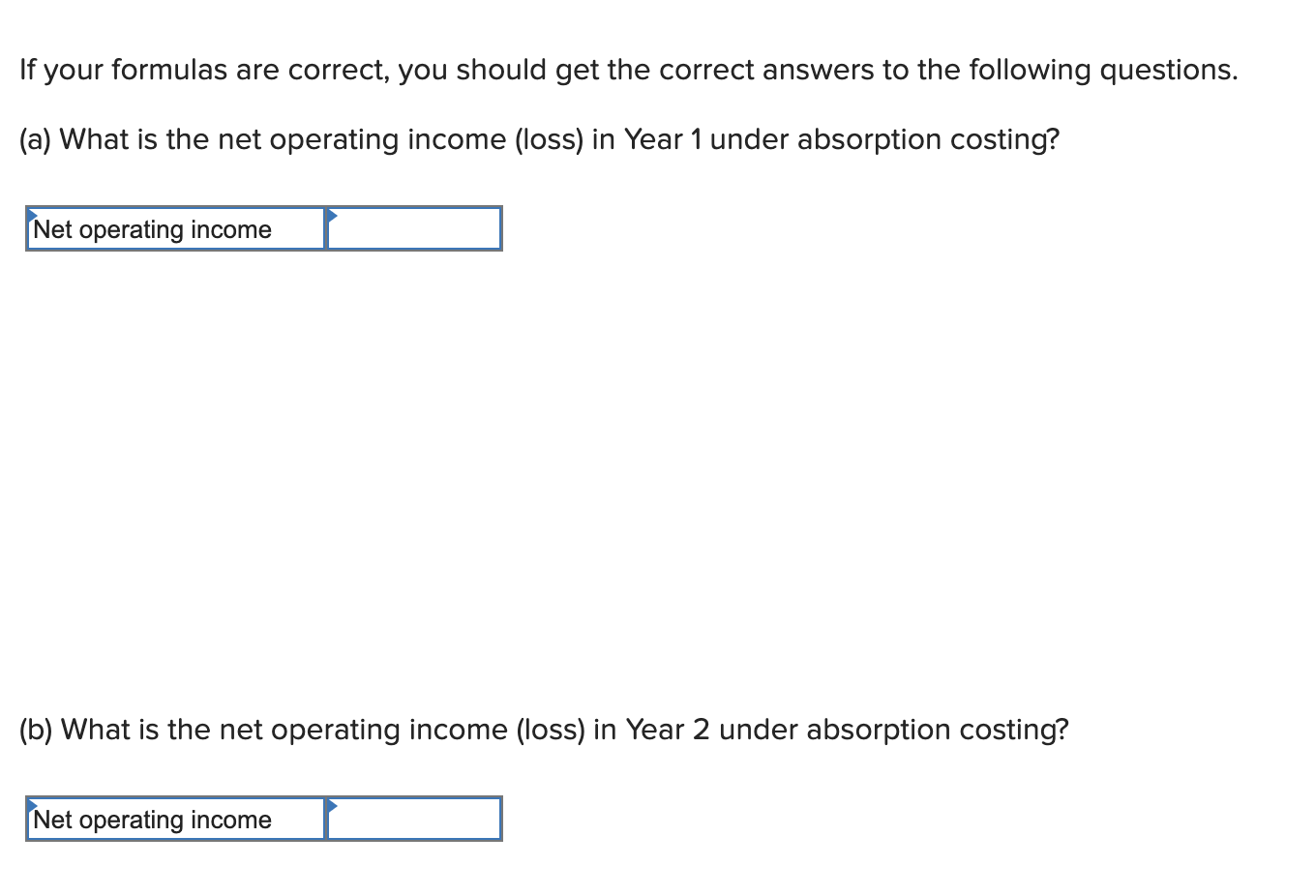



D E F G 1 . B C 1 Chapter 6: Applying Excel 2 3 Data 4 Selling price per unit $50 5 Manufacturing costs: 6 Variable per unit produced: 7 el materials $11 8 Direct labor $6 9 Variable manufacturing overhead $3 10 Fixed manufacturing overhead per year $120,000 11 Selling and administrative expenses: 12 Variable per unit sold $4 13 Fixed per year $70,000 14 17 15 Year 1 Year 2 16 Units in beginning inventory 0 17 Units produced during the year 10,000 6,000 18 Units sold during the year 8,000 8,000 19 12 20 Enter a formula into each of the cells marked with a ? below 21 Review Problem 1: Contrasting Variable and Absorption Costing 22 23 Compute the Ending Inventory 24 Year 1 Year 2 25 Units in beginning inventory 0 18,000 26 Units produced during the year 10,000 6,000 27 Units sold during the year 8,000 8,000 28 Units in ending inventory 18,000 16,000 29 30 Compute the Absorption Costing Unit Product Cost 31 Year 1 Year 2 32 Direct materials $11 $11 33 Direct labor 6 6 34 Variable manufacturing overhead 3 3 35 Fixed manufacturing overhead 12 20 36 Absorption costing unit product cost $32 $40 37 38 Construct the Absorption Costing Income Statement 39 Year 1 Year 2 40 Sales $ 400,000 $ 400,000 41 Cost of goods sold (256,000) 320,000 42 Gross margin 656,000 80,000 43 Selling and administrative expenses 102.000 44 Net operating income $ 554,000 $ 45 46 Compute the Variable Costing Unit Product Cost 47 Year 1 Year 2 48 Direct materials $11 $11 49 Direct labor 6 6 50 Variable manufacturing overhead 3 3 51 Variable costing unit product cost $20 $20 52 53 Construct the Variable Costing Income Statement 54 Year 1 55 Sales $ 400,000 56 Variable expenses: 57 Variable cost of goods sold $ 160,000 58 Variable selling and administrative expenses 32,000 192,000 59 Contribution margin 208,000 60 Fixed expenses: 61 Fixed manufacturing overhead $120,000 62 Fixed selling and administrative expenses $70,000 $190,000 63 Net operating income $ 18,000 64 65 102,000 (22,000) Year 2 $ 400,000 $160,000 32,000 $192,000 208,000 $120,000 $70,000 $190,000 18,000 $ 2. Change all of the numbers in the data area of your worksheet so that it looks like this: A B 1 Chapter 6: Applying Excel 2 Data $ 331 000 vow Selling price per unit Manufacturing costs: Variable per unit produced: Direct materials $ 118 $ 55 $ 38 10 Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead per year Selling and administrative expenses: Variable per unit sold $ 178,200 11 12 $ Fixed per year $ 96,000 STBBB Year 1 Year 2 0 17 Units in beginning inventory Units produced during the year Units sold during the year 2,700 3,300 2,900 18 2,900 If your formulas are correct, you should get the correct answers to the following questions. (a) What is the net operating income (loss) in Year 1 under absorption costing? Net operating income (b) What is the net operating income (loss) in Year 2 under absorption costing? Net operating income (c) What is the net operating income (loss) in Year 1 under variable costing? Net operating income (d) What is the net operating income (loss) in Year 2 under variable costing? Net operating income (e) The net operating income (loss) under absorption costing is less than the net operating income (loss) under variable costing in Year 2 because: (You may select more than one answer. Single click the box with the question mark to produce a check mark for a correct answer and double click the box with the question mark to empty the box for a wrong answer. Any boxes left with a question mark will be automatically graded as incorrect.) ? Units were left over from the previous year. ? The cost of goods sold is always less under variable costing than under absorption costing. ? Sales exceeded production so some of the fixed manufacturing overhead of the period was released from inventories under absorption costing. 3. Make a note of the absorption costing net operating income (loss) in Year 2. At the end of Year 1, the company's board of directors set a target for Year 2 of net operating income of $140,000 under absorption costing. If this target is met, a hefty bonus would be paid to the CEO of the company. Keeping everything else the same from part (2) above, change the units produced in Year 2 to 5,400 units. (a) Would this change result in a bonus being paid to the CEO? Yes No (b) What is the net operating income (loss) in Year 2 under absorption costing? Net operating income (c) Would this doubling of production in Year 2 be in the best interests of the company if sales are expected to continue to be 2,900 units per year? Yes
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


