Question: D Question 1 1.5 pts A corn grower expects a harvest of 8,000 bushels of corn. He decide to hedge his position by buying one
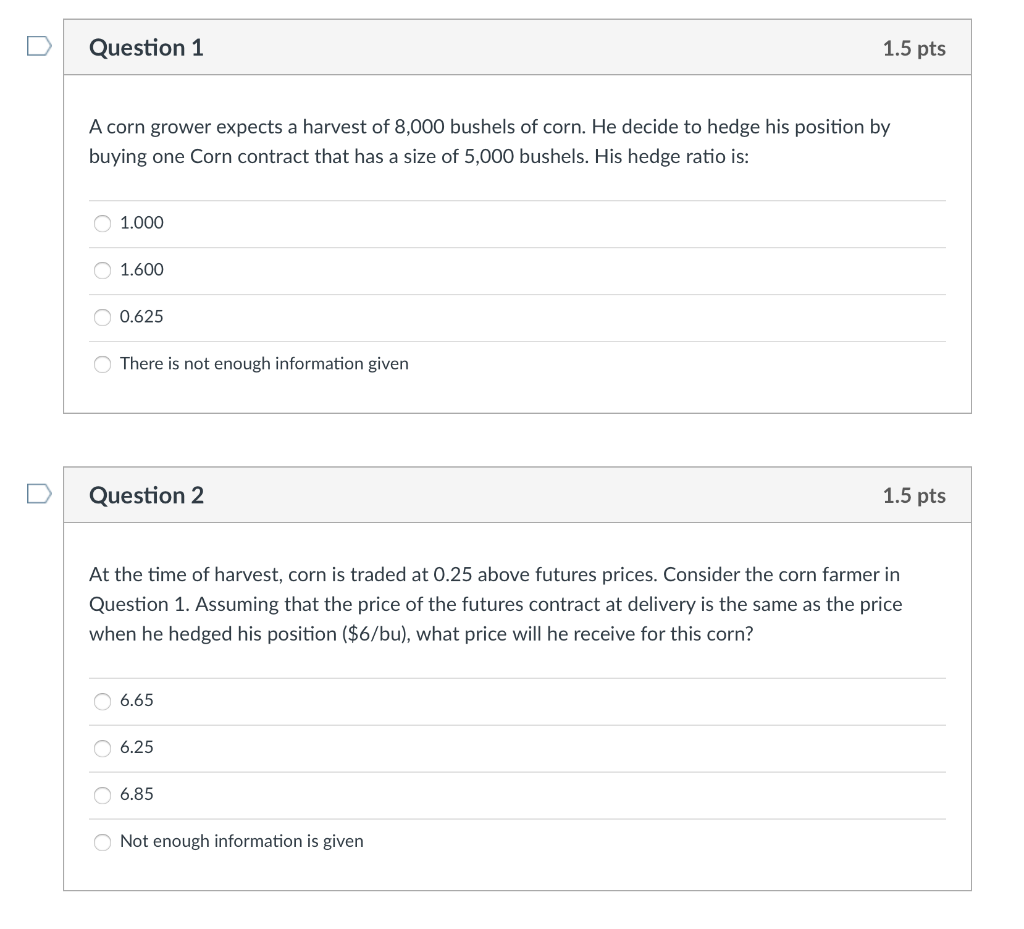
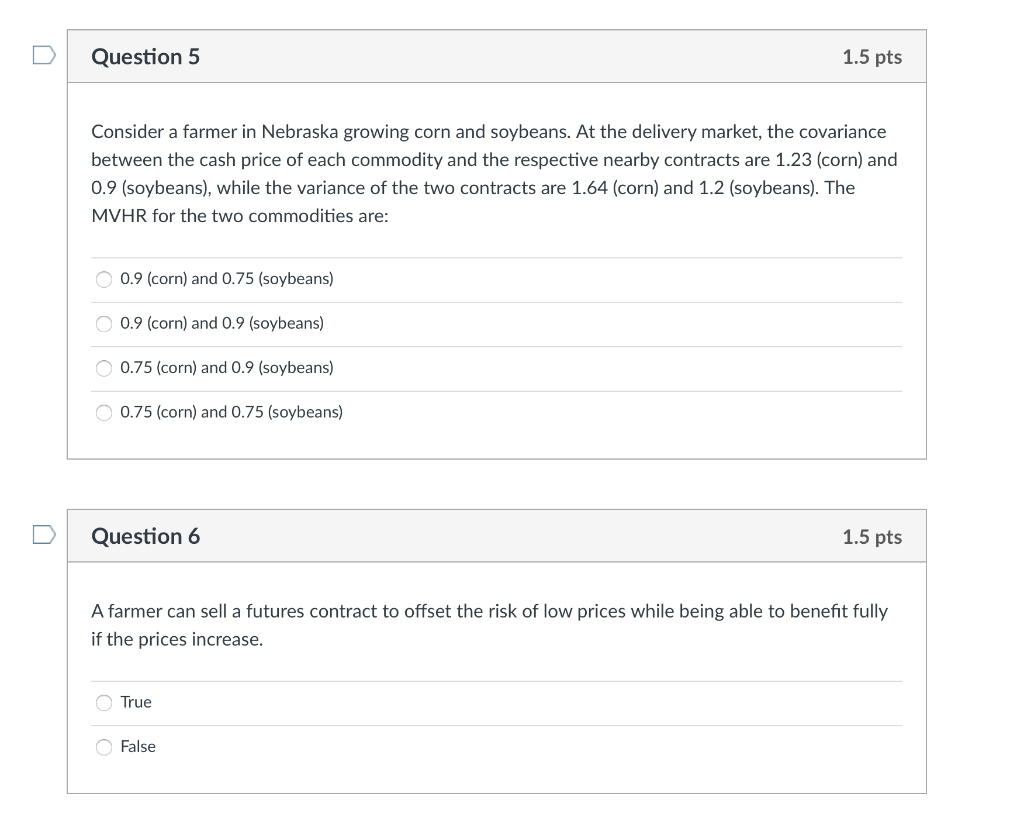
D Question 1 1.5 pts A corn grower expects a harvest of 8,000 bushels of corn. He decide to hedge his position by buying one Corn contract that has a size of 5,000 bushels. His hedge ratio is 1.000 1.600 0.625 There is not enough information given D Question 2 1.5 pts At the time of harvest, corn is traded at 0.25 above futures prices. Consider the corn farmer in Question 1. Assuming that the price of the futures contract at delivery is the same as the price when he hedged his position ($6/bu), what price will he receive for this corn? 6.65 6.25 6.85 Not enough information is given D Question 5 1.5 pts Consider a farmer in Nebraska growing corn and soybeans. At the delivery market, the covariance between the cash price of each commodity and the respective nearby contracts are 1.23 (corn) and 0.9 (soybeans), while the variance of the two contracts are 1.64 (corn) and 1.2 (soybeans). The MVHR for the two commodities are: 0.9 (corn) and 0.75 (soybeans) 0.9 (corn) and 0.9 (soybeans) 0.75 (corn) and 0.9 (soybeans) 0.75 (corn) and 0.75 (soybeans) Question 6 1.5 pts A farmer can sell a futures contract to offset the risk of low prices while being able to benefit fully if the prices increase. True False
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


