Question: D. We need to determine the angle between the strings, but use of a protractor at the ceiling is usually too difficult. Instead, measure
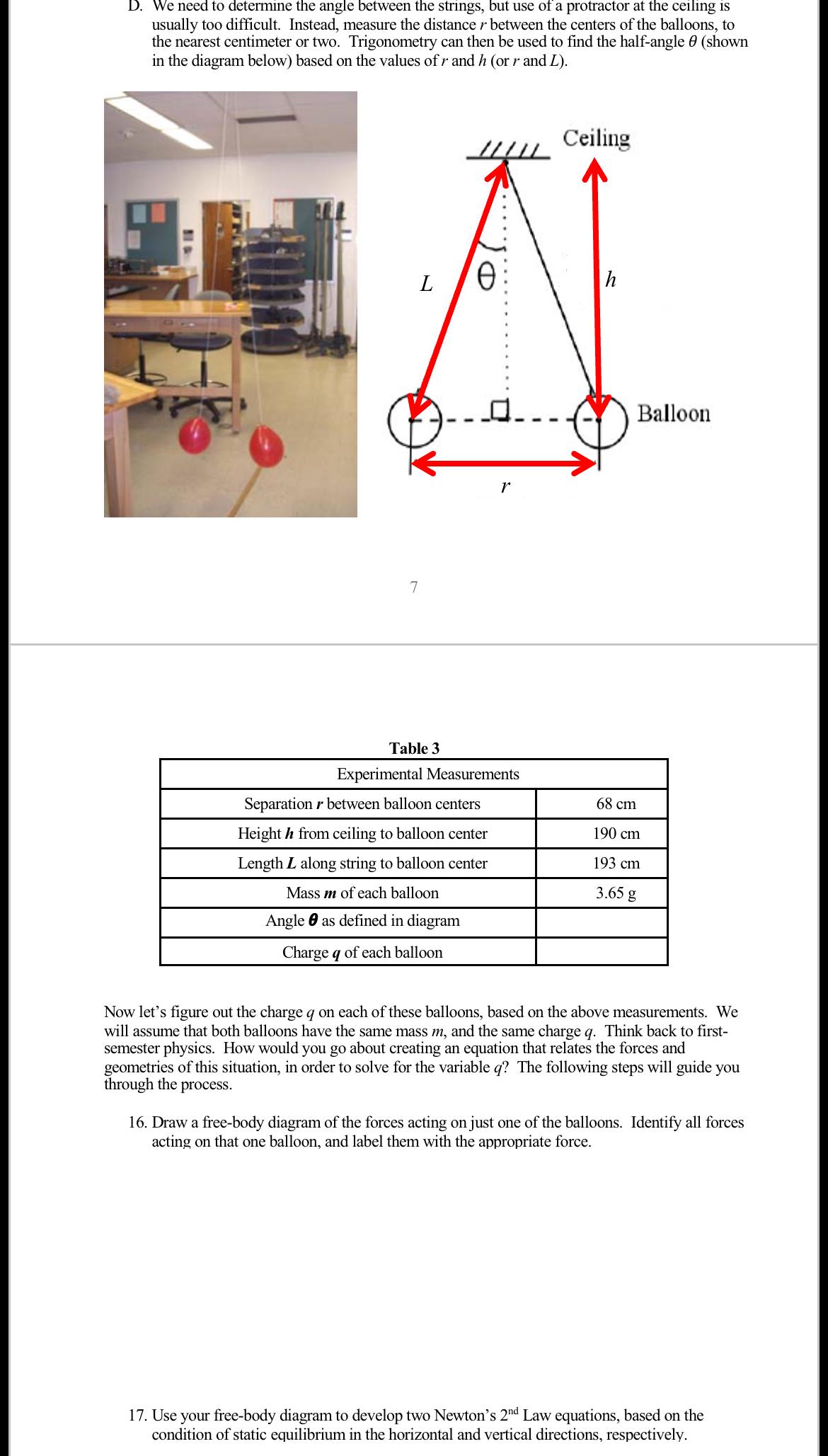
D. We need to determine the angle between the strings, but use of a protractor at the ceiling is usually too difficult. Instead, measure the distance r between the centers of the balloons, to the nearest centimeter or two. Trigonometry can then be used to find the half-angle 0 (shown in the diagram below) based on the values of r and h (or r and L). L Ceiling h N Balloon 7 r Table 3 Experimental Measurements Separation between balloon centers 68 cm Height h from ceiling to balloon center 190 cm Length L along string to balloon center 193 cm Mass m of each balloon 3.65 g Angle as defined in diagram e Charge q of each balloon Now let's figure out the charge q on each of these balloons, based on the above measurements. We will assume that both balloons have the same mass m, and the same charge q. Think back to first- semester physics. How would you go about creating an equation that relates the forces and geometries of this situation, in order to solve for the variable q? The following steps will guide you through the process. 16. Draw a free-body diagram of the forces acting on just one of the balloons. Identify all forces acting on that one balloon, and label them with the appropriate force. 17. Use your free-body diagram to develop two Newton's 2nd Law equations, based on the condition of static equilibrium in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


