Question: data Expr Var Name | App Expr Expr l Lambda Name Exp a variable function application r -- lambda abstraction deriving (Eq, Show) - the
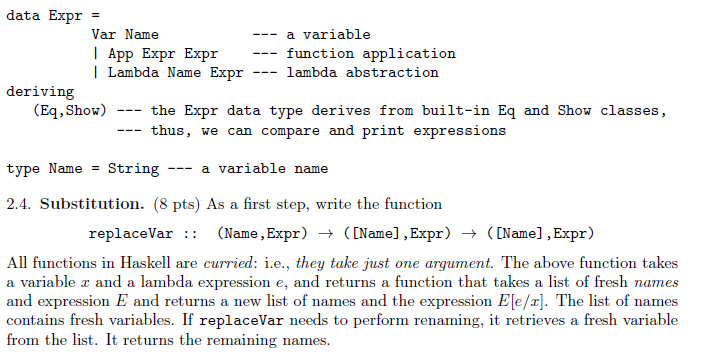
data Expr Var Name | App Expr Expr l Lambda Name Exp a variable function application r -- lambda abstraction deriving (Eq, Show) - the Expr data type derives from built-in Eq and Show classes, thus, we can compare and print expressions type Name g -- a variable name 2.4. Substitution. (8 pts) As a first step, write the function replaceVar :: (Name ,Expr) ([Name],Expr) ([Name],Expr) All functions in Haskell are curried: i.e., they take just one argument. The above function takes a variable r and a lambda expression e, and returns a function that takes a list of fresh names and expression E and returns a new list of names and the expression Ele/r]. The list of names contains fresh variables. If replaceVar needs to perform renaming, it retrieves a fresh variable from the list. It returns the remaining names. data Expr Var Name | App Expr Expr l Lambda Name Exp a variable function application r -- lambda abstraction deriving (Eq, Show) - the Expr data type derives from built-in Eq and Show classes, thus, we can compare and print expressions type Name g -- a variable name 2.4. Substitution. (8 pts) As a first step, write the function replaceVar :: (Name ,Expr) ([Name],Expr) ([Name],Expr) All functions in Haskell are curried: i.e., they take just one argument. The above function takes a variable r and a lambda expression e, and returns a function that takes a list of fresh names and expression E and returns a new list of names and the expression Ele/r]. The list of names contains fresh variables. If replaceVar needs to perform renaming, it retrieves a fresh variable from the list. It returns the remaining names
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


