Question: Data structure type 2: Array of AVL trees or linked lists In Java8, a similar structure is kept, but, when a position in the array
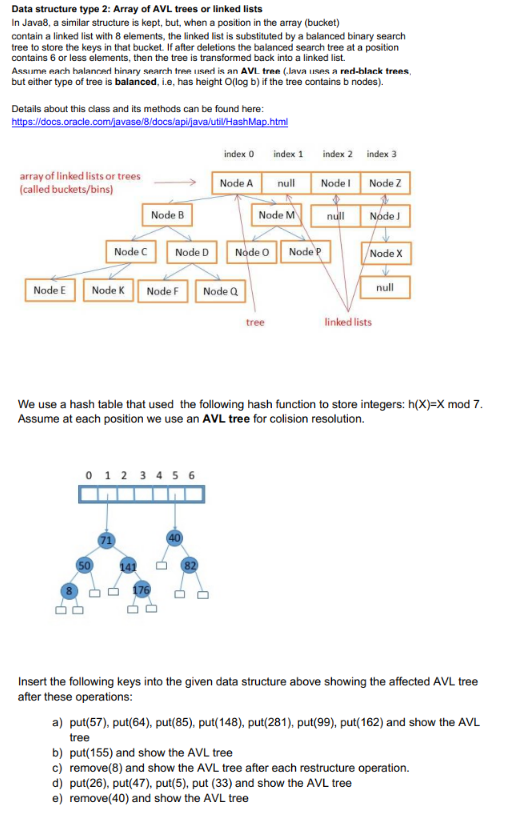
Data structure type 2: Array of AVL trees or linked lists In Java8, a similar structure is kept, but, when a position in the array (bucket) contain a linked list with 8 elements, the linked list is substituted by a balanced binary search tree to store the keys in that bucket. If after deletions the balanced search tree at a position contains 6 or less elements, then the tree is transformed back into a linked list. Assim, :h halanned hinary searrh tree used is an AVL tree (.lava lises a red-black trees but either type of tree is balanced, i.e, has height Ollog b) if the tree contains b nodes). Details about this class and its methods can be found here oracle ava/utiHashMap html index 0 index 1 index 2 index 3 array of linked lists or trees called buckets/bins) Node A null NodeNode Z Node B Node M null Node J Node C Node D Node O Node P Node X Node E Node K Node F Node Q null tree linked lists We use a hash table that used the following hash function to store integers: h(X)-X mod 7 Assume at each position we use an AVL tree for colision resolution. Insert the following keys into the given data structure above showing the affected AVL tree after these operations: a) put(57), put(64), put(85), put(148), put(281), put(99), put( 162) and show the AVL tree b) put(155) and show the AVL tree c) remove(8) and show the AVL tree after each restructure operation. d) put(26), put(47), put(5), put (33) and show the AVL tree e) remove(40) and show the AVL tree
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


