Question: data structure using c++ please don't use predefined functions when you answer, for ex: void arrayListType::duplicateORremove(elemType num) { for(int i =0; i if(list[i] num) {
data structure using c++
please don't use predefined functions when you answer, for ex:
void arrayListType::duplicateORremove(elemType num) { for(int i =0; i if(list[i] num) { insertAt(i, list[i]); ++i;
dont use removeAt(), insertAt(),insertEnd, retrieveAt(),replaceAt, etc inside implementation of the functions.
Starting from the arrayListType.h (attached with this assignment) and without using any of the predefined member functions, Write the required code to do the following:
1. Modify the arrayListType by adding a member function that increase each element in the list by a constant number that it takes as a parameter. This member function does not return any value.
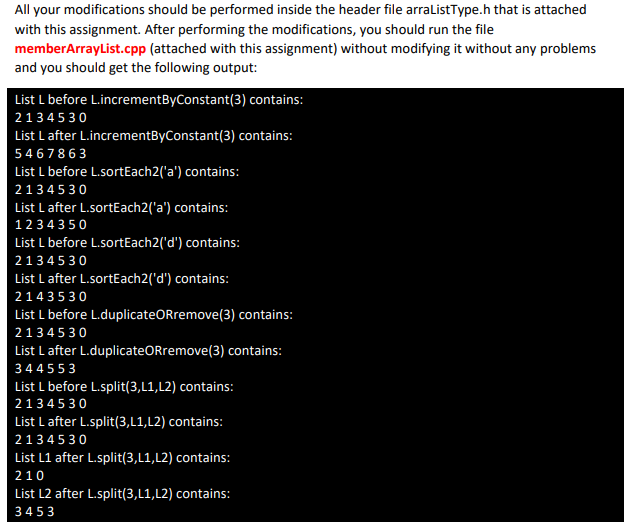
For example, if the list L contains the elements 2,1,3,4,5,3,0 and you call the member function as in L.incrementByConstant(3); The list content will then be changed to 5,4,6,7,8,6,3
2. Modify the arrayListType by adding a member function that checks every 2 consecutive elements and make them in ascending or descending order depending on a parameter value (letter a means ascending and letter d means descending).
For example, if the list L contains the elements 2,1,3,4,5,3,0 and you call the member function as in L.sortEach2(a); The list content will then be changed to 1,2,3,4,3,5,0 if the list L contains the elements 2,1,3,4,5,3,0 and you call the member function as in L.sortEach2(d); The list content will then be changed to 2,1,4,3,5,3,0
3. Modify the arrayListType by adding a member function that duplicate each item that is greater than a value that is sent to the function as a parameter and remove the items that are smaller than the parameter.
For example, if a list L contains the elements 2,1,3,4,5,3,0 and you call the member function as in L.duplicateORremove(3); The list content will then be changed to 3,4,4,5,5,3
4. Modify the arrayListType by adding a member function that creates 2 new lists from the elements in the list. The fist list should store the elements that are less than a parameter value and the rest of the elements should go to the second list. The original list should not be modified. The 2 new lists can be returned from the function through reference parameters.
For example, if a list L contains the elements 2,1,3,4,5,3,0 And you have tow other lists, L1,L2 and you call the member function as in L.split(3,L1,L2); The list L content will not be changed, list L1 will contain 2,1,0 and the list l2 will contain 3,4,5,3.
this is arrayListType.h
#ifndef ARRAY_LIST_TYPE #define ARRAY_LIST_TYPE #include #include using namespace std; // This class specifies the members to implement the basic // properties of array-based lists. template class arrayListType { public: const arrayListType & operator = (const arrayListType & ); //Overloads the assignment operator bool isEmpty() const; bool isFull() const; int listSize() const; int maxListSize() const; //Function to determine the size of the list. //Postcondition: Returns the value of maxSize. void print() const; //Function to output the elements of the list //Postcondition: Elements of the list are output on the // standard output device. bool isItemAtEqual(int location,const elemType & item) const; //Function to determine whether the item is the same //as the item in the list at the position specified by //Postcondition: Returns true if list[location] // is the same as the item; otherwise, // returns false. void insertAt(int location,const elemType & insertItem); //Function to insert an item in the list at the //position specified by location. The item to be inserted //is passed as a parameter to the function. //Postcondition: Starting at location, the elements of the // list are shifted down, list[location] = insertItem;, // and length++;. If the list is full or location is // out of range, an appropriate message is displayed. void insertEnd(const elemType & insertItem); //Function to insert an item at the end of the list. //The parameter insertItem specifies the item to be inserted. //Postcondition: list[length] = insertItem; and length++; // If the list is full, an appropriate message is // displayed. void removeAt(int location); //Function to remove the item from the list at the //position specified by location //Postcondition: The list element at list[location] is removed // and length is decremented by 1. If location is out of // range, an appropriate message is displayed. void retrieveAt(int location, elemType & retItem) const; void replaceAt(int location,const elemType & repItem); //Function to replace the elements in the list at the //position specified by location. The item to be replaced //is specified by the parameter repItem. //Postcondition: list[location] = repItem // If location is out of range, an appropriate message is // displayed. void clearList(); int seqSearch(const elemType & item) const; void insert(const elemType & insertItem); //Function to insert the item specified by the parameter //insertItem at the end of the list. However, first the //list is searched to see whether the item to be inserted //is already in the list. //Postcondition: list[length] = insertItem and length++ // If the item is already in the list or the list // is full, an appropriate message is displayed. void remove(const elemType & removeItem); //Function to remove an item from the list. The parameter //removeItem specifies the item to be removed. //Postcondition: If removeItem is found in the list, // it is removed from the list and length is // decremented by one. arrayListType(int size = 100); //constructor //Creates an array of the size specified by the //parameter size. The default array size is 100. //Postcondition: The list points to the array, length = 0, // and maxSize = size arrayListType(const arrayListType & otherList); //copy constructor ~arrayListType(); //destructor //Deallocates the memory occupied by the array. protected: elemType * list; //array to hold the list elements int length; //to store the length of the list int maxSize; //to store the maximum size of the list }; template bool arrayListType ::isEmpty() const { return (length == 0); } template bool arrayListType ::isFull() const { return (length == maxSize); } template int arrayListType ::listSize() const { return length; } template int arrayListType ::maxListSize() const { return maxSize; } template void arrayListType ::print() const { for (int i = 0; i bool arrayListType ::isItemAtEqual(int location, const elemType & item) const { if (location = length){ cerr void arrayListType ::insertAt(int location, const elemType & insertItem) { if (location length) cerr = maxSize) //list is full cerr location; i--) list[i] = list[i - 1]; //move the elements down list[location] = insertItem; //insert the item at the //specified position length++; //increment the length } } //end insertAt template void arrayListType ::insertEnd(const elemType & insertItem) { if (length >= maxSize) //the list is full cerr void arrayListType ::removeAt(int location) { if (location = length) cerr void arrayListType ::retrieveAt(int location, elemType & retItem) const { if (location = length) cerr void arrayListType ::replaceAt(int location, const elemType & repItem) { if (location = length) cerr void arrayListType ::clearList() { length = 0; } //end clearList template arrayListType ::arrayListType(int size) { if (size arrayListType ::~arrayListType() { delete[] list; } template arrayListType ::arrayListType(const arrayListType & otherList) { maxSize = otherList.maxSize; length = otherList.length; list = new elemType[maxSize]; //create the array assert(list != NULL); //terminate if unable to allocate //memory space for (int j = 0; j const arrayListType & arrayListType ::operator = (const arrayListType & otherList) { if (this != & otherList) //avoid self-assignment { delete[] list; maxSize = otherList.maxSize; length = otherList.length; list = new elemType[maxSize]; //create the array assert(list != NULL); //if unable to allocate memory //space, terminate the program for (int i = 0; i int arrayListType ::seqSearch(const elemType & item) const { int loc; bool found = false; for (loc = 0; loc void arrayListType ::insert(const elemType & insertItem) { int loc; if (length == 0) //list is empty list[length++] = insertItem; //insert the item and //increment the length else if (length == maxSize) cerr void arrayListType ::remove(const elemType & removeItem) { int loc; if (length == 0) cerr #include //Line 1 #include //Line 2 #include #include "arrayListType.h" //Line using namespace std; //Line 4 int main() //Line 5 { arrayListType L,L1,L2; L.insertEnd(2); L.insertEnd(1); L.insertEnd(3); L.insertEnd(4); L.insertEnd(5); L.insertEnd(3); L.insertEnd(0); cout All your modifications should be performed inside the header file arraListType.h that is attached with this assignment. After performing the modifications, you should run the file memberArrayList.cpp (attached with this assignment) without modifying it without any problems and you should get the following output: List L before L.incrementByConstant(3) contains: 2134530 List Lafter LincrementByConstant(3) contains: 5467863 List L before L.sortEach2('a') contains: 213 45 30 List Lafter L.sortEach2('a') contains: 12 34350 List L before L.sortEach2('d') contains: 2134530 List Lafter L.sortEach21'd") contains: 2143530 List L before L.duplicate Orremove(3) contains: 2134530 List Lafter L.duplicate Rremove(3) contains: 344553 List L before L.split(3,L1,L2) contains: 2134530 List Lafter L.split(3,L1,L2) contains: 2134530 List L1 after L.split(3,L1,L2) contains: 210 List L2 after L.split(3,L1,L2) contains: 3453 Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


