Question: ** Data Structures and Algorithms Using Java by: William McAllister** *****The chapter is Chapter 4: Linked Lists and Iterators***DO NOT CREATE AN ACTUAL DATABASE** ONLY
** Data Structures and Algorithms Using Java by: William McAllister** *****The chapter is Chapter 4: Linked Lists and Iterators***DO NOT CREATE AN ACTUAL DATABASE** ONLY USE JAVA PLEASE***
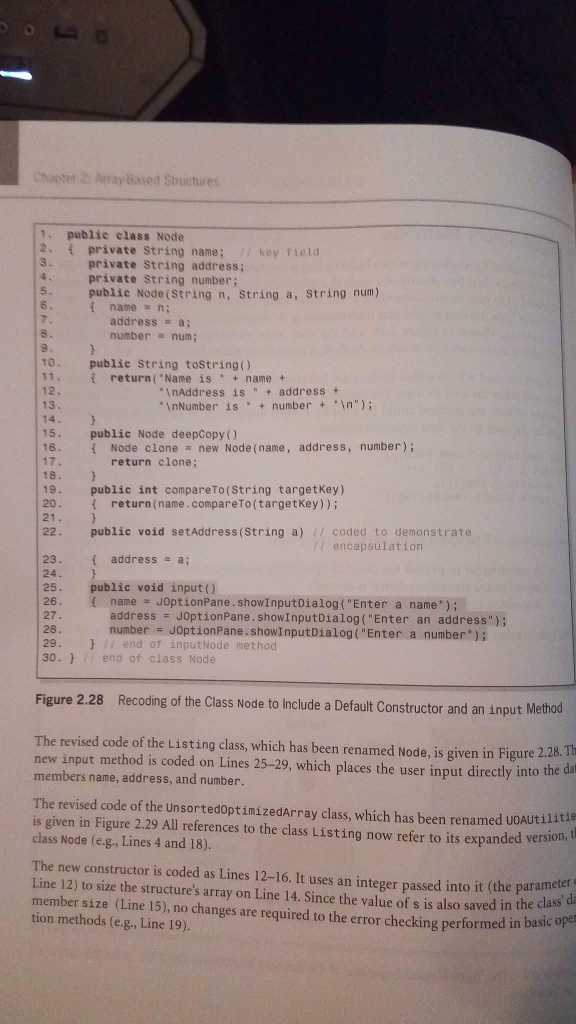
A database is to be developed to keep track of student information at your college. It will include their names, identification numbers, and grade point averages. The data set will be accessed in the key field mode, with the student's name being the key field. Code a class named Listing that defines the nodes. Your class should include all the methods in the class shown in Figure 2.28. Test it with a progressively developed driver program that demonstrates the functionality of all of its methods.
***********************
Code an application program that keeps track of student information at your college (see Exercise Above). Include their names, identification numbers, and grade point averages in a fully encapsulated, homogeneous singly linked list. When launched, the user will be asked to input the initial number of students and the initial data set. Once this is complete, the user will be presented with the following menu:
Enter: 1 to insert a new student's information,
2 to fetch and output a student's information,
3 to delete a student's information,
4 to update a student's information,
5 to output all the student information, and
6 to exit the program.
The program should perform an unlimited number of operations until the user enters a 6 to exit the program. If the user requests an operation on a node not in the structure, the program output should be "node not in structure." Otherwise, the message "operation complete" should be output.
hapter Array Based Structures 1. publie class Node 2 private String name; 7 key .private String address; field private String number; 5 6 public Node (String n, String a, String num) { name= n; address a number num; 9 10. public String tostring) 11 return("Name is +name + 12. 13 InAddress is address InNumber is numbern"); 14. 15. public Node deepCopy () 16. Node clone new Node (name, address, number); return clone; 18. 19. 20. public int compareTo(String targetkey) return(name.compareTo(targetkey)); 21 22. public void setAddress(String a) coded to demonstrate /1 encapsulation { address=a; 23. 24 25. 26. public void input() { name JOptionPane . ShowinputDialog ( "Enter a name.); address = JOptionPane . Show InputDialog ("Enter an address"); number # JOptionPane . show! nputDialog ( "Enter a number"); 28. 29 30.7/ end of class Node } / end of input/dode method Figure 2.28 Recoding of the Class Node to Include a Default Constructor and an input Method The revised code of the Listing class, which has been renamed Node, is given in Figure 2.28. new input method is coded on Lines 25-29, which places the user input directly into the members name, address, and number Th The revised code of the UnsortedoptimizedArray class, which has been renamed uoAUtilitie is given in Figure 2.29 All references to the class Listing now refer to its expanded vers class Node (e.g., Lines 4 and 18) ion, t The new constructor is coded as Lines 12-16. It uses an integer passed into it (the parameter Line 12) to size the structure's array on Line 14. Since the value of s is also saved in the class member size (Line 15), no changes are required to the error checking performed in basic o tion methods (e.g., Line 19)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


