Question: Data Structures in C++ please use template and class not struct implement in file HW3.cpp BST.h #pragma once #include BSTNode.h #include DLList.h #include QueueDLL.h #include
Data Structures in C++ please use template and class not struct
implement in file HW3.cpp

BST.h
#pragma once #include "BSTNode.h" #include "DLList.h" #include "QueueDLL.h" #include "StackDLL.h"
template class BST { public: BST(); BST(const BST& other); ~BST(); bool is_empty() const; bool contains(const T& val) const;
T max() const; T min() const; T remove_max(); T remove_min();
void insert(const T& val); bool remove(const T& val); void clear(); DLList elements() const; DLList elements_level_ordered() const; BSTNode* get_root() const { return root; }
BST& operator=(const BST& other); // exercises BST(const DLList& list); int find_second_minimum() const; DLList get_longest_path() ; void BFT() ; BST copy_subTree(const T& n);
template BST::BST() { root = nullptr; }
// uses pre-order traversal template void BST::copy_from(BSTNode* node) { if (node == nullptr) return; insert(node->val); copy_from(node->left); copy_from(node->right); }
template BST::BST(const BST& other) { root = nullptr; copy_from(other.root); }
template BST::~BST() { clear(); }
template bool BST::is_empty() const { return root == nullptr; }
template bool BST::contains(const T& val) const { BSTNode* node = root; // always start the search from the root while(node != nullptr) { // If the current node has the value we are looking for if (val == node->val) return true;
// If the value that we are looking for is smaller than the // value of the current tree node, go left; else, go right if(val val) node = node->left; else node = node->right; }
return false; }
template bool BST::contains(const T& val, BSTNode* node) const { // if a nullptr is reached, val does not exist in the tree if (node == nullptr) return false;
// search value is found in the current node if(val == node->val) return true;
// search in either the left sub-tree or the right sub-tree, // depending on the value of val if(val val) return contains(val, node->left); else return contains(val, node->right); }
template void BST::insert(const T& val) { // if the tree is empty, the root needs to point at the new node. if (is_empty()){ root = new BSTNode(val, nullptr, nullptr); return; }
BSTNode* curr = root; BSTNode* prev = nullptr;
// Loop to search for the right position for val while(curr != nullptr) { prev = curr; if (val val) curr = curr->left; else if (val > curr->val) curr = curr->right; else return; }
BSTNode* new_node = new BSTNode(val, nullptr, nullptr);
if (val val) prev->left = new_node; else prev->right = new_node; }
// Breadth-first traversal template DLList BST::elements_level_ordered() const { DLList result;
if (root == nullptr) return result;
// a queue of pointers to BSTNode objects. QueueDLL*> queue; BSTNode* node = root; queue.enq(node);
while (!queue.is_empty()) { // Take a node out of the queue, process it and then insert // its children into the queue. node = queue.deq(); result.add_to_tail(node->val);
if (node->left != nullptr) queue.enq(node->left); if (node->right != nullptr) queue.enq(node->right); }
return result; }
// returns the tree elements in-order template DLList BST::elements() const { DLList result; elements(result, root); return result; }
// recursive helper version: returns the elements in-order template void BST::elements(DLList& result, BSTNode* node) const { if (node == nullptr) return;
elements(result, node->left);
// Process the node after processing its left subtree // and before processing its right subtree result.add_to_tail(node->val); elements(result, node->right); }
template bool BST::remove(const T& val) { BSTNode* node = root; BSTNode* prev = nullptr; if (is_empty()) return false;
// This loop searches for the node to be deleted while (node != nullptr) { if (node->val == val) break; prev = node; if (val val) node = node->left; else node = node->right; } // if node is not found, return false without deleting anything if (node == nullptr) return false; // if the node has 0 or 1 children, call del_single() else call del_double() if (node->left == nullptr || node->right == nullptr) del_single(node, prev); else del_double(node); return true; }
// Deletes a node with at most one child. // This function is O(1) in the best and worst case. template void BST::del_single(BSTNode* ptr, BSTNode* prev) { // if the node to be deleted is the root if (ptr == root) { // the new root becomes the child that is not null. // if both children are null, the root becomes null. if (root->left != nullptr) root = root->left; else root = root->right; } // if the node to be deleted is the left child of its parent, // set the parent's left child to the only child of the deleted node // or to null if it has no children else if (ptr == prev->left) { if (ptr->right != nullptr) prev->left = ptr->right; else prev->left = ptr->left; } // if the node to be deleted is the right child of its parent, // set the parent's right child to the only child of the deleted node // or to null if it has no children else { if (ptr->right != nullptr) prev->right = ptr->right; else prev->right = ptr->left; } delete ptr; }
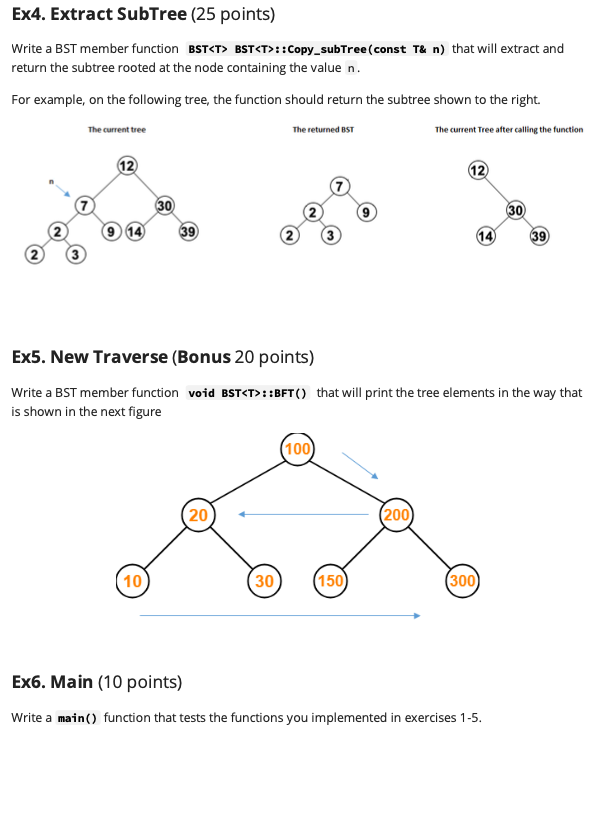
BST Programming Challenges - Provide your implementation for all the functions in the following exercises, as well as your implementation of main() in Hw3.cpp - Adding private functions (in BST.h only) is allowed but modifying anything else is not allowed - Do not add or remove any files. Ex1. DLL2BST (15 points) Add a constructor that constructs the binary search tree from the given DLList. BST:: BST (const DLL& list) Ex2. Find the Second Minimum (25 points) Write a member function called int BST::Find_Second_Minimum() const. The function retrieves the value of the node that has the second minimum value in the current BST. The second minimum is the element just greater than the minimum number. The running time of your implementation should be och). Ex3. Get the Longest Path (25 points) Write a member function called DLList BST:: get_longest_path() that returns a DLL of the longest path in the tree. For example, the red nodes in the following tree are on the longest path and should be added to the list. In case there are multiple longest paths, retrieve any of them. Ex4. Extract SubTree (25 points) Write a BST member function BST BST::Copy_subTree(const T& n) that will extract and return the subtree rooted at the node containing the value n. For example, on the following tree, the function should return the subtree shown to the right. The returned BST The current Tree after calling the function The current tree 12 12 30 30 9 14 39 39 Ex5. New Traverse (Bonus 20 points) Write a BST member function void BST::BFT() that will print the tree elements in the way that is shown in the next figure 100 20 (200 10 30 (150 (300) Ex6. Main (10 points) Write a main() function that tests the functions you implemented in exercises 1-5. 00 + BST.h BSTNode.h HW3.cpp 1 #pragma once 2 template class BST; 3 template 4 class BSTNode{ 5 private: 6 I val; 7 BSTNode* left; 8 BSTNode* right; 9 int depth; 10 int height; 11 friend class BST; 12 public: 13 BSTNode (const T& v, BSTNode* left, BSTNode* right); 14 ~BSTNode() {}; 15 I get_val() { return val;} 16 BSTNodex getLeft() { return left; } 17 BSTNode* getRight() { return right; } 18 }; 19 20 template 21 BSTNode::BSTNode (const T& v, BSTNode* left, BSTNode* right) { 22 val = v; 23 this->left: left; 24 this->right:right; 25 depth = height= -1; // Not computed yet 26 } ou = = /home/BSTNode.h Tabs (Auto) + CBST.h BSTNode.h HW3.cpp 1 #include "BST.h" 2 #include 3 using namespace std; 4 5 // Implement the functions required in exercises 1-5 here // 6 7 8 9 // Provide your solution for exercise 6 here // 10 11 int main() { 12 13 cout







