Question: Data We will use the abdata.npz dataset for this problem. This dataset has two keys In [3] ab_datanp.load(data/abdata.npz) ab data.keys () Out[3]: ['train_data', 'testdata'] The
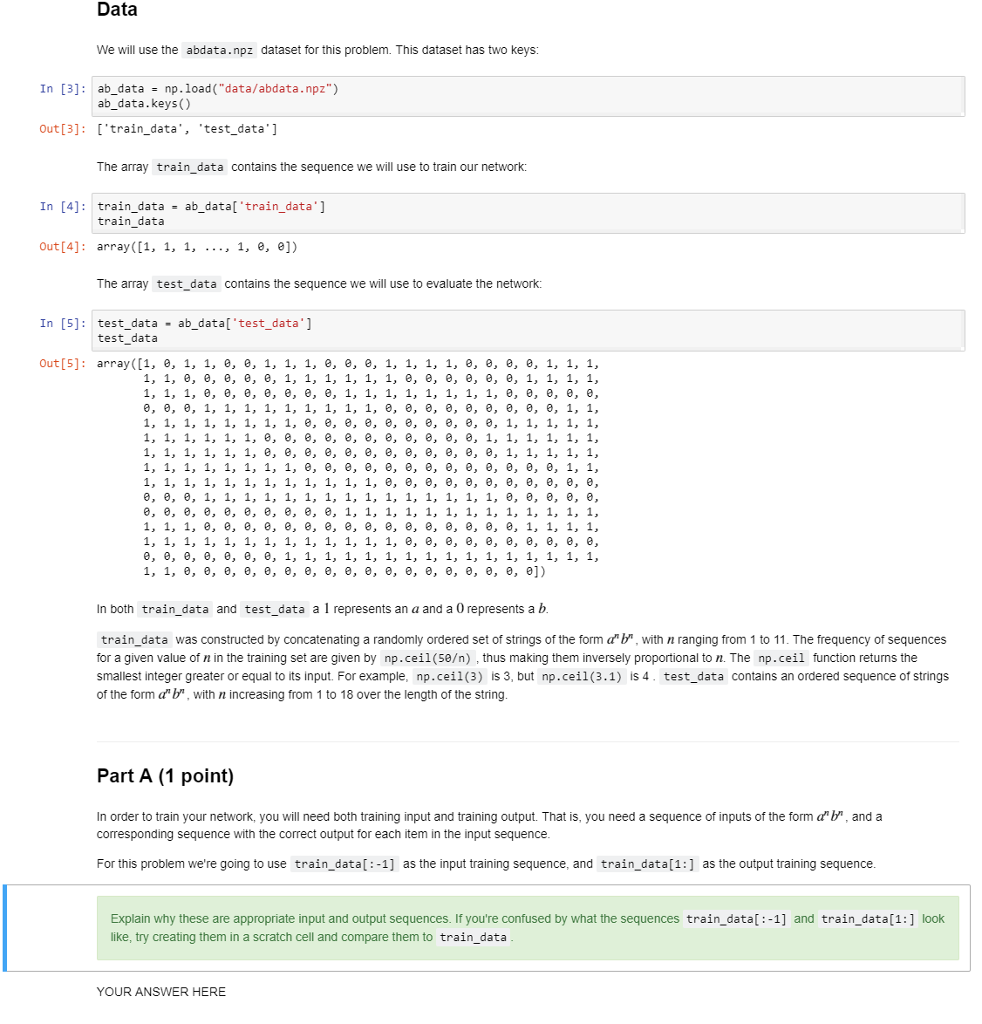
Data We will use the abdata.npz dataset for this problem. This dataset has two keys In [3] ab_datanp.load("data/abdata.npz") ab data.keys () Out[3]: ['train_data', 'testdata'] The array train_data contains the sequence we will use to train our network: In [4]: train_data ab_datal'train_data' train data Out [4]: array ([1, 1, 1, ..., 1, e, e]) The array test_data contains the sequence we will use to evaluate the network: In [5]: test_data ab_datal'test_data'] test data Out[S]: array([1, e, 1, 1, e, e, 1, 1, 1, e, e, e, 1, 1, 1, 1, e, e, e, e, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e]) In both train_data and test_data a 1 represents an a and a 0 represents a b train_data was constructed by concatenating a randomly ordered set of strings of the form a b, with n ranging from 1 to 11. The frequency of sequences for a given value of n in the training set are given by np.ceil(50) , thus making them inversely proportional to n. The np.ceil function returns the smallest integer greater or equal to its input. For example, np.ceil(3) is 3, but np.cei1 (3.1) is 4. test_data contains an ordered sequence of strings of the form a"b, with n increasing from 1 to 18 over the length of the string Part A (1 point) In order to train your network, you will need both training input and training output. That is, you need a sequence of inputs of the form ab, and a corresponding sequence with the correct output for each item in the input sequence For this problem we're going to use train_data[:-1] as the input training sequence, and train_data[1:] as the output training sequence Explain why these are appropriate input and output sequences. If you're confused by what the sequences train_data[:-1] and train_data[1:] look like, try creating them in a scratch cell and compare them to train_data YOUR ANSWER HERE Data We will use the abdata.npz dataset for this problem. This dataset has two keys In [3] ab_datanp.load("data/abdata.npz") ab data.keys () Out[3]: ['train_data', 'testdata'] The array train_data contains the sequence we will use to train our network: In [4]: train_data ab_datal'train_data' train data Out [4]: array ([1, 1, 1, ..., 1, e, e]) The array test_data contains the sequence we will use to evaluate the network: In [5]: test_data ab_datal'test_data'] test data Out[S]: array([1, e, 1, 1, e, e, 1, 1, 1, e, e, e, 1, 1, 1, 1, e, e, e, e, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e, e]) In both train_data and test_data a 1 represents an a and a 0 represents a b train_data was constructed by concatenating a randomly ordered set of strings of the form a b, with n ranging from 1 to 11. The frequency of sequences for a given value of n in the training set are given by np.ceil(50) , thus making them inversely proportional to n. The np.ceil function returns the smallest integer greater or equal to its input. For example, np.ceil(3) is 3, but np.cei1 (3.1) is 4. test_data contains an ordered sequence of strings of the form a"b, with n increasing from 1 to 18 over the length of the string Part A (1 point) In order to train your network, you will need both training input and training output. That is, you need a sequence of inputs of the form ab, and a corresponding sequence with the correct output for each item in the input sequence For this problem we're going to use train_data[:-1] as the input training sequence, and train_data[1:] as the output training sequence Explain why these are appropriate input and output sequences. If you're confused by what the sequences train_data[:-1] and train_data[1:] look like, try creating them in a scratch cell and compare them to train_data YOUR ANSWER HERE
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


