Question: databases, in the Unix system's sort utility, and in many other places. > Part 3 Closely related to sorting is searching, in which we are
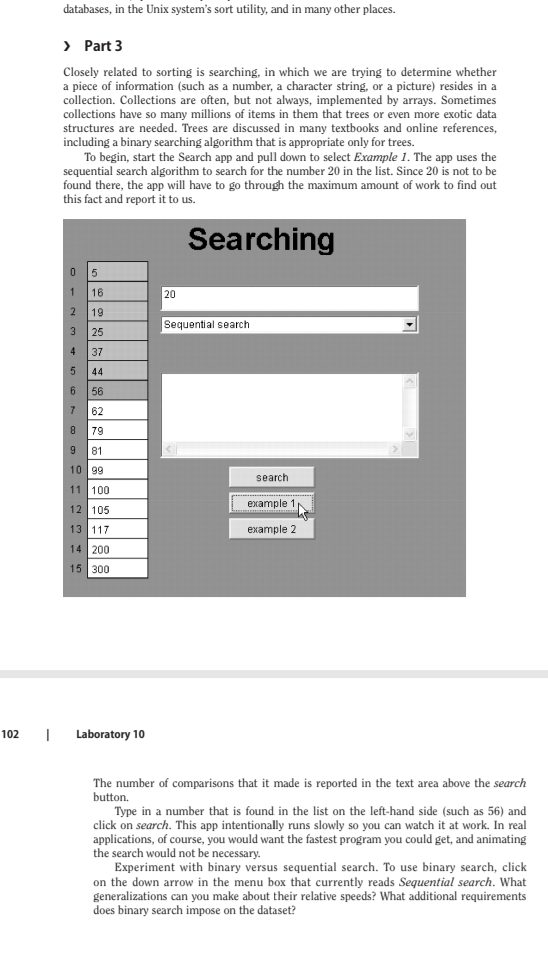


databases, in the Unix system's sort utility, and in many other places. > Part 3 Closely related to sorting is searching, in which we are trying to determine whether a piece of information (such as a number, a character string, or a picture) resides in a collection. Collections are often, but not always, implemented by arrays. Sometimes collections have so many millions of items in them that trees or even more exotic data structures are needed. Trees are discussed in many textbooks and online references, including a binary searching algorithm that is appropriate only for trees. To begin, start the Search app and pull down to select Example 1. The app uses the sequential search algorithm to search for the number 20 in the list. Since 20 is not to be found there, the app will have to go through the maximum amount of work to find out this fact and report it to us. Searching 0 0 5 16 20 1 2 3 19 Sequential search 25 4 37 5 44 6 56 7 62 8 79 9 9 81 10 99 search 11100 example 1 12 105 13117 example 2 14200 15300 102 Laboratory 10 The number of comparisons that it made is reported in the text area above the search button. Type in a number that is found in the list on the left-hand side (such as 56) and click on search. This app intentionally runs slowly so you can watch it at work. In real applications, of course, you would want the fastest program you could get, and animating the search would not be necessary. Experiment with binary versus sequential search. To use binary search, click on the down arrow in the menu box that currently reads Sequential search. What generalizations can you make about their relative speeds? What additional requirements does binary search impose on the dataset? EXERCISE 4 Date Name Section 1) Start the Searching app. The dataset in the numbered list on the left is fixedyou can't change it. However, you can select an algorithm and a value to search for. 2) Run all four searches that are in the examples and write down how many comparisons were made: Example 1: Something in the list (sequential) Example 2: Something not in the list (sequential) Example 3: Something in the list (binary) Example 4: Something not in the list (binary) 3) Select binary search as your algorithm and try to find 301." How many tries does this algorithm need to find it? 4) Try to find 301" using sequential search. How many tries does this algorithm need? 5) Which searching algorithm is clearly superior on this search query on this dataset? Why? 6) is the numbered list on the left sorted? Is this a prerequisite for binary search? Is it a prerequisite for sequential search
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


