Question: Dataset: Average annual hours actually worked per In this section, we will consider the following question tackled by Prescott (2004). Prescott (2004) wanted to examine
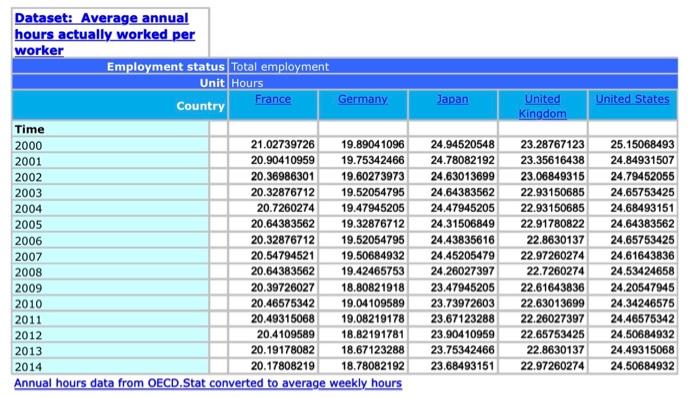


Dataset: Average annual hours actually worked per In this section, we will consider the following question tackled by Prescott (2004). Prescott (2004) wanted to examine how important tax rates were in determining labor supply across different major industrialized countries. We will consider a simplified version of the problem he considered and see how distortionary labor income tax rates may affect the hours an individual chooses to work. First, assume that households only consume consumption goods ct and leisure. Denote nt as the hours of labor the household supplies to the labor market. Let the total amount of hours a household has per week be h. Then the preferences of the household in a period can be described with the following utility function: U(ct,nt)=maxct,ntlog(ct)+log(hnt) where is a parameter that governs the relative value of leisure to consumption. The household's budget constraint is given by: ct=(1n)wtntTt+t where n is a distortionary labor income tax, wtnt represents the household's labor income, Tt is the lump sum tax and t is the dividend the household receives from the firm. Questions 1. Write down the household's problem. State what are the household's choice variables. 2. Derive the optimality conditions of the household's problem. In particular, show how the household's marginal rate of substitution between leisure and consumption depends on the wage rate, labor income tax, and parameters of the model. Label this relation to the consumptionleisure optimality condition in your answer. 3. Solve for the optimality conditions of the household's problem from above
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


