Question: datastructure.hpp /* * DO NOT CHANGE THIS FILE */ #include #include #include using namespace std; typedef struct TreeNode { int key; int val; bool flag;
| datastructure.hpp |
/* * DO NOT CHANGE THIS FILE */ #include |
| main.cpp |
/* * DO NOT CHANGE THIS FILE! * */ #include |
| tree.cpp |
#include "datastructure.hpp" #include |
| input file |
t 4 c the tree will have at most four children i 1 1 h l i 2 2 i 3 2 i 4 2 i 5 2 h l |
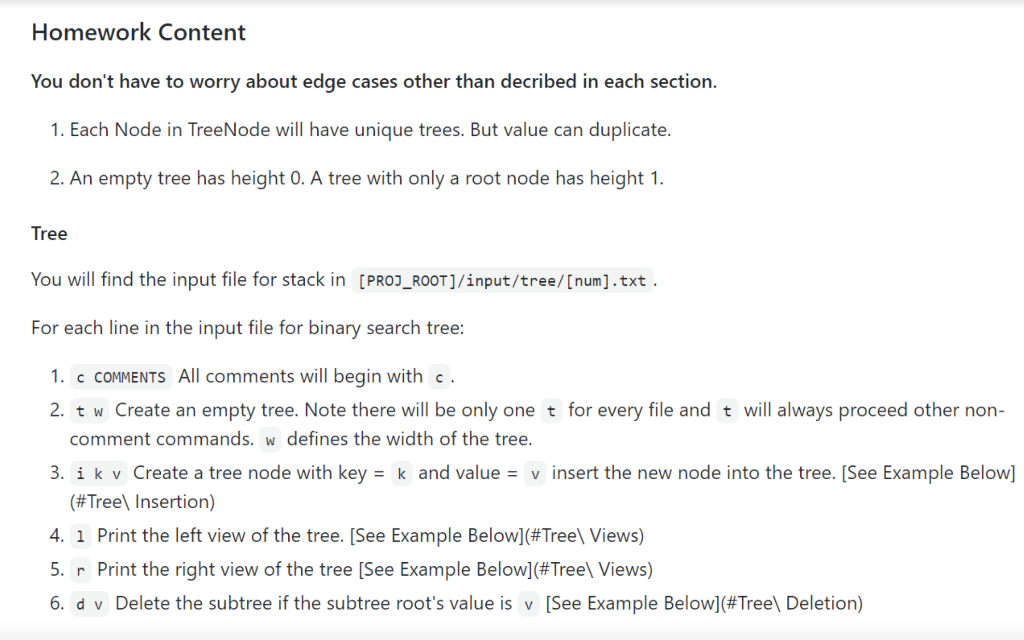
Homework Content You don't have to worry about edge cases other than decribed in each section. 1. Each Node in TreeNode will have unique trees. But value can duplicate. 2. An empty tree has height 0. A tree with only a root node has height 1. Tree You will find the input file for stack in [PROJ_ROOT]/input/tree/[num].txt. For each line in the input file for binary search tree: 1. c COMMENTS All comments will begin with c. 2. tw Create an empty tree. Note there will be only one t for every file and t will always proceed other non- comment commands. w defines the width of the tree. 3. ik v Create a tree node with key = k and value = v insert the new node into the tree. (See Example Below] (#Tree Insertion) 4. i Print the left view of the tree. (See Example Below](#Tree Views) 5. r Print the right view of the tree (See Example Below](#Treel Views) 6. d v Delete the subtree if the subtree root's value is v [See Example Below](#Tree Deletion) Homework Content You don't have to worry about edge cases other than decribed in each section. 1. Each Node in TreeNode will have unique trees. But value can duplicate. 2. An empty tree has height 0. A tree with only a root node has height 1. Tree You will find the input file for stack in [PROJ_ROOT]/input/tree/[num].txt. For each line in the input file for binary search tree: 1. c COMMENTS All comments will begin with c. 2. tw Create an empty tree. Note there will be only one t for every file and t will always proceed other non- comment commands. w defines the width of the tree. 3. ik v Create a tree node with key = k and value = v insert the new node into the tree. (See Example Below] (#Tree Insertion) 4. i Print the left view of the tree. (See Example Below](#Tree Views) 5. r Print the right view of the tree (See Example Below](#Treel Views) 6. d v Delete the subtree if the subtree root's value is v [See Example Below](#Tree Deletion)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


