Question: Define the function, improved_bubble_sort(), which performs the same bubble sort as shown in lectures but stops the function execution as soon as all the elements
Define the function, improved_bubble_sort(), which performs the same bubble sort as shown in lectures but stops the function execution as soon as all the elements in the parameter list are sorted. This function is passed a Python list of numbers as a parameter and the function returns a tuple containing the total number of swaps and the total number of comparisons made during
the sorting process.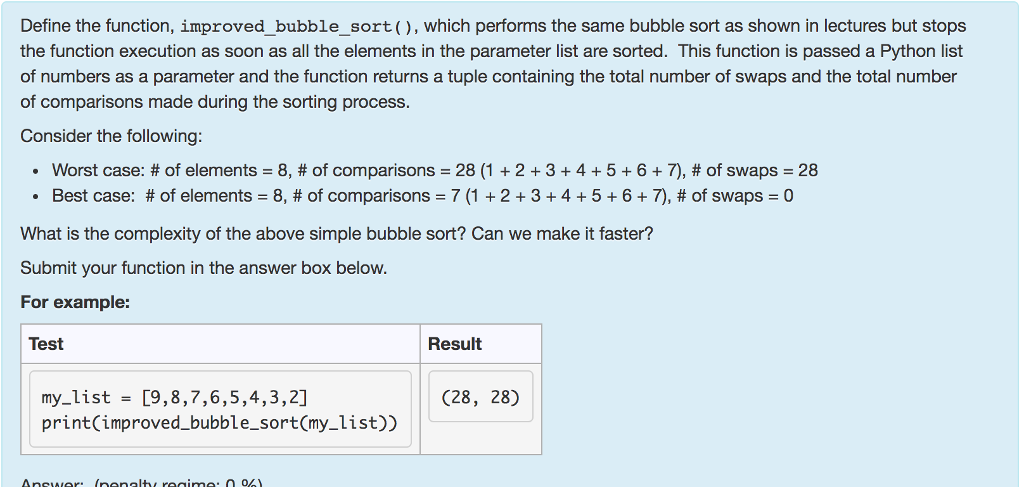
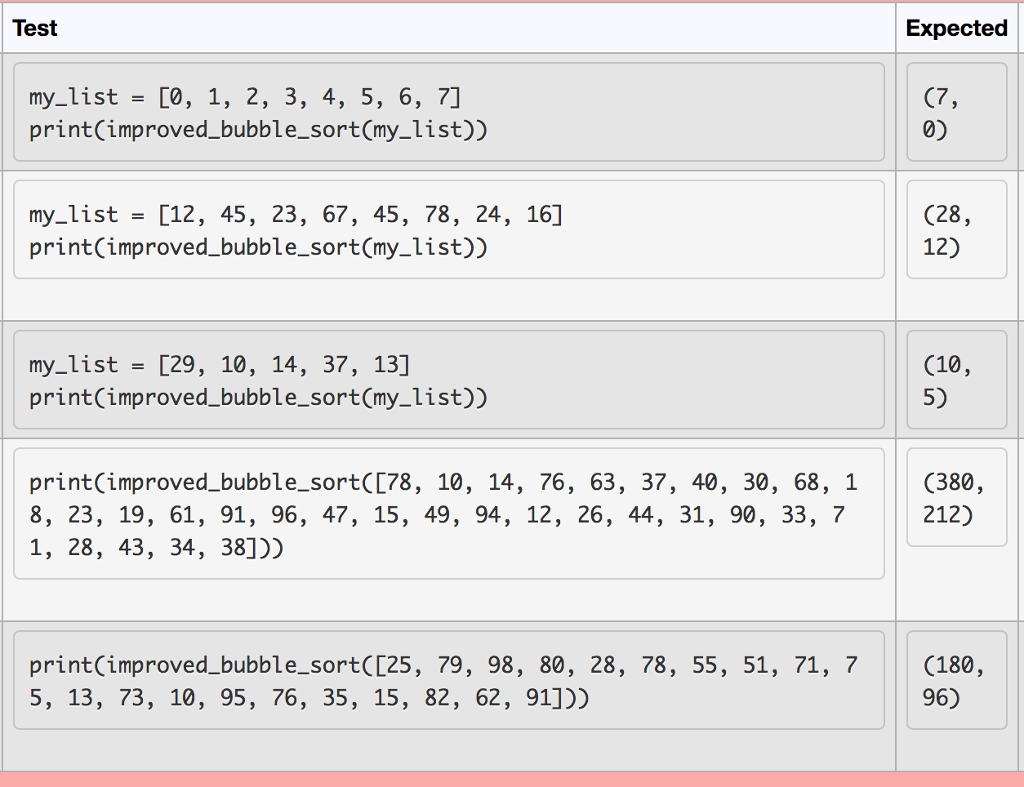
Define the function, improved_bubble_sort(), which performs the same bubble sort as shown in lectures but stops the function execution as soon as all the elements in the parameter list are sorted. This function is passed a Python list of numbers as a parameter and the function returns a tuple containing the total number of swaps and the total number of comparisons made during the sorting process. Consider the following: . Worst case: # of elements-8, # of comparisons-28 (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7), # of swaps-28 . Best case: # of elements-8, # of comparisons-7 (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7, # of swaps-0 What is the complexity of the above simple bubble sort? Can we make it faster? Submit your function in the answer box below. For example: Test Result my list - [9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2] print(improved_bubble_sort(my_list)) (28, 28) Answer. (penalty regime. 0 %)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


