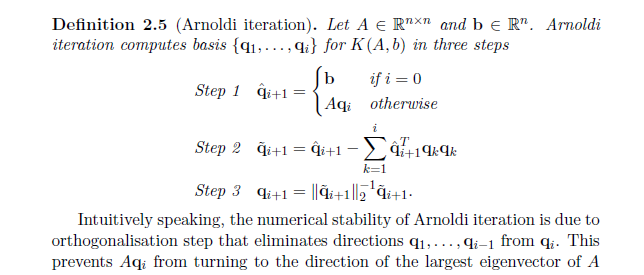
Question: Definition 2.5 (Arnoldi iteration). Let A e Rxn and be R. Arnoldi iteration computes basis {q1, .... qi} for K(A, b) in three steps b

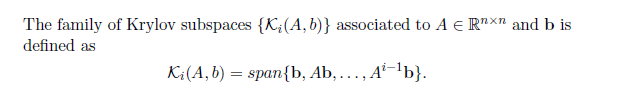
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


