Question: Density Introduction: Why do some things float and others do not? Is floating determined by the weight of the object? A large ocean liner

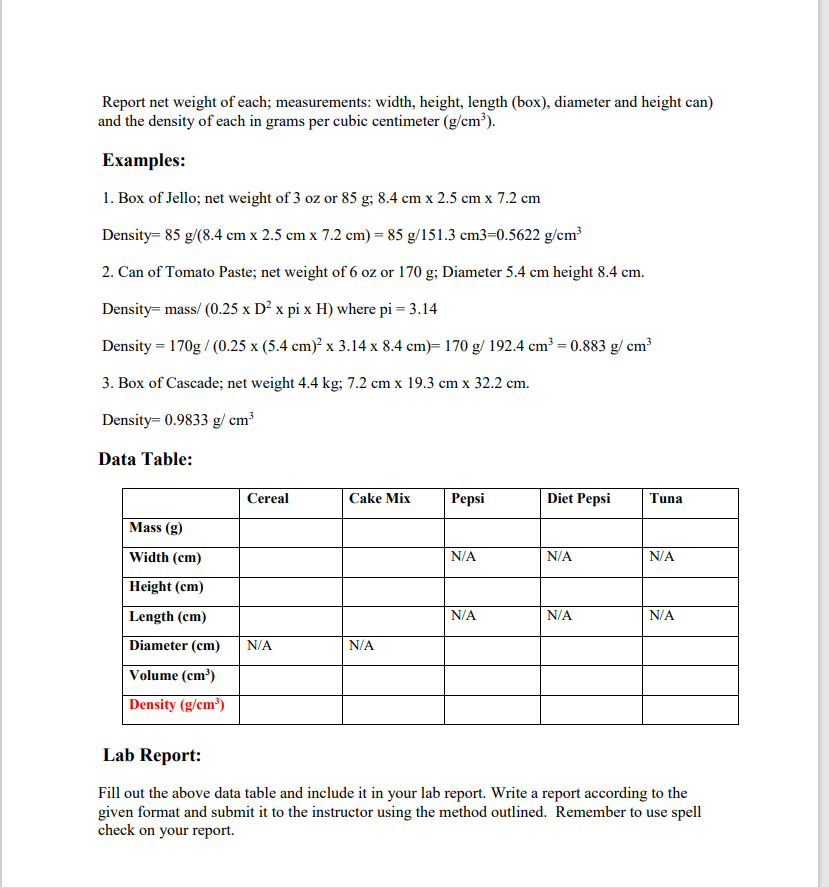
Density Introduction: Why do some things float and others do not? Is floating determined by the weight of the object? A large ocean liner floats, but a small pebble quickly sinks. Clearly, it is not a matter of the total weight of the object. The density of the object is the key. Objects that are denser than the fluid they are immersed in will sink-those less dense will float. A block of wood floats, but a metal block of the same shape and size will sink. The metal block weighs more than the wood, even though it is the same size, which means the metal is denser than the wood. Density is the ratio of the mass to the volume (or mass per unit of volume). Learning Objectives: 1. Measure different objects 2. Determine the volume of objects with different shapes. 3. How to find the net weight of objects 4. Calculate the densities from net mass and volume. Lab Procedures: 1. 2. 3. 4. Select a box of cereal, a box of cake mix, a can of regular Pepsi, a can of diet Pepsi and a can of tuna or salmon. For most of the items, the net weight or mass can be found on the outside of the box or can. Use the metric value given in grams for the calculation of density. For the soda, you need to use a scale to measure the mass of a full soda can, and measure the mass of an empty soda can. The difference is the mass of the liquid. Remember to use only the mass of the liquid in your calculation of density. The 355ml listed on the soda can is the volume of the liquid, not the mass of the liquid. For the box and can, you will need a ruler to measure the width, height and length of a box. It is easier if you do your measurements in centimeters (cm). Also, you will measure the diameter and height of the can. These values will be used for the calculation of the volume in cubic centimeters (cm). The volume of a box equals the product of length times width times height. The volume of the can equals 3.142 times the height times radius squared. Calculate the density by using the formula Density-mass/volume or D=m/V Report net weight of each; measurements: width, height, length (box), diameter and height can) and the density of each in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm). Examples: 1. Box of Jello; net weight of 3 oz or 85 g; 8.4 cm x 2.5 cm x 7.2 cm Density=85 g/(8.4 cm x 2.5 cm x 7.2 cm) = 85 g/151.3 cm3=0.5622 g/cm 2. Can of Tomato Paste; net weight of 6 oz or 170 g; Diameter 5.4 cm height 8.4 cm. Density= mass/ (0.25 x D x pi x H) where pi = 3.14 Density = 170g / (0.25 x (5.4 cm) x 3.14 x 8.4 cm)= 170 g/ 192.4 cm = 0.883 g/cm 3. Box of Cascade; net weight 4.4 kg; 7.2 cm x 19.3 cm x 32.2 cm. Density=0.9833 g/cm Data Table: Cereal Cake Mix Pepsi Diet Pepsi Tuna Mass (g) Width (cm) N/A N/A N/A Height (cm) Length (cm) N/A N/A N/A Diameter (cm) N/A N/A Volume (cm) Density (g/cm) Lab Report: Fill out the above data table and include it in your lab report. Write a report according to the given format and submit it to the instructor using the method outlined. Remember to use spell check on your report.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


