Question: [Depth-first search: algorithm tracing] Consider the recursive depth-first search algorithm, the graph, and its adjacency list representation shown below. Consider the nodes in a linked
[Depth-first search: algorithm tracing] Consider the recursive depth-first search algorithm, the graph, and its adjacency list representation shown below. Consider the nodes in a linked list of the adjacency list in the order from left to right exactly as shown. Do algorithm tracing on the graph twice, once for the start vertex 2 and once for the start vertex 6, and show the tracing output. The tracing output should include the sequence of recursive calls and returnsfrom those calls in the following format: call DFS(a); call DFS(b); call DFS(c); return from DFS(c); call DFS(d); return from DFS(d); return from DFS(b); return from DFS(a).Additionally, show the depth-first search tree resulting from each run of the algorithm; use the format shown in Figure 3.5(g).
![[Depth-first search: algorithm tracing] Consider the recursive depth-first search algorithm, the graph,](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3ca7c74fb3_11566f3ca7bec8db.jpg)
Figure 3.5: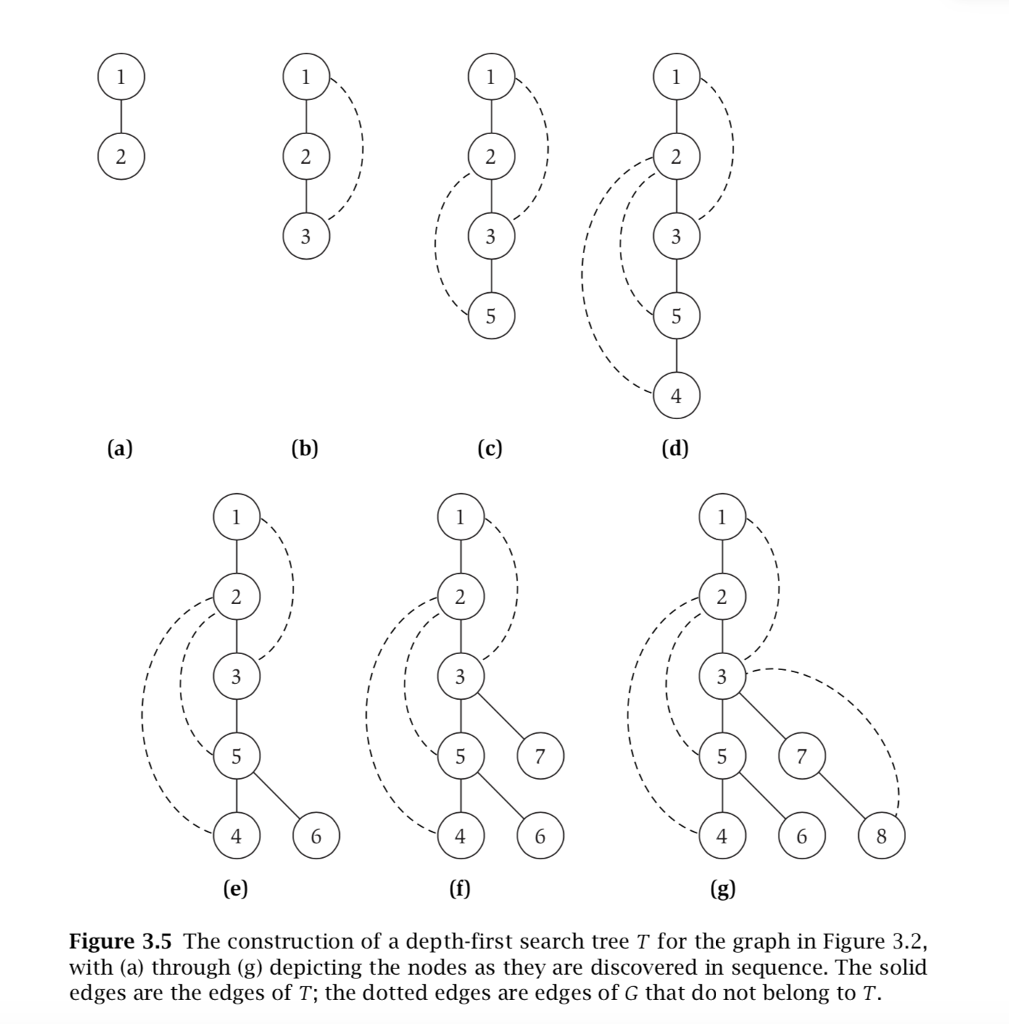
DFS(u): Depth-first search tree Mark u as "Explored" and add uto T For each edge (u, v) incident to u If v is not marked "Explored" then Recursively invoke DFS(v) Endif Endfor 2 1 4 4 4 7 3 4 4 4 4 6 Figure 3.5 The construction of a depth-first search tree T for the graph in Figure 3.2, with (a) through (g) depicting the nodes as they are discovered in sequence. The solid edges are the edges of T; the dotted edges are edges of G that do not belong to T
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


