Question: Derive equation 1 to equation 2 ...equation 1 i = nFAC*/d ...equation 2 A diffusion-limited steady-state current for a two-electrode cell Assumptions: - Electrode surfaces
Derive equation 1 to equation 2
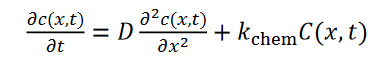 ...equation 1
...equation 1
i = nFAC*/d ...equation 2
A diffusion-limited steady-state current for a two-electrode cell
Assumptions:
- Electrode surfaces are parallel and opposite to each other and are separated by a distance, d.
- A redox reaction, O + e = R
- Only the species O is present in the solution at the start of the experiment at concentration C*
- D_O = D_R = D.
- The bottom electrode is held at a potential (EbE 0) where O is reduced and the top electrode is held at a potential (EtE 0) where R is oxidized.
- The solution contains excess supporting electrolytes and is not being stirred.
- k is the rate constant
tc(x,t)=Dx22c(x,t)+kchemC(x,t)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


