Question: Deriving cash flows and computing net present value. Oceana Inc., is contemplating selling a new product. Oceana Inc., can acquire the equipment necessary to distribute
Deriving cash flows and computing net present value. Oceana Inc., is contemplating selling a new product. Oceana Inc., can acquire the equipment necessary to distribute and sell the product for $100,000. The equipment has an estimated life of 10 years and has no salvage value. Does the following schedule show the expected sales volume, selling price, and variable cost per unit of production (please see photo). Production in each year must be sufficient to meet each year's sales. In addition, Oceana, Inc., will purchase 5,000 extra units in Year 1 to provide a continuing inventory of 5,000 units. Thus, production in Year 1 will be 15,000 units but in Year 10 will be only 10,000 units, so at the end of Year 10, ending inventory will be zero. Oceana will use a LIFO (last in, first out) cost flow assumption. Oceana's income tax rate is 40 percent, and its after-tax cost of capital is 9 percent per year. It receives cash at the end of the year when it makes sales and spends cash at the end of the year when it incurs costs. Oceana estimates variable selling expenses at $1 per unit sold. Depreciation on the new distribution equipment is not a product cost but is an expense each period. For tax reporting, depreciation will follow these accelerated depreciation schedule percentages: 20 percent in the first year, 32 percent in the second, 19.2 percent in the third, 11.5 percent in the fourth, 11.5 percent in the fifth, 5.8 percent in the sixth, and zero thereafter. Oceana generates sufficient cash flows from other operations so that it can use all depreciation deductions to reduce current taxes otherwise payable. What is the net present value of the project?
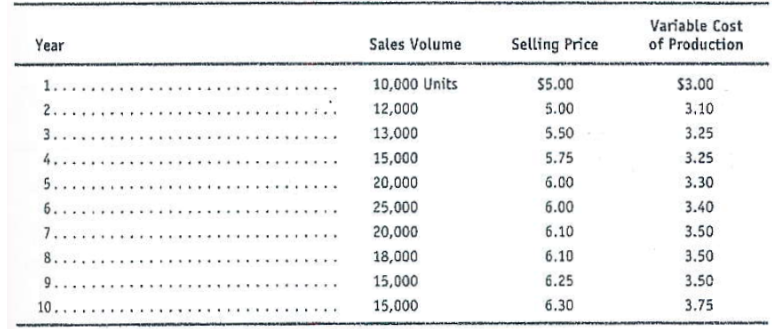
Variable Cost Year Sales Volume Selling Price of Production 1. 10,000 Units $5.00 $3.00 2 12,000 5.00 3,10 3 13,000 5.50 3.25 4 15,000 5.75 3.25 5 20,000 6.00 3.30 6. 25,000 6.00 3.40 7 20,000 6.10 3.50 8. 18,000 6.10 3.50 9 15,000 6.25 3.50 10. 15,000 6.30 3.75
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


