Question: Description: The tiny encryption algorithm ( TEA ) is a symmetric key block cipher designed for simplicity and efficiency, especially in resource - constraint environments.
Description:
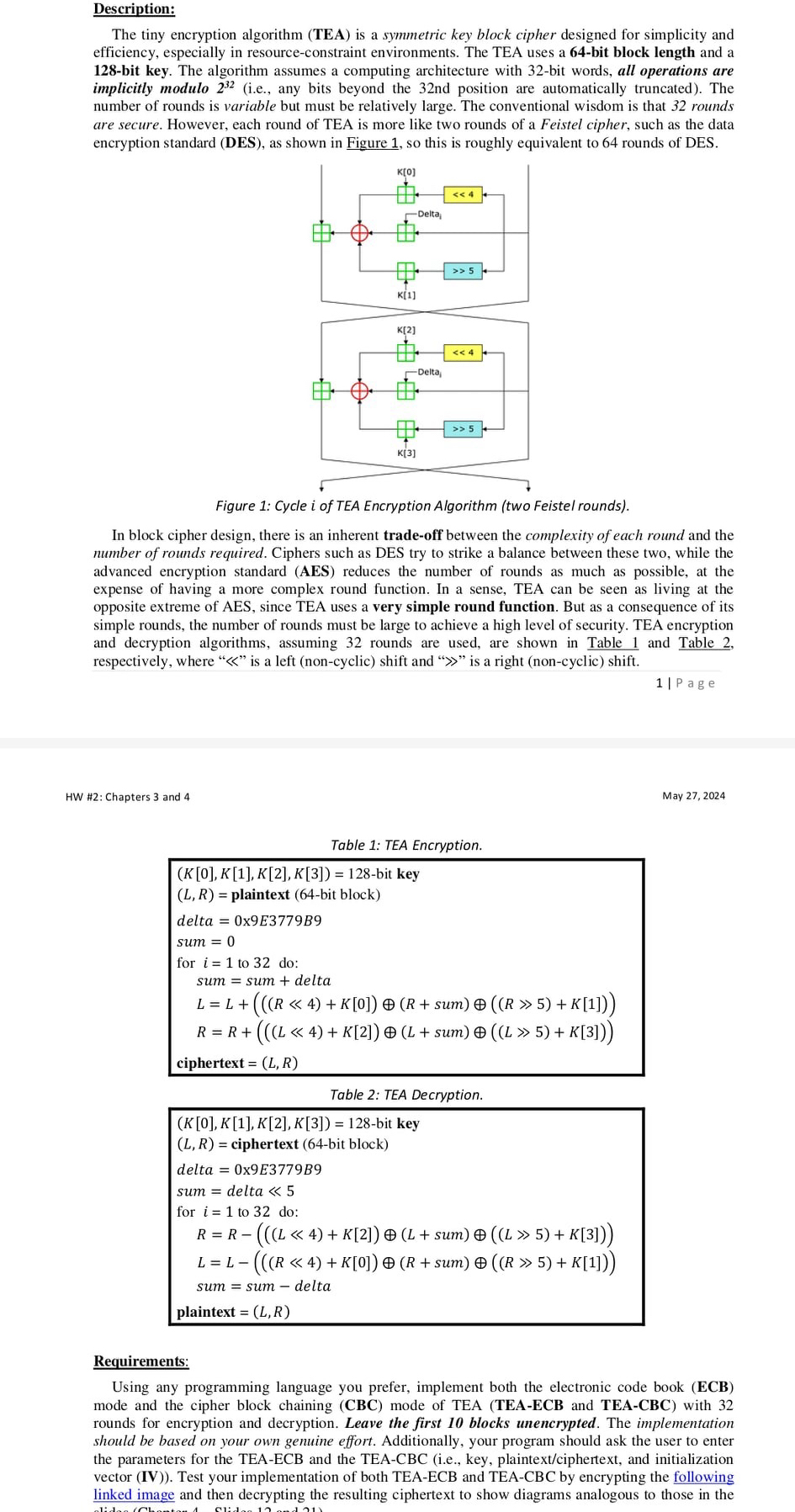
The tiny encryption algorithm TEA is a symmetric key block cipher designed for simplicity and efficiency, especially in resourceconstraint environments. The TEA uses a bit block length and a bit key. The algorithm assumes a computing architecture with bit words, all operations are implicitly modulo ie any bits beyond the nd position are automatically truncated The number of rounds is variable but must be relatively large. The conventional wisdom is that rounds are secure However, each round of TEA is more like two rounds of a Feistel cipher, such as the data encryption standard DES as shown in Figure so this is roughly equivalent to rounds of DES.
Figure : Cycle of TEA Encryption Algorithm two Feistel rounds
In block cipher design, there is an inherent tradeoff between the complexity of each round and the number of rounds required. Ciphers such as DES try to strike a balance between these two, while the advanced encryption standard AES reduces the number of rounds as much as possible, at the expense of having a more complex round function. In a sense, TEA can be seen as living at the opposite extreme of AES, since TEA uses a very simple round function. But as a consequence of its simple rounds, the number of rounds must be large to achieve a high level of security. TEA encryption and decryption algorithms, assuming rounds are used, are shown in Table and Table respectively, where is a left noncyclic shift and is a right noncyclic shift.
Page
HW #: Chapters and
May
Table : TEA Encryption.
delta
Table : TEA Decryption.
delta
Requirements:
Using any programming language you prefer, implement both the electronic code book ECB mode and the cipher block chaining CBC mode of TEA TEAECB and TEACBC with rounds for encryption and decryption. Leave the first blocks unencrypted. The implementation should be based on your own genuine effort. Additionally, your program should ask the user to enter the parameters for the TEAECB and the TEACBC ie key, plaintextciphertext and initialization vector IV Test your implementation of both TEAECB and TEACBC by encrypting the following linked image and then decrypting the resulting ciphertext to show diagrams analogous to those in the
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


