Question: design a program The purpose of programming assignment 1 is: a) Practicing computational/algorithmic thinking to solve an Astronomy problem b) Using variables and simple arithmetic
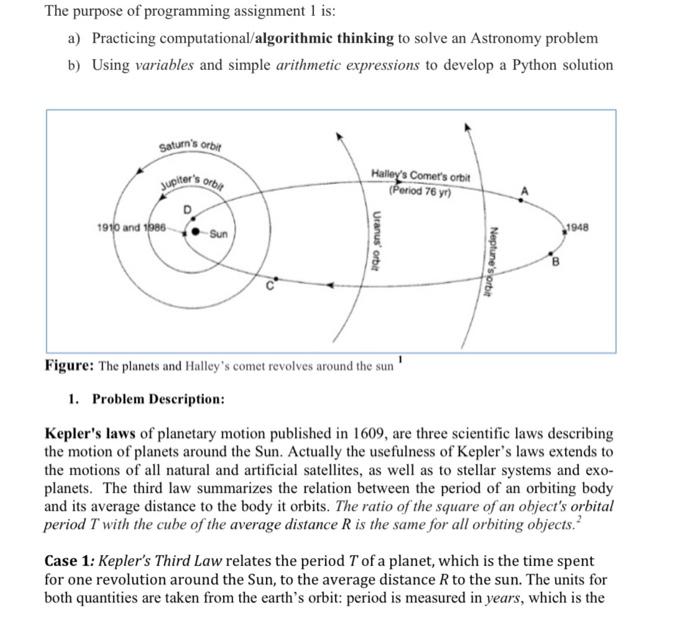
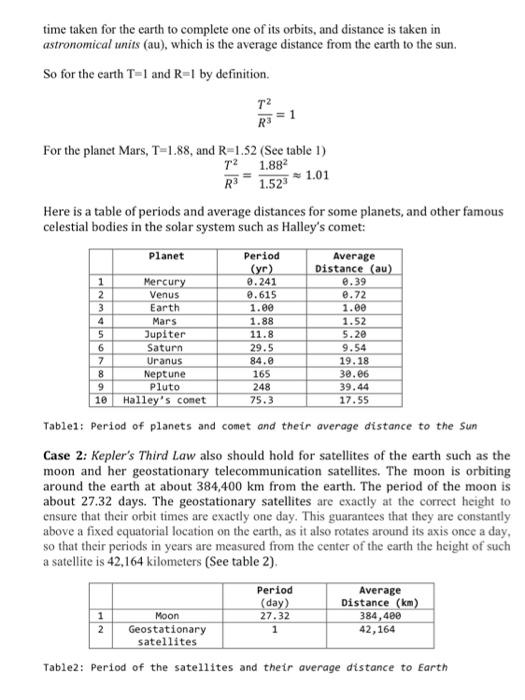

The purpose of programming assignment 1 is: a) Practicing computational/algorithmic thinking to solve an Astronomy problem b) Using variables and simple arithmetic expressions to develop a Python solution Saturn's orbir Jupiter's orbiy Halley's Comer's orbit Period 76 yn 1910 and 1988 Sur 1948 Uranus orbit Neptune's orbit 10 Figure: The planets and Halley's comet revolves around the sun 1. Problem Description: Kepler's laws of planetary motion published in 1609, are three scientific laws describing the motion of planets around the Sun. Actually the usefulness of Kepler's laws extends to the motions of all natural and artificial satellites, as well as to stellar systems and exo- planets. The third law summarizes the relation between the period of an orbiting body and its average distance to the body it orbits. The ratio of the square of an object's orbital period T with the cube of the average distance R is the same for all orbiting objects.? Case 1: Kepler's Third Law relates the period T of a planet, which is the time spent for one revolution around the Sun, to the average distance R to the sun. The units for both quantities are taken from the earth's orbit: period is measured in years, which is the Period Average Distance (au) time taken for the earth to complete one of its orbits, and distance is taken in astronomical units (au), which is the average distance from the earth to the sun. So for the earth T=1 and R=1 by definition. T2 R> For the planet Mars, T-1.88, and R-1.52 (See table 1) T2 1.882 R 1.52 - 1.01 Here is a table of periods and average distances for some planets, and other famous celestial bodies in the solar system such as Halley's comet: Planet (yr) Mercury 0.241 @.39 Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn 7 Uranus 8 Neptune 9 Pluto 10 Halley's conet Table1: Period of planets and comet and their average distance to the Sun Case 2: Kepler's Third Law also should hold for satellites of the earth such as the moon and her geostationary telecommunication satellites. The moon is orbiting around the earth at about 384,400 km from the earth. The period of the moon is about 27.32 days. The geostationary satellites are exactly at the correct height to ensure that their orbit times are exactly one day. This guarantees that they are constantly above a fixed equatorial location on the earth, as it also rotates around its axis once a day, so that their periods in years are measured from the center of the earth the height of such a satellite is 42,164 kilometers (See table 2). 0.615 1.00 1.88 11.8 29.5 84. 165 248 75.3 0.72 1.ee 1.52 5.20 9.54 19.18 30.06 39.44 17.55 1 2 Period (day) 27.32 1 Average Distance (km) 384,400 42,164 Moon Geostationary satellites Table2: Period of the satellites and their average distance to Earth It is worth noticing that the distance from Earth to the sun is one a.u. equivalent to about 150 million km, and time taken for Earth to complete one of its orbits is 1 year, which is equivalent to 365 days. We want to investigate whether the law of harmonies holds for a selection of planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars), and for the Halley's comet that revolves around the Sun (See table 1), as well as for the satellites of the earth such as the moon and the geostationary satellites (See table 2). 2. Input/output: Expected Input and Output. 3 In 193]: runfitel /Users/hamzazidoum/Documents/2101/2181_32821/Programming Assignments/pal_solution.py", wdir="/Users/hamzazidoum/Documents/ 2101/2101_S2021/Programming Assignments) Welcome to Keppler's Third Law Software @hamzaZidoun Orbiting Period Radius T^2/R^3 Object (yr) (au) yr2/au^3 Mercury 2.24 2.39 0.98 Venus 2.61 0.72 1.01 Earth 1.00 1.00 1.00 Mars 1.88 1.52 Halley's Conet 75.30 17.55 1.es Moon 8.875 0.002560 333441.51 Satellite 0.003 0.889281 337093.75 Bye! 1.01 3. Deliverable Submit a Python source file: pai_xxxXXX.py. For instance, if your ID is 38000, then you should submit a file pa1_38000.py Your source file will consist of three parts: a) Header: includes documentation with your name, your student id, and section number, the problem statement (a short description of the purpose of your code), data description (input, and output variables used in the program including constants), and the algorithm in pseudocode. b) Python program c) Your conclusion in few sentences as a comment in the file header. 4. Grading Table Marks 16 /2 12 Item Problem Solving: Student Info, Program design, Conclusion (Header) Programming Style: Comments, Naming in accordance to Python convention Variables: including constants Arithmetic Expressions Displaying the results with correct format) Debugging: Program compiles and runs without errors Proper File naming & submission TOTAL 14 /3 /2 71 /20
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


