Question: detailed explanation, if possible thank you Dependent Variable: RP_EX Method: Least Squares Date: 03/24/22 Time: 15:56 Sample: 1980M01 2021M09 Included observations: 501 Variable Coefficient Std.
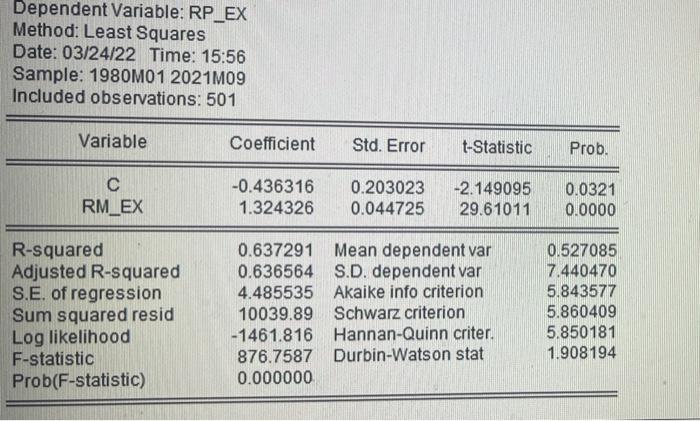

Dependent Variable: RP_EX Method: Least Squares Date: 03/24/22 Time: 15:56 Sample: 1980M01 2021M09 Included observations: 501 Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. RM_EX -0.436316 1.324326 0.203023 0.044725 -2.149095 29.61011 0.0321 0.0000 R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood F-statistic Prob(F-statistic) 0.637291 Mean dependent var 0.636564 S.D. dependent var 4.485535 Akaike info criterion 10039.89 Schwarz criterion -1461.816 Hannan-Quinn criter. 876.7587 Durbin-Watson stat 0.000000 0.527085 7.440470 5.843577 5.860409 5.850181 1.908194 5) [15 marks] Test the null hypothesis that B. = 1 against a two-sided alternative hypothesis at a significance level of 5%. Clearly show your calculation of the test statistic and explain how you reach your conclusion. Make sure that you state the null and alternative hypotheses, the degrees of freedom used and the critical value you use. Note: you may use the default EViews coefficient standard errors that are valid for the case of homoscedastic errors. Dependent Variable: RP_EX Method: Least Squares Date: 03/24/22 Time: 15:56 Sample: 1980M01 2021M09 Included observations: 501 Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob. RM_EX -0.436316 1.324326 0.203023 0.044725 -2.149095 29.61011 0.0321 0.0000 R-squared Adjusted R-squared S.E. of regression Sum squared resid Log likelihood F-statistic Prob(F-statistic) 0.637291 Mean dependent var 0.636564 S.D. dependent var 4.485535 Akaike info criterion 10039.89 Schwarz criterion -1461.816 Hannan-Quinn criter. 876.7587 Durbin-Watson stat 0.000000 0.527085 7.440470 5.843577 5.860409 5.850181 1.908194 5) [15 marks] Test the null hypothesis that B. = 1 against a two-sided alternative hypothesis at a significance level of 5%. Clearly show your calculation of the test statistic and explain how you reach your conclusion. Make sure that you state the null and alternative hypotheses, the degrees of freedom used and the critical value you use. Note: you may use the default EViews coefficient standard errors that are valid for the case of homoscedastic errors
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


